Red eyes
Lisa Vogel studied departmental journalism with a focus on medicine and biosciences at Ansbach University and deepened her journalistic knowledge in the master's degree in multimedia information and communication. This was followed by a traineeship in the editorial team. Since September 2020 she has been writing as a freelance journalist for
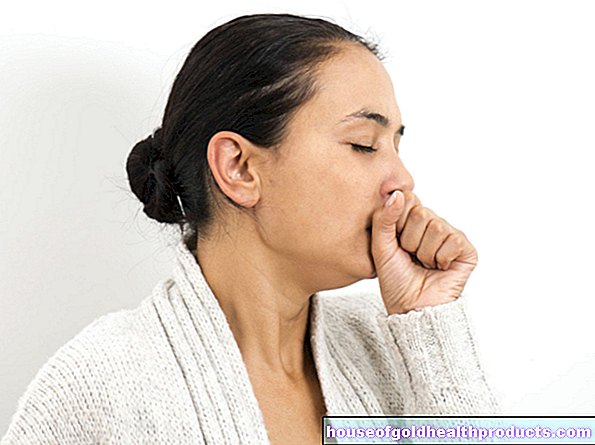
More posts by Lisa Vogel All content is checked by medical journalists.Red eyes are usually a harmless symptom. Lifestyle is often the reason when the whites of the eyes are completely or partially red - for example, lack of sleep. However, various diseases can also cause reddening of the eyes. Read here why the eyes can be red and what you can do about it!

Brief overview
- Causes: e.g. dry eyes, conjunctivitis (e.g. as a result of an allergy), corneal inflammation, iris inflammation, glaucoma, broken veins in the eye, lack of sleep, dry room air, dust or cigarette smoke, trauma, UV rays, drafts, toxins, cosmetics, contact lenses; reddened eyelids with hailstones and stye, among other things
- When to the doctor If accompanying symptoms occur such as severe eye pain, fever, nausea and vomiting, loss of visual acuity, visual disturbances, rash and open eye injuries.
- What helps against red eyes? Depending on the cause, e.g. moisturizing eye drops, antiallergic drugs (antihistamines), antibiotics, antivirals, cortisone, treatment of any underlying diseases
- You can do that yourself: e.g. sleep enough, avoid tobacco smoke, drafts and UV radiation, avoid allergy triggers if possible, avoid contact lenses, relaxation exercises for the eyes, cold compresses
Red eyes: causes
Almost everyone has red eyes at least once in their life.Bloodshot eyes can look quite dangerous. The reddening of the eyes is caused by the fact that the blood vessels in the surface of the eye are widened and are supplied with more blood.
In most cases, there is a harmless cause behind it. For example, after a night of partying in a smoky room, more red veins are often visible in the eye. With enough sleep and avoidance of smoke-laden air, this reddening of the eyes generally disappears on its own. Sometimes red eyes are caused by (serious) illnesses.
Here is an overview of common factors that can cause red and irritated eyes:
- lack of sleep
- Cigarette smoke
- Dry room air
- dust
- Air conditioning or drafts
- UV rays
- Eye irritation from contact lenses or cosmetic products
Conditions that can cause red eyes include:
- Conjunctivitis, such as allergic conjunctivitis
- Inflammation of the cornea (keratitis)
- Inflammation of the middle skin of the eye in the anterior segment (anterior uveitis such as iris inflammation)
- Inflammation of the connective tissue between the dermis and the conjunctiva (episcleritis)
- Inflammation of the dermis (scleritis)
- Inflammation of the eyelids (blepharitis)
- Glaucoma or acute glaucoma attack (glaucoma)
- Sjogren's syndrome
- Ocular herpes
- Tumors
- Ophthalmorosacea (type of rosacea that affects the eyes)
- Atopic diseases (e.g. neurodermatitis)
Blunt trauma such as a blow to the eye, heavy rubbing or an operation on the eye can also cause reddened eyes.
A red spot in the eye is usually an area of bleeding under the conjunctiva, called a hyposphagma.
