Burning sensation when urinating
Luise Heine has been an editor at since 2012. The qualified biologist studied in Regensburg and Brisbane (Australia) and gained experience as a journalist in television, in the Ratgeber-Verlag and in a print magazine. In addition to her work at , she also writes for children, for example for the Stuttgarter Kinderzeitung, and has her own breakfast blog, “Kuchen zum Frühstück”.
More posts by Luise Heine All content is checked by medical journalists.A burning sensation when urinating (medical: alguria) makes every trip to the toilet a torture. Most of the time, the cause lies in the urinary tract. For example, the urethra, renal pelvis, or prostate may be inflamed. But bladder stones also cause pain when urinating. In addition, sexually transmitted diseases (sexually transmitted diseases) are also possible triggers for the complaints. Read more about urination urination and its treatment here.

Brief description
- Causes: often inflammation of the lower urinary tract (e.g. urethritis, cystitis), sometimes also bladder stones, venereal diseases (syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydial infection, ulcus molle etc.), diseases of the prostate or bladder cancer
- What helps with a burning sensation when urinating? depending on the cause z. B. drink enough, always empty your bladder completely, keep your abdomen warm, use condoms, clean from front to back, get medical treatment for the underlying disease (e.g. with medication)
- When to the doctor If it occurs for the first time or suddenly and / or if you have other symptoms such as blood in the urine, fever, chills, pain in the lower abdomen or blisters in the genital area.
Burning sensation when urinating: causes and possible diseases
Pain when urinating is a common reason why people in this country see a doctor. This is not surprising, because the symptoms can be very uncomfortable. There can be various causes behind the painful burning sensation when urinating:
Bacterial inflammation
In most cases, bacterial inflammation in the lower urinary tract is the cause of the burning sensation when urinating, such as inflammation of the urethra (urethritis) or cystitis (cystitis). Women are more prone to the latter than men:
The kidneys, bladder and urethra are almost the same in men and women. In women, however, at around three centimeters in length, the urethra is much shorter than in men - this makes it easier for pathogens to get through the urethra up into the bladder and start an inflammation here. Most of these germs are intestinal bacteria of the type Escherichia coli (E. coli): When you wipe yourself from the back to the front after using the toilet (instead of the other way around, as it would be correct), you can easily bring these and other intestinal bacteria close to the urinary opening.
In addition to pain in the lower abdomen, the agonizing need to urinate is typical of a cystitis, although only a small amount of urine is excreted (dysuria).
If the cystitis remains untreated, the pathogens can further ascend the urinary tract and lead to inflammation of the renal pelvis (pyelonephritis). Affected people feel very sick and have a fever. In addition to the burning sensation when urinating, severe pain in the kidney area also occurs in the case of inflammation of the kidney.
Especially diabetics and pregnant women are more often affected by inflamed urinary tract.
Sick prostate
In men, prostate disease can cause a burning sensation when urinating. As people get older, urethritis or bladder infections become more common because the prostate is enlarged and the urine flow is restricted. Risk factors include unprotected anal intercourse and the presence of a urinary catheter.
In addition, an inflammation of the prostate (prostatitis) can cause acute or chronic pain when urinating. Pain during bowel movements, in the perineal area and pelvis and - in the case of acute inflammation - fever and chills can occur.
Prostate inflammation is usually caused by bacteria that have entered the prostate gland through the urethra. However, germs cannot be detected in every prostatitis.
Painful bladder cancer
A burning sensation when urinating can also be an indication of bladder cancer (bladder cancer). As with most malignant tumors, bladder cancer does not have any symptoms for a long time that indicate the disease. The first sign is usually blood in the urine. In advanced stages, however, urination can be difficult and / or a burning sensation can occur.
Sexually transmitted diseases
Sometimes painful urination is related to sexual diseases, which are infectious diseases that are transmitted through unprotected sex:
- Syphilis (hard chancre): The caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum STD has been on the rise again for several years, especially in men. It runs in several stages. Initially, ulcers often form on the vulva or penis, which can be painful when urinating.
