Urinary tract infection
Dr. med. Julia Schwarz is a freelance writer in the medical department.
More about the experts All content is checked by medical journalists.Urinary tract infections are various inflammations of the mucous membranes of the urinary tract. These include the organs that transport urine from the kidneys to the outside (ureters, bladder and urethra). Most of the time, the bacteria rise from the urethra to the bladder and sometimes further up towards the kidneys. Here you can read everything you need to know about the various forms of urinary tract infection.
ICD codes for this disease: ICD codes are internationally recognized codes for medical diagnoses. They can be found, for example, in doctor's letters or on certificates of incapacity for work. N28O23N34
Urinary Tract Infection - Common Causes
A urinary tract infection is usually triggered by intestinal bacteria that travel from the anus to the outer urethra and then ascend into the urogenital tract. Bad hygiene after using the toilet is often responsible for this. In other cases, urinary tract inflammation occurs after unprotected sexual intercourse
Urinary tract infection - special risk factors
Women are significantly more likely to develop urinary tract infections. This is because women have a shorter urethra than men, which is why germs can more easily get into the urinary bladder. Young women in particular are often affected by urinary tract infections. Older people with a urinary catheter are also more likely to develop urinary tract infections. Here the bacteria use the catheter like a “guide rail”.
In addition, children can also be affected by a urinary tract infection. There is an increased risk of infection, especially in diaper age, as bacteria can multiply rapidly in a damp environment. Further risk factors for urinary tract infections are a weakened immune system (for example due to serious illnesses or drugs that suppress the body's immune system), metabolic diseases (such as diabetes mellitus) and urinary flow disorders (for example due to urinary stones, tumors or an enlarged prostate).
Urinary tract infection - symptoms
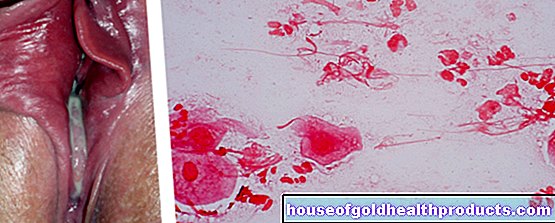
The urinary tract infection, like most bacterial infections, causes redness and swelling of the tissues. Typical symptoms of urinary tract infections are pain and burning sensation when urinating, blood in the urine, and a general feeling of illness. If the course is severe, the urinary tract infection can also be accompanied by fever and chills.
Many sufferers who repeatedly suffer from urinary tract infections recognize the first signs of a urinary tract infection early and can avert the impending cystitis with the help of home remedies.
Urinary Tract Infection - Uncomplicated, Complicated, or Symptom-Free?
Doctors differentiate the so-called uncomplicated urinary tract infection from the complicated urinary tract infection. A urinary tract infection is considered complicated if it occurs in certain groups of people or due to certain causes:
- in the case of anatomical peculiarities in the area of the lower urinary tract (for example urethral constrictions due to scarring or tumors, etc.).
- as a urinary tract infection in children, men or pregnant women
- if the person has kidney stones and these may be the cause of the urinary tract infection
- if you have an immune deficiency or severe metabolic disorders (such as diabetes mellitus)
The distinction between complicated and uncomplicated urinary tract infection is important because the complicated urinary tract infection is usually more severe (risk of so-called urosepsis) and / or lengthy and must be treated differently.
However, a proliferation of bacteria in the urinary tract does not always lead to symptoms of the disease. Doctors then speak of asymptomatic bacteriuria.
Urinary tract infection - this is how it is diagnosed
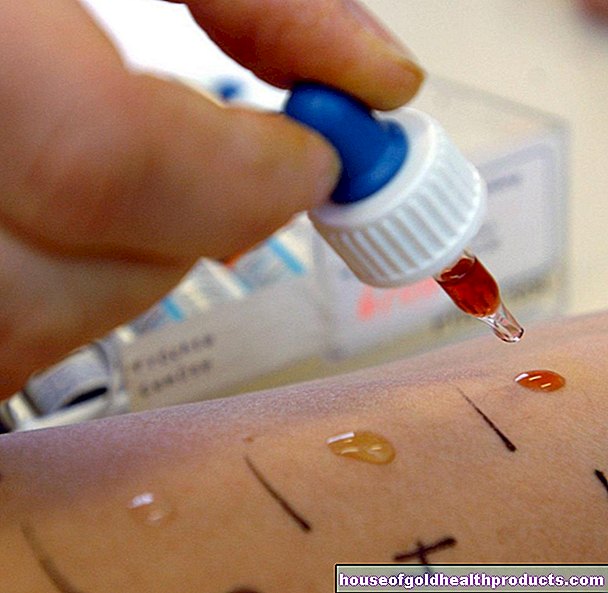
The doctor can usually make the diagnosis of "urinary tract infection" based on the typical symptoms and with a urine test strip. The test strip determines various typical changes in the urine such as the content of (parts of) red and white blood cells or certain products of bacterial metabolism (nitrate).
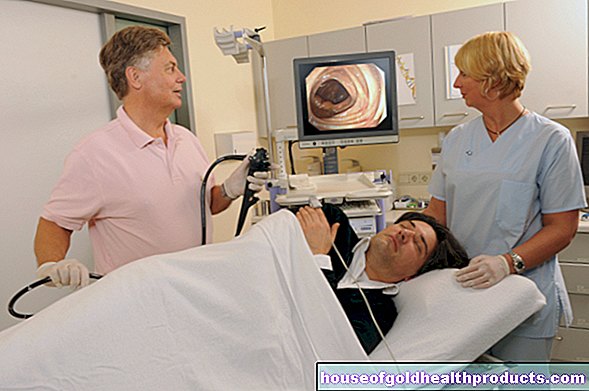
In the case of complicated or frequently recurring urinary tract infections (medical: recurrent urinary tract infections), further diagnostics are necessary. For this purpose, the bacteria responsible for the urinary tract infection are identified with so-called urine cultures and tested for their sensitivity to antibiotic treatment. In such cases, a cystoscopy can also be performed in order to discover previously unrecognized pathological changes in the urinary tract.
Urinary tract infection: therapy
Urinary tract infection therapy depends on the cause. A urinary tract infection can heal on its own, depending on the severity and the defenses of the body. If the body is unable to fight the urinary tract infection with its immune system, a doctor should be consulted immediately who will initiate appropriate treatment. Usually antibiotics are used, which cause a reliable cure for an uncomplicated urinary tract infection very quickly.
The complicated urinary tract infection is also treated with antibiotics, but the therapy takes longer and other antibiotics are used. For example, only certain antibiotics may be used to treat urinary tract infections in pregnant women and children
Tags: eyes prevention menopause