Laryngitis
All content is checked by medical journalists.When the larynx is inflamed, the lining of the larynx and vocal cords become inflamed. This often happens with a respiratory infection - like a cold - or when the larynx is severely irritated. The main symptom of laryngitis is hoarseness. It can last for several weeks - then it becomes chronic. Read here how to get a laryngitis, how to recognize it and how to treat it.
ICD codes for this disease: ICD codes are internationally recognized codes for medical diagnoses. They can be found, for example, in doctor's letters or on certificates of incapacity for work. J05J38J04J06J37
Brief overview: laryngitis
Causes: Infection with viruses or bacteria, stressed vocal cords, irritants in the air, allergies, chronic heartburn (reflux), crooked nasal septum, sinusitis,
Symptoms: hoarseness, voicelessness, sore throat, difficulty swallowing, dry cough, sensation of foreign bodies in the throat, frequent clearing of throat
Therapy: protection of the voice, avoidance of spicy or hot food, smoking, alcohol, inhalation, antibiotics only in the case of bacterial infection
Diagnosis: On the basis of typical symptoms, with a laryngoscope by the ear, nose and throat doctor, laboratory determination of the pathogens.
Prognosis: The acute form usually heals quickly on its own, the chronic form can always recur, under certain circumstances changes in the mucous membranes in the form of polyps, an increase or drying up of the mucous glands.
Laryngitis: causes
Laryngitis can have several causes:
Viruses and bacteria
Mostly the reason is an infection of the respiratory tract with viruses. Possible pathogens are, for example, parainfluenza and influenza viruses (flu viruses), rhino (cold viruses) and adenoviruses. In addition, bacteria, especially streptococci, can subsequently settle on the attacked mucous membranes.
Heavily stressed vocal cords
People like singers or teachers who use their voices a lot are more likely to get laryngitis. The vocal apparatus is then irritated and overwhelmed.
Irritating air to breathe
People who very often inhale dry air, dust, chemical vapors or irritating pollutants such as cigarette smoke can also quickly develop laryngitis.
Allergies
Other diseases can also cause laryngitis. For example, those who have a chronically blocked nose due to allergies almost only breathe through the mouth and thus promote a sore throat and larynx. This also applies to chronic sinus infections.
Crooked nasal septum
A bent nasal septum also makes breathing difficult. It can therefore also promote laryngitis.
Chronic heartburn (reflux disease)
In people with reflux disease, gastric juice repeatedly gets into the esophagus - this can also cause the larynx to become inflamed.
Is laryngitis contagious?
If an infection with viruses and / or bacteria is the cause of the laryngitis, it can be contagious. For example, influenza viruses spread as tiny droplets when they speak or cough and are inhaled again by other people.
Anyone who is infected can then just get a runny nose or the flu without them spreading to the larynx. How strong and how long a laryngitis is contagious varies depending on the pathogen.
Doctors differentiate between two forms of laryngitis, depending on the duration:
Acute laryngitis
Acute laryngitis is usually triggered by an infection with viruses or bacteria. Sufferers usually feel sick for a few days, have a sore throat, cough and, most of all, are hoarse - sometimes their voice no longer works at all. The acute laryngitis usually heals without consequences.
Chronic laryngitis
Chronic laryngitis lasts longer than three weeks. It can develop from acute laryngitis that has not healed, but also when the area of the larynx and vocal cords is permanently stressed. Sometimes other conditions (such as gastric reflux disease) cause chronic laryngitis as well.
In addition to normal laryngitis, two other special forms are possible that play a role especially in children:
Pseudo croup (croup syndrome)
Krupp syndrome is another name for acute stenosing laryngotracheitis. To distinguish it from the "real" croup disease, doctors often refer to it as pseudo croup. This condition occurs mostly in children between six months and three years of age.
The Krupp syndrome manifests itself primarily in a hoarse voice, a barking cough and abnormal noises when inhaling (inspiratory stridor). In addition to the laryngitis, the mucous membrane of the affected children is so swollen in the area of the larynx and windpipe that the airways are narrowed and the throat feels constricted. Severe swelling can cause the affected child to breathlessly.
Epiglottitis
Another, meanwhile rare disease is the so-called epiglottitis. It mostly affects children between the ages of two and six. This is a special form of larynx inflammation in which the epiglottis, which is located at the "entrance" of the larynx, becomes inflamed.
In epiglottitis, the epiglottis and larynx swell significantly. The child has a high fever, severe swallowing difficulties, shortness of breath and speaks “lumpy”. Epiglottitis is an emergency that requires immediate medical attention!
