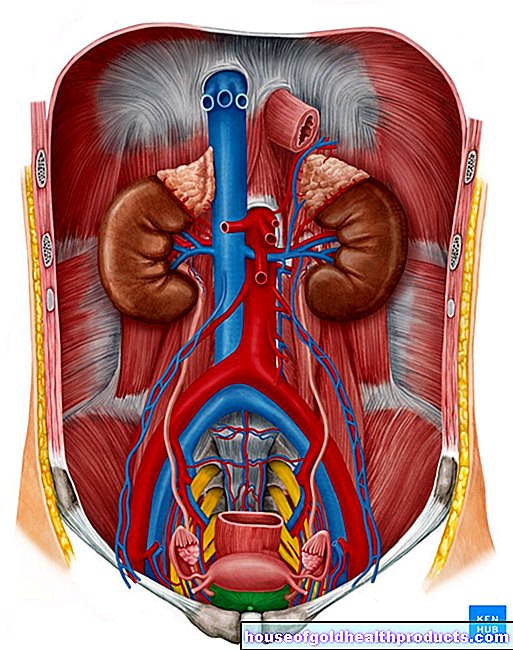
Prostate biopsy
All content is checked by medical journalists.During a prostate biopsy, the doctor takes tissue samples from the patient's prostate gland. It is used to diagnose cancer or precancerous lesions and is carried out if the doctor reveals anything unusual during a palpation or ultrasound examination of the prostate. Read everything about the procedure and the risks of prostate biopsy here.
How is the prostate biopsy performed?
The procedure is carried out on an outpatient basis and under local anesthesia. The patient lies in the so-called lithotomy position (supine position with bent, slightly raised legs) or on the side. The doctor carefully inserts a lubricated ultrasound probe into the patient's rectum. A thin hollow needle is inserted through a guide channel, which pops out through a spring mechanism and punches out a tissue cylinder with a size of ten to fifteen millimeters (punch biopsy).
Prostate biopsies can also be performed using what is known as an aspiration biopsy. The cells are sucked in through the hollow needle. The punch biopsy, however, is the common procedure, as it provides more sample material for a reliable diagnosis.
During an examination, the doctor removes around ten to twelve cylinders of tissue from different areas of the prostate within a few minutes. The specimens are then examined finely under the microscope in a laboratory.
Prostate biopsy: yes or no?
Prostate biopsy is a safe procedure with few complications. Symptoms that occur after the procedure usually subside within a few days. These include:
- Difficulty urinating, possibly requiring a urinary catheter
- Blood in urine, stool or ejaculate
- Circulatory disorders
- Fever, infection
Malignant neoplasms of the prostate are very treatable, provided they are recognized in good time. Prostate biopsy is currently the only way to reliably diagnose prostate cancer. So if cancer of the prostate is suspected, a biopsy is essential and enables rapid therapy.
What do I have to consider after a prostate biopsy?
Symptoms usually only occur in the first few days after the prostate biopsy and then regress. To avoid the risk of infection, the doctor prescribes antibiotic prophylaxis. If you still notice a fever or a general feeling of illness, you should contact your urologist or the urological outpatient department of the clinic immediately.
Tags: alternative medicine Menstruation foot care