Fish relieves asthma
Lisa Vogel studied departmental journalism with a focus on medicine and biosciences at Ansbach University and deepened her journalistic knowledge in the master's degree in multimedia information and communication. This was followed by a traineeship in the editorial team. Since September 2020 she has been writing as a freelance journalist for
More posts by Lisa Vogel All content is checked by medical journalists.If fatty sea fish lands on the plate twice a week, asthma improves in children: the inflammatory processes in the lungs decrease significantly.
“Fatty fish contains many omega-3 fatty acids, which have anti-inflammatory properties,” explains Maria Papamichael's researchers from La Trobe University in Melbourne, explaining the effect.
Oily fish inhibits inflammation
The Australian scientists divided 64 children between five and twelve years with mild asthma into two groups. The children in the experimental group ate fish at least twice a week for six months. The children in the control group kept their usual eating habits.
Nitric oxide in the air we breathe indicates asthma
Before the beginning and at the end of the study period, the researchers determined the nitric oxide concentration in the exhaled air of the children (FeNO measurement). With its help, inflammatory processes in the airways can be determined. If the value is over 50 points in adults or over 35 points in children, this indicates asthma or another inflammatory lung disease.
The regular fish meals had an effect: In children who had regularly eaten fish, the value of the second FeNO measurement was 14 points lower than at the start of the study. The inflammation in her airways had therefore decreased significantly.
"A traditional Mediterranean diet with lots of vegetables and high-fat fish could be an easy and safe way to improve asthma symptoms in children," says co-author Prof. Catherine Itsiopoulos. High-fat types of fish are herring, tuna, salmon and mackerel. The study cannot answer whether fish also helps adult asthmatics.
Permanently inflamed airways
In asthma sufferers, the lower airways, i.e. the bronchi and bronchioles, are permanently inflamed. That makes them over-sensitive. As a result, they already react to harmless stimuli with a strong defense reaction. They constrict like spasms, the mucous membranes swell and produce thick mucus. Dry cough, tightness in the chest and shortness of breath are the result.
In addition to the typical symptoms, the diagnosis of asthma is also based on various lung function tests and nitric oxide measurements.
Asthma: the most common chronic disease in children
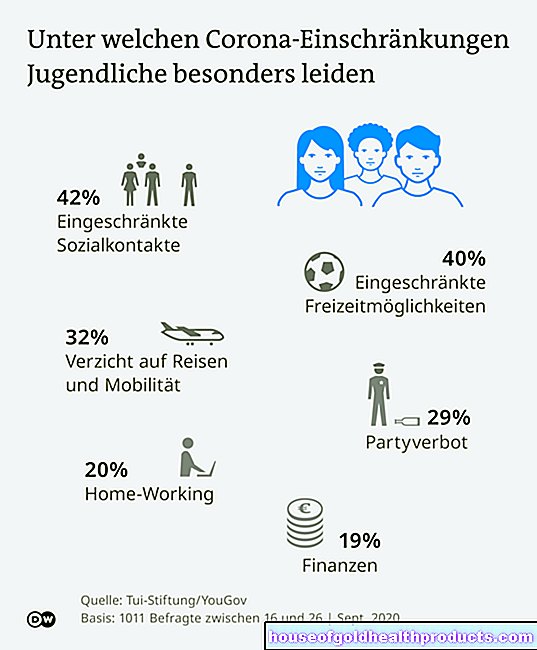
In children, bronchial asthma is the most common chronic disease. In Germany, every eighth child under the age of ten and every 15th child under the age of 15 suffers from the disease. Boys are affected about twice as often as girls.
Tags: hospital digital health nourishment