Cefuroxime
Updated on All content is checked by medical journalists.Cefuroxime is an antibiotic from the group of cephalosporin antibiotics. It can kill bacteria, so it is used to treat bacterial infections (such as those of the respiratory and urinary tracts). The active ingredient was originally from the mushroom Cephalosporium acremonium obtained, but can now be produced in the laboratory. Here you can read everything you need to know about cefuroxime.
This is how cefuroxime works
Cefuroxime irrevocably inhibits a certain enzyme in bacteria that they need to build up the cell wall during cell division. As a result, the cell wall is so damaged that water can flow into the bacterial cell. This causes the bacterial cell to swell and eventually break down.
This means that cefuroxime has a bactericidal (bactericidal) effect on dividing pathogens. It can also inhibit the growth of non-dividing pathogens (bakeriostatic effect).
Uptake, breakdown and excretion
Cefuroxime can be given by mouth in the form of cefuroxime axetil (ester compound) and is then absorbed into the body through the gastrointestinal tract. Direct administration into a venous blood vessel is also possible (intravenous administration).
The active ingredient is not broken down in the body, but excreted quickly and for the most part via the kidneys in an antibacterially active form.
When is cefuroxime used?
The areas of application (indications) of cefuroxime are infections with sensitive pathogens. These include:
- Respiratory infections
- Urinary tract infections such as cystitis or gonorrhea (gonorrhea)
- Infections of the ear, nose and throat
- Infections of the bones
- Skin and soft tissue infections
- Lyme disease
This is how cefuroxime is used
Cefuroxime tablets are taken immediately after a main meal. They should not be chewed or split as this would make the drug less effective and less well-tolerated.
A ready-to-use suspension (liquid with undissolved components = suspension) must be prepared from a cefuroxime dry juice before the first use. This is usually done at the pharmacy. If the dry juice is not needed immediately (e.g. on vacation), you can also prepare the ready-to-use suspension yourself. Cold, previously boiled water is added below the mark on the bottle.The bottle is then capped and gently shaken. As soon as the foam has completely settled, it is filled again up to the mark.
The ready-to-use suspension must be shaken well before each use. It is dosed by volume and (like the tablets) taken immediately after a main meal. Depending on the preparation, it may be necessary to store it in the refrigerator.
In order to keep the concentration of active substances in the body high enough, regular intake is recommended. If the doctor has prescribed it about twice a day, the antibiotic should be taken every 12 hours if possible.
The duration of use depends on the type and severity of the disease and is therefore determined by the doctor. Patients should strictly adhere to the prescribed duration of intake. If the treatment is stopped prematurely, some bacteria may still have survived in the body, which then lead to a new outbreak of the infection.
If used improperly, the pathogens can also develop resistance to the drug and then no longer respond to treatment with this antibiotic.
What are the side effects of cefuroxime?
When cefuroxime is given by mouth, up to one percent of patients experience gastrointestinal disorders such as nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, abdominal pain and diarrhea.
Allergic reactions are also common and predominantly take place on the skin - one to ten percent of patients experience rashes, itching and hives. Fever and breathing difficulties up to circulatory failure are also possible. Such allergic reactions can occur immediately or within days to weeks after treatment and are independent of the amount of active ingredient ingested.
At the first signs of an allergic reaction, therapy should be interrupted and a doctor should be consulted immediately.
Other side effects (in one to ten percent of patients) are headaches, dizziness and fungal infections.
What should be considered when taking cefuroxime?
Contraindications
Cefuroxime must not be used if there is hypersensitivity to a cephalosporin antibiotic or a beta-lactam antibiotic (penicillins, carbapenems, monobactams).
Interactions
Cefuroxime and aminoglycoside antibiotics (such as amikacin, gentamicin, netilmicin, tobramycin) should not be taken at the same time, as this increases the likelihood of kidney damage.
Simultaneous use of probenecid (for increased uric acid or gout) inhibits the excretion of the antibiotic. The doctor will then adjust the dose of cefuroxime so that there is no increased concentration of the active ingredient in the blood.
Anti-acidic medicines (antacids) can make cefuroxime less effective. They should therefore be taken two hours apart from the antibiotic.
Cefuroxime can make contraceptive pills less effective. During and for a few days after treatment with cefuroxime, women and their partner should therefore also use mechanical contraception (e.g. with condoms).
In patients with previously damaged kidneys, cefuroxime is excreted more slowly. The dosage must therefore be adjusted accordingly by the doctor so that there is no accumulation of the active ingredient in the body.
Cefuroxime can affect the results of laboratory tests. Blood tests may show increases in liver enzymes and a type of white blood cell (eosinophils).
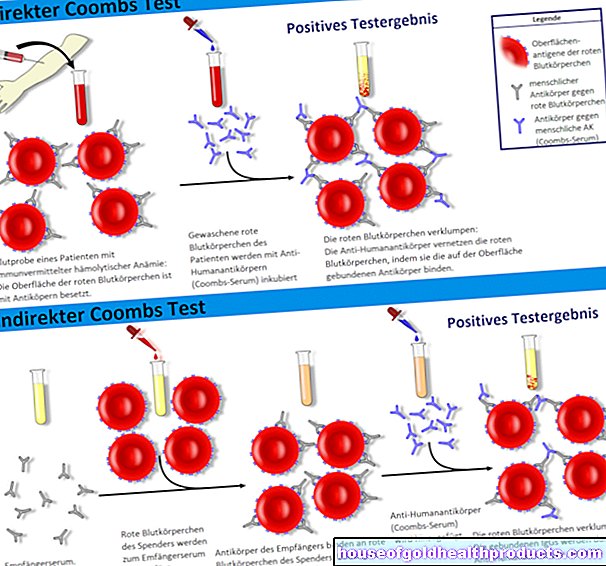
In addition, the antibiotic can lead to a false positive Coombs test (for the detection of antibodies against red blood cells) and an incorrect determination of glucose in the urine. Patients should therefore inform their doctor about taking cefuroxime prior to laboratory tests.
Age restriction
Oral cefuroxime preparations are approved from three months of age. Intravenous preparations can be administered from birth.
pregnancy and breast feeding period
Cefuroxime is generally suitable for use during pregnancy. So far there has been no evidence of an increased risk of malformations. Cefuroxime is one of the antibiotics of choice during pregnancy.
Cefuroxime is also one of the antibiotics of choice when breastfeeding. In individual cases, an impairment of the intestinal flora of the breastfed child is possible, as cefuroxime passes into breast milk. In addition, it can theoretically lead to a sensitization of the infant, so that a later contact of the child with cefuroxime can trigger an allergic reaction.
How to get medicines with cefuroxime
Preparations with cefuroxime require a prescription in Germany, Austria and Switzerland and are only available with a prescription in pharmacies. Cefuroxime dry juice for the preparation of a suspension is not on the market in Austria.
How long has cefuroxime been known?
Cefuroxime belongs to the group of cephalosporins. The oldest representative of this group is the cephalosporin, which Guy G. F. Newton and Edward Penley Abraham found in the fungus in 1955 Cephalosporium acremonium was obtained in pure form.
In the years that followed, many more potent derivatives of cephalosporin were made, which came onto the market from the mid-1960s.
What else you should know about cefuroxime
The gastrointestinal complaints (such as diarrhea), which often occur as a side effect of the cefuroxime treatment, can be explained by the fact that the antibiotic also damages the beneficial germs in the intestine (intestinal flora). Preparations with special medicinal yeast (such as Saccharomyces boulardii) recommended. You can start taking them during treatment with cefuroxime.
Tags: tcm skin therapies