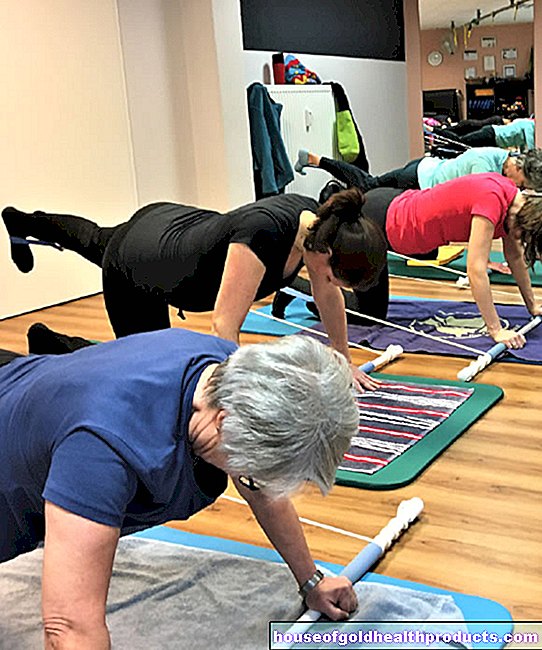
Strength training also breaks down body fat
Christiane Fux studied journalism and psychology in Hamburg. The experienced medical editor has been writing magazine articles, news and factual texts on all conceivable health topics since 2001. In addition to her work for, Christiane Fux is also active in prose. Her first crime novel was published in 2012, and she also writes, designs and publishes her own crime plays.
More posts by Christiane Fux All content is checked by medical journalists.Good news for those who don't like running: Strength training is just as effective in dealing with excess fat as with endurance training.
"A lot of people think that the only way to lose weight is by running," says Dr. Mandy Hagstrom, exercise physiologist at UNSW Medicine & Health. Together with colleagues, she evaluated 58 studies with a total of almost 3000 participants on the subject in an overview study. "However, our results show that strength training alone also has a beneficial effect on body fat loss, without having to consciously go on a diet or go for a run."
Fat loss is the same as with endurance training
Through strength training alone, the test subjects were able to reduce about 1.4 percent of their body fat, which corresponds roughly to what can also be got rid of through endurance training. To achieve this, the participants had trained for an average of 45 to 60 minutes 2.7 times a week over a period of five months.
Fat loss cannot be measured by weighing alone
The myth that weight training doesn't burn fat is related to the fact that most people only look at weight to measure success. Unlike endurance training, strength training not only reduces fat, but also builds up muscle mass. And this is heavier than adipose tissue. Therefore, the body weight often does not change as a result of training.
The studies that Hagstrom and colleagues evaluated therefore precisely measured the body fat mass and distribution of the trainees using body scans, for example.
Another positive effect of strength training is that muscle mass burns more energy than fat tissue, for example, even at rest. The basal metabolic rate of calories increases when the body is more muscular.
Exercise so it's fun
Nevertheless, the researchers ideally recommend a mixture of strength and endurance training. "Through endurance training we improve our cardiovascular fitness and benefit from numerous other health and functional advantages," says Hagstrom.
It is crucial, however, to do sport in any way on a regular basis. "Do the training that you feel like doing and that you are most likely to persevere," recommends the scientist - regardless of whether it is in the form of strength training or running.
Tags: drugs Diagnosis womenshealth