Dextromethorphan
All content is checked by medical journalists.Dextromethorphan is an active ingredient used to relieve coughs. It is related to morphine. Dextromethorphan is mainly used to treat dry, irritable cough. Here you can read everything you need to know about the effects, side effects and use of the active ingredient.
This is how dextromethorphan works
Coughing is an important reflex for getting foreign objects out of the airways. These include bacteria, viruses or smoke particles that can damage the bronchial mucosa. They are covered with a little mucus and transported outwards by strong coughs. Dry irritable cough, on the other hand, has no particular physiological benefit; it is triggered by an excessive activity of the cough center in the brain stem after irritation of the mucous membrane.
Dextromethorphan suppresses the cough reflex by dampening the cough center in the brain stem. Since dextromethorphan can also block so-called NMDA receptors and thus suppress the perception of pain, the active ingredient has also been approved for the treatment of certain painful nerve diseases since 2013.
Uptake, breakdown and excretion of dextromethorphan
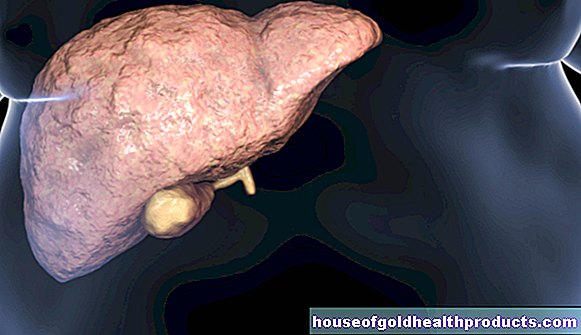
After ingestion through the mouth (orally) in the gastrointestinal tract, the active ingredient is very quickly absorbed into the bloodstream. The effect occurs after 15 to 30 minutes and lasts for three to six hours. After its distribution in the body, dextromethorphan is broken down in the liver and the metabolic products are mainly excreted via the kidneys.
When is dextromethorphan used?
Dextromethorphan is used to treat dry irritable cough and, if necessary, to treat neuronal pain.
This is how dextromethorphan is used
The active ingredient can be taken as a cough syrup, hard capsule or lozenge with different active ingredient concentrations. Adolescents over the age of twelve and adults usually take one hard capsule containing 30 milligrams of active ingredient every six hours. The daily dose of 120 mg milligrams should not be exceeded, otherwise symptoms of overdose can occur.
What are the side effects of dextromethorphan?
Common side effects of dextromethorphan are digestive tract symptoms such as nausea, gastrointestinal discomfort, and vomiting. Fatigue and slight dizziness are also possible after ingestion. Hallucinations and impaired consciousness have been observed very rarely in patients. If the active substance is misused, dependence can develop.
Overdose
Depending on the dose, dextromethorphan occupies the so-called opioid receptors. If the dose is too high, this can lead to significant perception disorders, euphoria and unintentional attenuation and increases the risk of addiction. Due to the opiate-like effect, breathing difficulties, drop in blood pressure, disorders of movement sequences (ataxia) and muscle cramps are possible.
If you experience any side effects or symptoms not mentioned in connection with the use of the active ingredient or if you have accidentally taken too much dextromethorphan, please contact your doctor immediately and discontinue the active ingredient on his advice if necessary.
When should I not take dextromethorphan?
You should not take dextromethorphan if you are allergic to the active substance. Likewise, the drug must not be used if you suffer from respiratory diseases (e.g. bronchial asthma) or inflammation of the lung tissue (pneumonia).
If you take dextromethorphan at the same time as other medications, there may be interactions. You should only take the following drugs together with dextromethorphan on medical advice:
- MAOI-type antidepressants
These substances can increase or decrease the effectiveness of dextromethorphan.
Since dextromethorphan is broken down in the liver, the use of the active ingredient in patients with impaired liver function is only recommended under medical supervision.
pregnancy and breast feeding period
Dextromethorphan must be avoided during breastfeeding, as the active ingredient can cause the infant to flatten and slow down breathing (respiratory depression). During pregnancy, mothers should also avoid the drug, as not enough studies are available to safely rule out a deformity of the unborn child.
Driving and using machines
Even when used correctly, the active ingredient often leads to slight tiredness. This can impair the ability to react to such an extent that it is not possible to safely participate in road traffic. You should therefore avoid driving or using machines during dextromethorphan therapy.
This is how they get drugs with dextromethorphan
Dextromethorphan is available from pharmacies without a prescription as a cough syrup, lozenge or hard capsule.
Tags: anatomy diet menshealth
















.jpg)