Red eyes & allergy
Red eyes are a common symptom of an allergy. The conjunctiva contains many immune cells that can react over-sensitive to actually harmless substances such as pollen, mold spores or the excrement of house dust mites. They then release chemical substances that trigger inflammatory processes in the eye - allergic conjunctivitis develops (allergic conjunctivitis). A distinction is made between three forms:
- Seasonal allergic conjunctivitis (hay fever): It is caused by the pollen of various plants (trees, grass, etc.). The symptoms such as red, burning, itchy eyes and a runny or blocked nose occur during the flowering period of those plants to which the person concerned is allergic.
- Atopic conjunctivitis: It is an allergic reaction of the eyes that is possible all year round: Red, burning and itchy eyes are caused by dust mites, animal dander (e.g. from cats) or other non-seasonal allergens.
- Vernal keratoconjunctivitis: It is also probably the result of an allergy to the eye. It is a combined inflammation of the conjunctiva and cornea that occurs preferentially in spring. It mainly affects male children and adolescents with eczema, asthma or seasonal allergies. Inflamed eyes with redness are typical symptoms.
Conjunctivitis - whether caused by an allergy or another cause - is one of the most common reasons for reddened eyes.
Contact dermatitis (contact allergy) can also cause reddened eyes or reddened skin around the eyes. For example, some people are allergic to eye drops, face creams, make-up or other cosmetic products and develop redness and / or a rash on the eye as a result. Itching, swelling of the eyelids and flaky skin changes are also possible.
Reddened eyelids
Red eyelids with sticky eyelashes are a typical symptom of eyelid inflammation (blepharitis). The conjunctiva is then often slightly reddened. The cause of the inflammation is blocked sebum glands on the edge of the eyelid. People who suffer from excessive sebum production and thus often also from acne, neurodermatitis or rosacea are susceptible to blepharitis.
Swollen, red eyelids are also found in hailstones and stye: The hailstones are also based on a blocked sebum gland. The resulting inflammation is limited to a narrow part of the eyelid - a painless, reddened swelling forms on the edge of the eyelid. In contrast, the stye shows up as a painful, reddened swelling on the edge of the eyelid, caused by a bacterial inflammation of a sebum gland.
Hyposhagma
Do you have a single red eye? The cause is often a ruptured blood vessel under the conjunctiva. Doctors speak of hyposphagma here. The bleeding under the conjunctiva is visible as a sharply defined red spot in the eye. It can look terrifying, but it is usually nothing to worry about. Broken veins in the eye heal on their own.
A hyposphagma can be caused, for example, by rubbing the eye vigorously. But even without this kind of mechanical irritation, an eye can be red underlayed - in people with high blood pressure, a blood vessel in the eye can burst on its own, especially if the patient is taking medication to thin the blood (oral anticoagulants).
If you see broken blood vessels frequently, you should have your blood pressure checked by a doctor.
Red eyes: accompanying symptoms
Red eyes often do not appear on their own. Common accompanying symptoms include:
- Watery eyes
- Burning eyes
- Dry eyes
- Itchy eyes
- Eye pain
- Swollen eyes
- Sensation of pressure on the eyeball
- Foreign body sensation in the eye
- Secretion discharge from the eye (purulent, watery, slimy)
- Clogged eyes (especially in the morning)
The combination of different symptoms often gives clues to the cause. For example, red, burning eyes can be the result of a lot of computer work or eye irritation from contact lenses or smoke, among other things. If one eye is red and itchy, conjunctivitis is often present.
Reddened eyes: when to see a doctor?
If your eye redness is accompanied by any of the following symptoms, you should see a doctor:
- sudden severe eye pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Rash on the face (especially around the eyes or on the tip of the nose)
- decreased visual acuity
- Visual disturbances
- open wound on the cornea
- fever
If the red eyes are caused by a foreign body in the eye (metal splinters, chemicals, etc.), you should see a doctor immediately.
Red eyes: examinations & diagnosis
First, the doctor will discuss your medical history (anamnesis) in detail with you. This is followed by various examinations to clarify the red eyes (and possibly other symptoms).
anamnese
When taking your medical history, the doctor can ask you the following questions, for example:
- How long has the eye redness existed?