- Tripper (gonorrhea): This bacterial sexually transmitted disease typically causes inflammation of the urinary and genital organs (including burning sensation when urinating and purulent discharge from the urethra). Oral and anal intercourse can also cause inflammation in the throat and rectum. However, many infected people show no symptoms at all.
- Genital herpes: Genital herpes is triggered (like cold sores) by herpes simplex viruses. Once infected with them, they remain in the body permanently - most of the time "asleep". But you can "wake up" from it at any time and cause symptoms - with genital herpes itchy and sometimes very painful blisters in the genital area.
- Chlamydial infections: This widespread bacterial sexually transmitted disease can cause inflammation of the urinary and genital organs, including a burning sensation when urinating and a purulent discharge. However, many chlamydial infections remain asymptomatic.
- Ulcus molle (soft chancre): The cause is the bacterium Haemophilus ducreyi. Typical symptoms of an infection are soft, painful ulcers in the genital area, for example on the glans of the penis or the labia). Depending on the location, they can cause a burning sensation when urinating.
- Mycoplasma infection: Mycoplasma are very small, cell wallless bacteria that parasitically attack other cells (including bacterial cells). Among other things, they can cause inflammation in the urinary and genital organs (e.g. urethritis, vaginal inflammation). Then urination can be painful.
- Bacterial vaginal infection: Infection of the vagina with bacteria (bacterial vaginosis) is very common - in many cases, however, affected women do not have any symptoms. Sometimes the infection can also make itself felt as a burning sensation when urinating and, above all, with a foul-smelling discharge and itching.
- Trichomonas infection: Trichomonads are flagellates. They always need a moist environment, such as that found in the vagina, for example. Therefore, women in particular are affected by a trichomonad infection. A burning sensation in the vagina and a pungent smelling discharge, which can be yellowish-green and foamy, are typical symptoms.
Bladder stones
Often there are also bladder stones behind burning when urinating. These usually form in the bladder itself, but sometimes also in the kidney pelvis, from where they are then washed into the bladder with the urine. Most bladder stones are made of potassium salts, and some also consist of uric acid or other salts. The stones themselves do not cause any pain at first. However, if they clog the duct of the bladder, it can cause significant pain when urinating. Other signs of such bladder stones include blood in the urine and colicky pelvic pain.
Other causes
In women, a dry vagina or an inflamed vagina (called colpitis or vaginitis) can also cause a burning sensation when urinating.Menopausal women particularly suffer from vaginal dryness; but sometimes younger women are also affected. A vaginal inflammation can be caused by pathogens, but also have other causes (e.g. irritants in foam baths).
Occasionally, a burning sensation occurs when urinating because a foreign object (such as a urinary catheter) has been inserted into the urethra or the urethra has been injured during sexual intercourse.
In rare cases, the burning sensation when urinating is a side effect of a gastrointestinal infection.
What helps with a burning sensation when urinating?
You can often do something yourself to relieve the uncomfortable feeling when urinating - especially if it is caused by a harmless urinary tract infection. In other cases, medical treatment is necessary.
Burning sensation when urinating: you can do it yourself
If it is burning while urinating, you should still make sure to drink enough - even if it is painful to urinate afterwards. Especially with urinary tract infections, drinks with plant-based active ingredients that have a diuretic effect and thus support the elimination of germs are helpful. These include lingonberry, cranberry, nettle, bearberry, juniper, nasturtium and horseradish.
To prevent a burning sensation when urinating (for example as a result of a bladder infection or sexually transmitted disease), you should heed the following advice:
- Drink at least two liters of fluids a day.
- Always empty your bladder completely (residual urine in the bladder is a good breeding ground for germs).
- Keep your abdomen warm.
- Always run the toilet paper from front to back when cleaning.
- Avoid excessive intimate hygiene.
