Gastric balloon
Dr. med. Fabian Sinowatz is a freelancer in the medical editorial team.
More about the experts All content is checked by medical journalists.The gastric balloon is a silicone balloon filled with fluid or air that is inserted into the stomach by means of a gastroscopy. Its size ensures that a feeling of satiety occurs more quickly when eating. However, a gastric balloon is only effective if the diet and lifestyle habits are changed at the same time and is removed after six months at the latest. Find out everything you need to know about the gastric balloon here.
What is a gastric balloon?
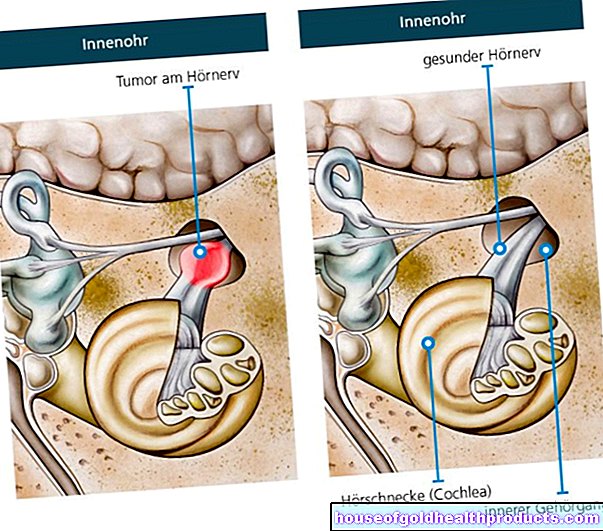
In contrast to the gastric band and stomach reduction, the gastric balloon is a non-surgical measure for the treatment of obesity. It is supposed to help overweight people lose weight.
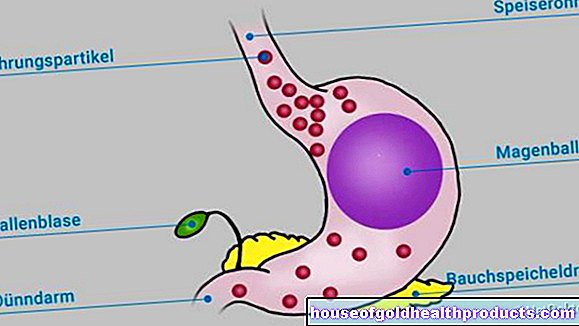
The way the gastric balloon works is based on a simple principle: the balloon filled with liquid or air takes up so much space in the stomach that the person wearing it becomes full more quickly and therefore eats less overall. A feeling of satiety is mainly caused by the stretching of the stomach wall. The gastric balloon can only be part of the therapy for obesity, as lifestyle habits and the composition of the diet also play an important role.
The gastric balloon is made of a soft silicone that is filled with liquid or air. The gastric balloon is inserted and removed again as part of a gastroscopy.
For whom a gastric balloon is suitable
In contrast to the other procedures for losing weight (gastric band, sleeve stomach, gastric bypass, etc.), which are only used for very heavily overweight people, the gastric balloon can also be used for people who are moderately overweight (body mass index between 28 and 40 kg / m2) will. The most common use of a gastric balloon is for people who weigh between 85 and 130 kilograms. In very obese patients, the method is sometimes used to prepare a stomach reduction in order to reduce the weight a little beforehand and thus reduce the risk of surgery.
For whom a gastric balloon is not suitable
A gastric balloon should not be used with certain physical and mental illnesses (contraindications). These include previous operations, illnesses or malformations of the stomach or esophagus, stomach ulcers, as well as addictions such as alcohol or drug addiction. Even with severe eating disorders such as bulimia or other severe mental illnesses, a gastric balloon must be avoided. Furthermore, this method is not approved for pregnant women. People who are permanently dependent on anticoagulant medication cannot receive a gastric balloon either.
How is a gastric balloon used?
Before the gastric balloon is inserted, the esophagus and stomach must be mirrored (esophagogastroscopy). This examination serves to rule out pathological changes that speak against the insertion of a gastric balloon. During a gastroscopy, the doctor pushes a so-called endoscope through the mouth over the esophagus to the stomach. It has a light source and a camera.In this way, the doctor can examine the esophagus and stomach for pathological changes.
