hemoglobin
and Eva Rudolf-Müller, doctorEva Rudolf-Müller is a freelance writer in the medical team. She studied human medicine and newspaper sciences and has repeatedly worked in both areas - as a doctor in the clinic, as a reviewer, and as a medical journalist for various specialist journals. She is currently working in online journalism, where a wide range of medicine is offered to everyone.
More about the experts All content is checked by medical journalists.Hemoglobin (Hb) is a protein found in the red blood cells, the erythrocytes. Because it gives the blood its red color, it is also known as the red blood pigment. The most important task of hemoglobin is to transport oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood. Read everything about hemoglobin, what the normal Hb value is, when it changes and what causes a changed Hb value can have.
What is hemoglobin?
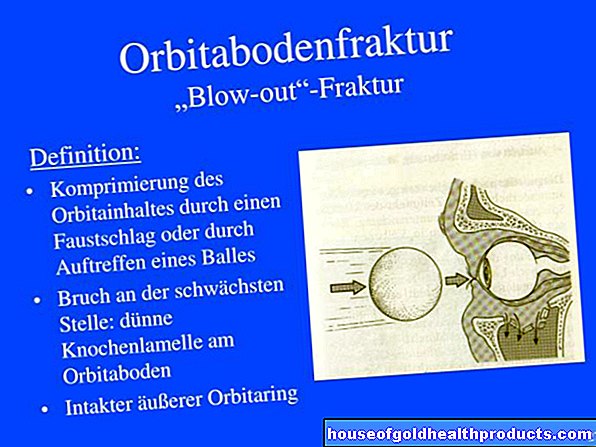
Hemoglobin is an important part of the red blood cells, the erythrocytes. It binds oxygen (O2) and carbon dioxide (CO2) and enables them to be transported in the blood. It is formed in the precursor cells of the erythrocytes (proerythroblasts, erythroblasts) and is mainly broken down in the spleen. On laboratory results, hemoglobin is usually abbreviated with "Hb" and is given in the unit grams per liter or grams per deciliter (g / L or g / dL).
Hemoglobin: Structure and Function
Hemoglobin is a protein complex consisting of the dye heme and the protein component globin. It has four subunits, each with a heme molecule. Each of these heme molecules is able to bind an oxygen molecule, so that a hemoglobin complex can carry a total of four oxygen molecules.
The hemoglobin in the small pulmonary vessels absorbs the oxygen from the air we breathe, transports it through the bloodstream throughout the body and releases it to the cells in the tissue. Hemoglobin loaded with oxygen is called oxyhemoglobin; once it has released all O2 molecules, it is called deoxyhemoglobin. In the discharged form, it can absorb carbon dioxide in the body, which it then brings back to the small vessels in the lungs. There the CO2 is released and exhaled.
Fetal hemoglobin
The hemoglobin of a still unborn child is called fetal hemoglobin (HbF) and has a different structure than the hemoglobin of an adult (HbA). HbF has a higher attraction for oxygen molecules than HbA, which facilitates the exchange of oxygen between maternal and child blood during pregnancy. After birth, the child's body curbs the production of HbF and increasingly replaces it with HbA. During this transition phase, decreased Hb levels often occur in the third month after birth, but this is normal and self-regulating.
HbA1c
HbA can be divided into various sub-forms, one of which is HbA1c. It plays an important role in diabetes therapy control. You can read more about this in the article HbA1c.
When is hemoglobin determined?
The hemoglobin concentration is a standard part of every blood test. The Hb blood level is of particular interest if anemia or an increase in red blood cells (polyglobulia) is suspected.The Hb level in the blood also provides indirect information about disorders of the water balance (dehydration, overhydration).
If certain diseases are suspected and as part of some preventive examinations, the doctor can also use special test procedures to check whether there is hemoglobin in the urine or stool. Example provides Hb in urine from a certain concentration on, among other things:
- Breakdown of red blood cells in the blood (haemolysis)
- Kidney disease (carcinoma, kidney tuberculosis, and others)
- Bleeding in the urinary tract
When is the hemoglobin level normal?
The normal hemoglobin value depends primarily on gender and age: a hemoglobin value between 14 - 18 g / dl is considered the normal Hb value for men. Women should have a blood Hb value of 12-16 g / dl. There is an Hb value table with reference ranges for children of different ages. In this way, the pediatrician can immediately see whether the Hb level is normal.
When is the hemoglobin level decreased?
Decreased laboratory values (Hb below 14 g / dl in men or below 12 g / dl in women) indicate anemia. However, this alone does not indicate the cause of the anemia: To do this, further parameters of the red blood cells must be determined, for example erythrocyte count, hematocrit, MCV and MCH. Examples of diseases with anemia are:
- Iron deficiency anemia (common in young women)
- Synthesis disorders of the globin chains (thalassemia, sickle cell disease)
- Chronic diseases (for example cancer, chronic inflammation or infectious diseases)
- Folic acid deficiency or lack of vitamin B12
Decreased hemoglobin also occurs in acute bleeding because the body is unable to produce new red blood cells quickly enough.
Overhydration (overhydration) also leads to a reduced Hb value in the laboratory. However, this is only a relative deficiency. The overall Hb level in the body remains the same, but the blood volume increases, which in turn causes the Hb level to decrease. It is, so to speak, a dilution anemia. Overhydration occurs, for example, with the rapid supply of infusion solutions or as part of kidney failure.
Further information: Hemoglobin too low
If you want to learn more about the causes of low hemoglobin levels, read the article Hemoglobin too low.
When is the hemoglobin increased?
An increased hemoglobin level is often an indication of an increased number of red blood cells. This is called polyglobulia in medicine. It occurs in the following situations, among others:
- Polycythemia vera (abnormal reproduction of various blood cells)
- chronic oxygen deficiency (heart or lung diseases as well as prolonged stays at high altitudes)
- Autonomous or external supply of EPO (in the context of kidney disease or doping)
Even if there is a lack of fluid in the body (dehydration), the Hb value can be too high. Analogous to dilution anemia, this is merely a relative excess of red blood cells, which is compensated for by the supply of fluid.
What to do if the hemoglobin value changes?
A slight deviation from the normal Hb value is usually harmless. However, changed hemoglobin values also occur in the context of various diseases that require further clarification.
If the hemoglobin is too high or too low, the doctor will do additional blood tests. If the decrease in hemoglobin is due to a deficiency, it is sometimes sufficient to give iron, folic acid or vitamin B12 supplements. After the patient has taken this for a while, the doctor will do another blood test to see if Hb has returned to normal. However, if the Hb level is very low, a blood transfusion may be necessary.
If a high hemoglobin value provides evidence of polyglobulia and this is confirmed, there is an increased risk of vascular occlusions due to the thicker blood. The polyglobulia is then treated with bloodletting, whereby the doctor continues to check the hemoglobin regularly.
Tags: stress gpp home remedies










.jpg)