Laryngitis: symptoms
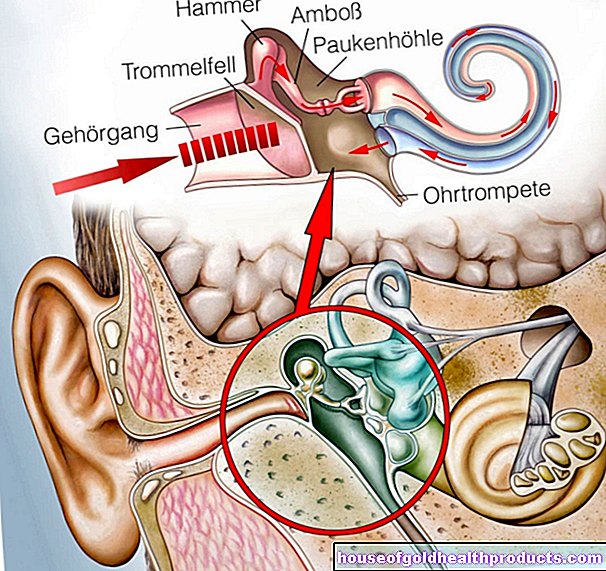
The main symptom of laryngitis is hoarseness: the voice is less resilient, sounds scratchy changed (dysphonia) or fails completely, so that only a whisper is possible (aphonia). The larynx with its vocal folds and cords is responsible for making sounds for speaking, singing and screaming. If it is swollen or covered, it affects the voice.
The following symptoms are characteristic of laryngitis:
- hoarseness
- Change in voice (dysphonia)
- Sore throat
- difficulties swallowing
- cough
- frequent throat clearing
- Foreign body sensation ("lump in the throat")
- possibly fever (acute laryngitis)
Laryngitis: treatment
If the larynx is caused by a viral infection, only the symptoms can be alleviated. Antibiotics don't help. Only if bacteria are also involved in the laryngitis will the doctor prescribe an antibiotic that specifically fights the pathogen.
Take care of your neck!
In addition, the only thing that helps is to go easy on the neck and let the larynx mucous membrane swell in peace.The following measures can support the body:
- Try to drink as much as possible despite difficulty swallowing - especially water and not lukewarm herbal teas.
- Save your voice.
- Do not smoke!
- Avoid dusty and dry air.
- Avoid hot and spicy food and alcohol.
Home remedies for laryngitis
Some people use home remedies to treat laryngitis. For example, it can be helpful to inhale hot water vapor and saline solutions to moisten the airways. You can also add eucalyptus oil or chamomile to the water. Potato wraps and quark wraps are also classic home remedies for laryngitis.
Chronic laryngitis: treatment often takes a long time
Chronic laryngitis is often less treatable than acute one. Then it is very important that you protect your voice and generally irritate the airways as little as possible. If you smoke, you should definitely take a break! The doctor may prescribe a cortisone supplement. It has an anti-inflammatory effect and allows the swelling to subside.
Sometimes chronic laryngitis is related to a problem with voice training. In this case, it can be helpful to see a speech therapist. If another condition is behind laryngitis, such as chronically inflamed sinuses or reflux disease, it is important to treat them.
Laryngitis: examinations and diagnosis
Most people with acute laryngitis see a doctor for typical cold symptoms. He will first do a general physical exam and look down the patient's throat to check if the throat is red or the tonsils are swollen.
If a larynx is suspected, the doctor asks about symptoms such as a sore throat, cough, and hoarseness. He may then refer you to an ear, nose and throat specialist (ENT specialist).
Larynx examination with a laryngoscope
If the patient is noticeably hoarse or complains of pain in the larynx area, the ENT doctor will look specifically at the larynx for diagnosis. To do this, he uses a so-called laryngoscope. This is a small hand-held device specifically designed to look at the larynx. The doctor can examine the larynx and vocal cords using a mirror. In children or people with a strong gag reflex, the doctor uses a flexible, tube-like laryngoscope that he inserts through the nose.
Reddened, thickened, slimy
When the larynx is inflamed, the laryngoscope shows red and thickened lining of the larynx. The vocal cords are also usually red and swollen. In the case of acute laryngitis, they are also often covered with thick mucus and whitish or purulent coatings. The doctor may take a swab of the inflamed tissue, which can be used to determine the exact pathogen.
Examination for cell changes
Laryngoscopy is also used to rule out other diseases, for example tuberculosis or a tumor on the larynx. This is especially important for smokers. In cases of doubt, the doctor takes a tissue sample from the larynx mucosa (biopsy) in order to have it examined in the laboratory for cell changes.
Laryngitis: disease course and prognosis
Acute laryngitis is usually straightforward and heals within a few days without any further consequences. However, those who do not take enough care of themselves, talk a lot or smoke a lot during this time, risk transitioning into a chronic form.
Chronic laryngitis can also regress completely if it is recognized and treated in good time. However, relapses are relatively common. If the chronic laryngitis persists for a long period of time, the laryngeal mucosa can change permanently.
Sometimes mucosal growths (polyps) then form. In some cases an excessive number of mucous glands develop (laryngitis hyperplastica) or the mucous glands completely stop working (laryngitis sicca).
With a pathologically altered and thickened larynx mucosa, the probability also increases that the cells will degenerate and develop larynx cancer.
Tags: drugs interview alternative medicine