To insert the balloon, the doctor pulls the endoscope back and pushes the folded gastric balloon on a tube into the stomach. When the balloon has reached the stomach, the doctor checks the correct position with the endoscope. The balloon is then filled with about 400 to 700 milliliters of blue saline solution through the tube. Then the doctor pulls off the tube and checks the correct placement of the balloon again via the endoscope.
The procedure takes an average of 20 to 30 minutes and takes place in light twilight sleep (sedation). It can be done on an outpatient basis. However, because of the anesthesia, the patient should not actively participate in road traffic.
Some patients experience bloating, nausea, and vomiting after balloon insertion. A hospital stay of about one to two days is then required in order to supply the patient with fluid via the vein.
How is the gastric balloon removed?
The gastric balloon is removed after six months at the latest in order to limit the risk of the balloon wall tearing due to the constant effects of gastric acid and gastric movement. A gastroscopy is necessary again to remove the gastric balloon. During the procedure, the balloon is pierced so that the fluid can escape. As a result, the gastric balloon loses its firm consistency and can simply be pulled back through the esophagus. The entire procedure usually only takes a few minutes.
Effectiveness of a gastric balloon
The effectiveness of the gastric balloon can vary greatly from person to person. A weight loss of around 10 to 25 kilograms is realistic. The weight loss is particularly pronounced in the first three months.
The success of losing weight largely depends on how well the patient succeeds in maintaining a changed eating behavior at the same time. Anyone who consumes a lot of sweet drinks or sweets can even continue to gain weight despite the gastric balloon. Overall, the effectiveness of the gastric balloon is significantly less than that of the surgical procedure.
Side effects
The side effects of a gastric balloon can be significant, especially in the first few days after insertion. Typical are nausea, abdominal cramps and a pronounced feeling of fullness. These complaints subside as soon as the stomach has got used to the foreign body. This is usually the case after about three to seven days. Even in the long term, however, some patients complain of a constant feeling of pressure or fullness, belching and heartburn. If the gastric balloon causes permanent problems, it should be removed early.
Risks and Complications
Like any medical procedure, the gastric balloon insert carries certain risks. Risks specific to the procedure include injuries to the teeth, esophagus, or stomach from the endoscope. However, this is very rare.
What should I do if a gastric balloon bursts?
Basically, there is also the risk that the balloon will burst. Then the blue colored liquid emerges from the balloon and is absorbed into the blood through the mucous membrane. This quickly turns the urine blue. Gastric balloon users must watch out for this blue coloration of the urine, as it indicates a leak in the balloon.
A damaged gastric balloon must be removed immediately with a gastroscopy (endoscopic), as the collapsed balloon can otherwise cause an intestinal obstruction. Anyone who suspects a ruptured gastric balloon should consult their doctor immediately. If the balloon bursts at night, a hospital emergency room should be headed for.
Air-filled or liquid-filled gastric balloon?
The gastric balloon can be filled with either liquid or air. Some doctors are critical of the air-filled variant for several reasons: On the one hand, a leak in the air-filled gastric balloon is not noticed so quickly because the urine is not blue. This also increases the risk of the balloon leaking into the intestine and thus of an intestinal obstruction. The weight reduction with the air-filled balloon may also be worse, since it only weighs about 30 grams. The liquid-filled gastric balloon, on the other hand, has a dead weight of around 450 to 700 grams and thus ensures a faster feeling of satiety. Also important for air travelers: Since gases expand at great heights, you are not allowed to fly with an air-filled gastric balloon.
Gastric balloon: costs
The costs for a gastric balloon differ considerably depending on the treatment effort and the doctor. As a rule, the gastric balloon costs are in the range between 1500 and 4500 euros. However, interested parties should not only pay attention to the price, but above all to the quality of treatment. This can often only be assessed by exchanging experiences with other patients or through doctor review portals. The personal impression made by the attending physician and the practice in the initial consultation should also be included in the overall assessment.
Gastric balloon health insurance
Like all surgical interventions for the treatment of obesity, the gastric balloon is not yet a standard benefit of the statutory health insurance companies. This means that the procedure is only paid for by the health insurance company upon request and only if certain criteria are met. Private patients should discuss the possibility of reimbursement with their health insurance company in advance.
Self-payers should note that in the event of complications from the gastric balloon, they also have to bear the costs of their treatment.
Tags: stress laboratory values Diagnosis