Blood test
Valeria Dahm is a freelance writer in the medical department. She studied medicine at the Technical University of Munich. It is particularly important to her to give the curious reader an insight into the exciting subject area of medicine and at the same time to maintain the content.
More about the experts All content is checked by medical journalists.Blood tests are one of the most helpful diagnostic methods in medicine. The ingredients and the number and nature of the individual solid components of the blood are compared with reference values and normal ranges. Read everything you need to know about the different types of blood tests, how they are done, and when they are needed.

What is a blood test?
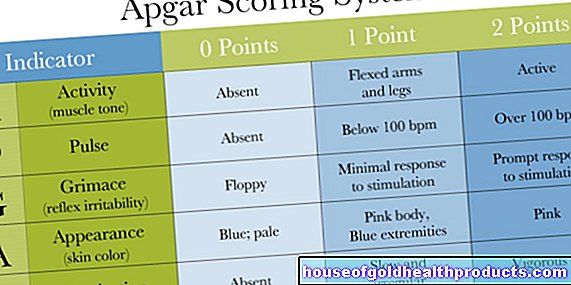
During a blood test, a blood sample is broken down into its components in the laboratory and examined with the help of various tests. This often includes a small blood count (counting the main cell types such as erythrocytes, leukocytes, thrombocytes and determining the Hb value and hematocrit) and a differential blood count (more precise differentiation of the various types of leukocytes.
In addition, numerous molecules, substances and substance compounds floating in the blood or physically dissolved can be determined, such as salts, trace elements, fats or metabolic products, enzymes and hormones.
When do you do a blood test?
On the one hand, a blood test can be carried out routinely to check the course and possible effects of an illness. A classic example of this is blood sugar control in diabetes mellitus.
On the other hand, a blood test helps in the diagnosis of many diseases, as conclusions can be drawn about the function of the organs on the basis of various blood values. A rapid test for the enzyme troponin helps to rule out a heart attack, as its concentration in the blood is increased when the heart muscles are damaged. In addition, pathogens in the blood or specific antibodies against a pathogen can usually be detected in the event of an infection.
What do you do with a blood test?
For a blood test, venous blood is usually drawn, usually from a vein in the crook of your arm. Sometimes a few drops of blood from the fingertip or the earlobe are enough, for example to determine blood sugar levels in diabetics.
This whole blood contains all the ingredients. Depending on the question, it is subjected to a wide variety of tests. The solid components in the blood can be separated from the liquid in which they swim (plasma) by centrifugation. To do this, the blood must first be mixed with an anticoagulant substance (such as citrate, EDTA). This is usually already contained in the tubes that are used to draw blood. For example, a blood count is created from EDTA blood or the blood group is determined. Citrated blood is used, for example, to measure the rate of sedimentation of the blood cells.
Blood serum is required to measure many parameters. It corresponds to the blood plasma minus the coagulation factors. To obtain the serum, whole blood is allowed to coagulate (clot) and the liquid phase (= serum) is then separated off by centrifugation. The blood serum can be tested for blood sugar, blood lipids, hormones, enzymes, iron and other minerals as well as antibodies, for example.
Blood cell determination
While blood counts used to be evaluated microscopically, nowadays automatic hematology devices count the number of erythrocytes, leukocytes and platelets. The breakdown into the individual subgroups of the leukocytes is also carried out by machine. Even today, a doctor only counts the blood cells under a microscope in rare cases.
What are the risks of a blood test?
The blood test as such does not involve any risks. In rare cases, the injection site may become infected when the blood is drawn. Bruises (hematomas) mainly form if the wound has not been compressed long enough. Wrong measurements are rare, but still possible. For example, too long a blood congestion during the decrease leads to incorrectly high potassium values.
What do I have to consider when doing a blood test?
Some blood tests require you to be on an empty stomach. This means that you shouldn't eat anything eight to twelve hours beforehand. You can consume water and tea without sugar. Once the laboratory has done the blood test, your doctor will discuss the results with you.
Tags: Diseases home remedies tcm