Cold sore
Marian Grosser studied human medicine in Munich. In addition, the doctor, who was interested in many things, dared to make some exciting detours: studying philosophy and art history, working on the radio and, finally, also for a Netdoctor.
More about the experts All content is checked by medical journalists.The cold sore (herpes labialis) is the most common form of herpes. It is usually caused by the herpes simplex virus type 1 and causes painful blisters at the transition between the lip and the skin of the face. Read the most important information about "cold sores" here.
ICD codes for this disease: ICD codes are internationally recognized codes for medical diagnoses. They can be found, for example, in doctor's letters or on certificates of incapacity for work. B00
Cold sores: description
When "herpes" is mentioned, it usually refers to the clinical pictures caused by herpes simplex viruses. The pathogens, which are further subdivided into type 1 (HSV1) and type 2 (HSV2), mainly cause genital and cold sores. Type 1 is mainly responsible for the "herpes lip", type 2 is found in genital herpes. If viruses are transmitted from the genital area to the lips - for example in sexual practices - it can also be the other way around.
How does cold sore come about? - The transmission route
Cold sores are usually transmitted by smear infection, i.e. through direct transmission of the virus from one person to another. In cold sores, the viruses are on the one hand directly at the infected area, especially in the vesicle fluid, on the other hand they are also distributed in the saliva. Infected saliva is the main source of infection in this form of herpes. Kissing carries a high risk of transmission when there is active virus shedding.
The viruses can also be transmitted over a short distance via the air, i.e. by droplet infection when sneezing or speaking. Herpes labialis is particularly common in children because they often hold their mouths with their fingers and there is close physical contact. The viruses then quickly get from one child's hand to another's mouth.
An indirect infection with cold sores through infected objects such as glasses, napkins and cutlery is also possible because the herpes virus can survive outside the body for up to two days.
During the initial infection, the viruses enter the body through the smallest cracks in the skin and mucous membranes and initially multiply there in epithelial cells on the surface of the skin, which leads to the typical symptoms. Even after these symptoms have healed, the herpes viruses remain in the body for a lifetime.
Because some of the pathogens migrate along nerve fibers to so-called nerve ganglia - collections of nerve cell bodies. There they evade the immune system and remain in a state of rest from which they can awaken under certain circumstances. The process of virus migration along the nerve fibers is known as retrograde axonal transport. In the case of cold sores, the viruses usually reach the ganglia via the fibers of the trigeminal nerve. This nerve, often just referred to as the trigeminal nerve, is largely a sensory nerve and is responsible for feeling on the skin of the face.
Why does cold sore break out again? - The risks of reactivation
The herpes viruses can wake up from their dormant state at any time and cause a new outbreak of cold sores. One then speaks of reactivation. This usually happens when the immune system is weakened. The frequency of reactivations varies greatly from person to person.
Such a weakening of the immune system can have a wide variety of causes, with a cold or flu-like infection often behind it. Cold sores therefore occur particularly often with a fever. Cold sores are therefore also called cold sores.
Emotional or physical stress can also trigger reactivation. Cold sores occur more frequently after intense physical exertion, but also in times of greater psychological stress. Other risk factors are external damage to the lip, for example in the form of injuries or skin damage from increased UV radiation. Reactivations after visiting the dentist are also possible, as the lips are stressed during the treatment.
Certain drugs and diseases that are associated with a general immune deficiency - such as AIDS - can cause frequent reactivations. Hormonal changes, for example during menstruation or pregnancy, can also cause cold sores to break out.
Herpes: lip as a weak point?
The reasons why herpes lips are particularly preferred are, on the one hand, the high density of sensory nerve fibers along which the viruses can move. On the other hand, the skin at the transition between the lip and the facial skin is particularly sensitive. Herpes at the corner of the mouth is also relatively common because this area is mechanically particularly stressed and can easily tear, especially in dry, cold and low temperatures.
How common is cold sores?
The type 1 herpes simplex virus is very widespread in the population. The infection often occurs within the family and usually already in childhood.According to research, around 33 percent of children and 74 percent of adults in Europe are infected with HSV1.
Cold sores: symptoms
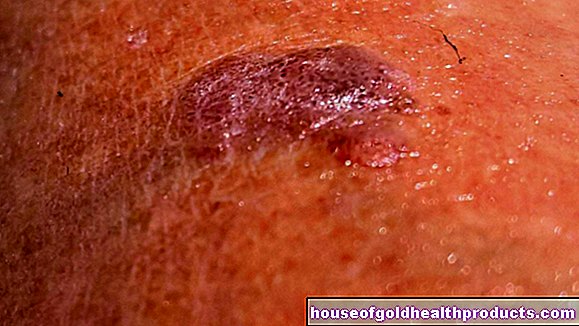
Anyone who has not yet been affected has probably already seen it in others, the classic "herpes lip". Symptoms such as itching, tingling and pain usually appear first before the typical vesicles finally appear.
Early symptoms of cold sores
Herpes on the lip often announces itself before the actual outbreak. The early symptoms include:
- Feelings of tension and numbness
- Tingling and itching
- Stinging and burning
- Reddening of the skin in the affected area
The extent of these early symptoms can vary widely, and sometimes they are completely absent. Before this, especially with initial infections, there are sometimes unspecific symptoms, the so-called prodromal symptoms.
Main symptoms
The herpes viruses multiply in the skin cells and thus destroy them. This causes tissue damage in the form of small ulcers and vesicles that can burst quickly when touched. The vesicle fluid contains a high concentration of herpes viruses and is therefore very contagious. If the vesicles burst on their own after a day or two, small open wounds develop, which close again after a few days and become encrusted.
After about a week, the scabs will gradually fall off, leaving new, healthy skin. The cold sore will usually heal up after about ten days.
Complications from cold sores
Herpes on the lip is basically harmless, but it can lead to a so-called superinfection. The affected areas are also infected with bacteria. Open wounds and a weakened immune system favor bacterial infection. The symptoms can be aggravated and last much longer.
Even with a first infection with herpes simplex, the symptoms can sometimes be more pronounced than with later reactivations. Especially in children, the clinical picture can then resemble a severe flu-like infection with a high fever and severe malaise.
How do you examine cold sores?
As a rule, in the case of herpes labialis, a visual diagnosis based only on the symptoms is completely sufficient. The classic "herpes lip" appears so typical that no further examination is necessary. A simple herpes reactivation does not require a visit to the doctor, only if complications arise or other diseases with similar symptoms have to be ruled out, special examinations are helpful.
In addition to detecting certain antibodies, the smallest virus components can be detected (antigen detection). The genetic material of the virus can also be reproduced using a special method and then detected. Finally, the herpes viruses can also be cultivated and then precisely determined.
How do you treat cold sores?
Ultimately, options for treating cold sores are limited. The active ingredients can be administered either in tablet form or as a cream to be applied to the lips. Herpes cannot be prevented with this, however, the duration of the illness can be shortened.
Cold sores: disease course and preventive measures
Herpes labialis is often very annoying for those affected, not least for cosmetic reasons. After two weeks at the latest, a cold sore will have healed without complications. Those affected should avoid stress of any kind if possible and support their immune system in the form of a healthy diet, adequate sleep and regular exercise.
In order to avoid transmission of the herpes virus from the lip to other parts of the body such as the eyes, the affected area should not be touched if possible. Never pierce or scratch the vesicles as the liquid is highly contagious. After unavoidable contact, wash your hands thoroughly immediately afterwards to reduce the spread of cold sores.
Tags: sleep menopause desire to have children