- Protect yourself from sexually transmitted diseases with condoms during sex.
- After intercourse, go to the toilet to urinate. This is how you flush out pathogens - the risk of an infection-related stinging sensation when urinating is reduced.
Burning sensation when urinating: what does the doctor do?
In order to be able to effectively treat a burning sensation when urinating, the doctor must first clarify the cause.
diagnosis
A burning sensation when urinating leads most patients to the family doctor first. But a gynecologist or urologist can also help.
The first step is to collect the medical history in a detailed interview (anamnesis). The doctor asks, for example, how long have you had pain when urinating, how severe it is and whether you have any other complaints (e.g. discharge, pain in the abdomen). The doctor also asks about previous and underlying illnesses (e.g. diabetes, previous bladder cancer).
A urine test can be used to determine whether a bacterial urinary tract infection is behind the burning sensation when urinating. Cloudiness and a strong odor in the urine also indicate an infestation with bacteria. The nitrite content in the urine can be measured using test strips; it can indicate certain bacteria.
If everything points to an uncomplicated urinary tract infection, a physical exam is not a must. It follows, however, when the symptoms are less clear and the person concerned complains about discharge in the genital area in addition to the burning sensation when urinating. In men, these symptoms can indicate a sexually transmitted disease, in women there is also the possibility of a vaginal yeast infection. A microscopic examination of a smear can provide information here.
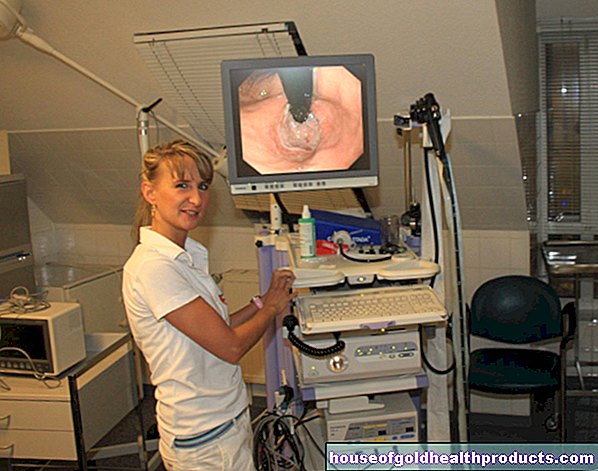
Blood tests will show whether certain levels of inflammation in the blood are increased. That would be the case with an inflammation of the prostate or kidney pelvis, for example. An ultrasound scan can be used to diagnose kidney stones or bladder cancer, for example. With the help of so-called excretory urography - a special form of X-ray examination - tumors or kidney malformations can be detected. Sometimes it is also necessary to look inside the bladder via an endoscopic examination of the bladder (cystoscopy).
therapy
Treatment for burning sensation when urinating depends on the cause. If a bacterial infection is causing your symptoms, the doctor will prescribe antibiotics for you. In the case of a fungal infection, on the other hand, you will be given fungicides.
If necessary, the doctor will prescribe pain medication to make it easier to go to the toilet again. This can be particularly necessary with painful bladder stones. Such stones can often be removed with medication or removed as part of a cystoscopy. Sometimes they are also shattered by shock waves. It rarely has to be surgically removed.
Individually adapted treatment is also necessary for bladder cancer (surgery, chemotherapy, etc.).
Burning sensation when urinating: when do you need to see a doctor?
If the painful urination occurs suddenly and for the first time, you should see a doctor. Anyone who has already suffered from uncomplicated urinary tract infections often waits and tries to get the inflammation under control with home remedies - often with success. Even so, even "experienced" patients should consult a doctor if the burning sensation worsens when urinating. This is especially true if the following symptoms also occur:
- Blood in the urine
- Urinary retention
- abnormal discharge from the penis or vagina
- sharp pelvic pain
- Pain in the flanks
- Ulcers or blisters in the genital area
- fever
- chills
- nausea
- Vomit