Thrombocytosis
and Martina Feichter, medical editor and biologistDr. med. Andrea Reiter is a freelance writer for the medical editorial team.
More about the expertsMartina Feichter studied biology with an elective subject pharmacy in Innsbruck and also immersed herself in the world of medicinal plants. From there it was not far to other medical topics that still captivate her to this day. She trained as a journalist at the Axel Springer Academy in Hamburg and has been working for since 2007 - first as an editor and since 2012 as a freelance writer.
More about the experts All content is checked by medical journalists.
If you have thrombocytosis, there are too many platelets in the blood. In most cases this has no health consequences and does not require treatment. But sometimes there are complications. Read here how thrombocytosis develops, which symptoms can occur and how to treat them.
What is thrombocytosis?
With thrombocytosis, the number of platelets is abnormally increased. Typically, it is between 150,000 and 400,000 per microliter (µl) of blood in adults. If the measured values are higher, there is thrombocytosis. However, platelet counts above 600,000 per microliter of blood are usually clinically relevant. Sometimes a value of over 500,000 per microliter is given as a criterion for thrombocytosis.
Thrombocytosis: causes
Very often it is a temporary (temporary) thrombocytosis that occurs after acute bleeding, surgery, childbirth or some infections. Even after surgical removal of the spleen (splenectomy), the number of platelets is increased.
Occasionally, certain inflammatory diseases lead to persistent thrombocytosis, for example rheumatoid arthritis, chronic inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis) or tuberculosis. The number of platelets can also be abnormally increased as a result of tumors (especially lung cancer).
Thrombocytosis: symptoms
Thrombocytosis usually does not cause any symptoms. Symptoms can only occur if it persists for a long time and / or is very pronounced. These include:
- headache
- dizziness
- Ringing in the ears (tinnitus)
- Nosebleeds
- Night sweats
- Bleeding gums
- Calf cramps
- Visual disturbances
Bleeding usually occurs when the platelets are not functioning properly. A disturbed blood circulation can also increase the tendency to form blood clots.
Thrombocytosis: what to do
Thrombocytosis usually does not require treatment. Blood-thinning therapy must only be started if the blood circulation in the small vessels of the body is disturbed due to a greatly increased platelet count. It is also important to clarify the cause of the thrombocytosis and, if necessary, treat it.
Tags: baby toddler symptoms desire to have children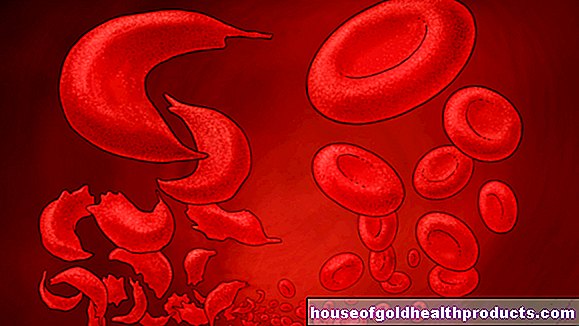







.jpg)