- Have you had reddened eyes before?
- Do you have any other symptoms besides eye redness (such as eye pain, itchy eyes, etc., fever, headache, etc.)?
- Is there more secretion from the eyes?
- Has your eyesight changed?
- Is there an injury to the eye?
- Do you wear contact lenses?
- Did you get foreign objects or other substances in your eyes (dust, splinters, etc.)?
- Do you take any medicine?
- Are you allergic?
Investigations
During the subsequent physical examination, the doctor takes a closer look at the area around the eyes. He pays attention to skin changes, swellings and other abnormalities, among other things. Depending on which complaints you have besides the red eyes, he can, for example, also examine the skin on the rest of your body or measure your body temperature.
Various examinations also help to find out the reason for the eye redness. The doctor will check the size of the pupil, the reaction of the eyes to incident light, and the movements of the eyes. The following examinations can also be informative:
- Eye test
- Slit lamp examination (to assess different eye sections)
- Examination of the tear fluid
- Allergy test
- Smear from the eye (if an infectious cause is suspected)
Red eyes: treatment
Treatment of red eyes is always based on its cause. The redness of the eyes themselves usually does not require treatment. It usually goes away on its own when the cause subsides or is eliminated.
Reddened, dry eyes can be dealt with
If the cause of red eyes is bacterial conjunctivitis, eye drops or ointments with added antibiotics often help. In certain cases it may also be necessary to take antibiotics, for example conjunctivitis caused by a chlamydial infection. Viral conjunctivitis can only be treated symptomatically, for example with artificial tears and eye drops containing cortisone.
However, if herpes viruses are the reason that the eyes are reddened and inflamed (eye herpes), causal treatment with antiviral agents, so-called antivirals, is possible. For this purpose, the doctor can, for example, prescribe eye drops with the active ingredient acyclovir.
If an allergy is responsible for inflamed conjunctiva (allergic conjunctivitis), the allergy trigger should be avoided if possible. In addition, antiallergic agents (antihistamines) in the form of eye drops or tablets can relieve reddened eyes and other possible allergy symptoms. In the case of severe allergies, eye drops containing cortisone can be useful.
Red eyes: you can do that yourself
You too can do something about red eyes. Getting enough sleep dispels red eyes caused by short nights. Avoid tobacco smoke, drafts or strong sunlight if this is the cause of the reddened eyes.
There are various moisturizing eye drops available over-the-counter for reddened, dry eyes. But it is better to talk to a doctor about their use first. Perhaps there is a disease that needs treatment behind dry eyes.
If contact lenses cause reddened, irritated eyes, you should not wear them for a few days and put on glasses instead. The strained eyes can then calm down. You may also need other contact lenses. Talk to your eye doctor or optician about it.
If the reddening of the eyes is caused by mascara, eye cream or other cosmetic products, keep your hands off it! Better to switch to a better tolerated product.
Do you have red, dry eyes from staring at a screen (computer, TV, etc.) for too long? Then relaxation exercises for the eyes are a good idea. Some examples:
- Consciously take a close look at things at different distances (focus your eyes on each one!).
- Occasionally cover your eyes with your hands and let them rest for a few minutes.
- Place your thumbs on your temples and use your index fingers to massage the top of the eye socket (from the bridge of the nose outwards).
- You should often close your eyes for a few seconds while working with the screen. You can also try to type a few sentences "blindly".
If the contact with chemicals (e.g. the splash of cleaning agent) has caused a red eye or red eyes, it is usually sensible to rinse the eyes with clear water (except if caustic lime has got into the eye - rinsing can then worsen the chemical burn! ). Then seek out a species immediately. Bring him the chemical, if necessary, so he can adjust the treatment accordingly.
If a solid foreign body such as dust or metal splinters causes the reddening of the eyes, first aid measures and a subsequent visit to the doctor are indicated.
Home remedies for red eyes
Irritated, red eyes can often be soothed with cool compresses. To do this, dip clean cotton cloths in cold water, wring them out and then place them on the red eye (s). Instead of water, you can also use cooled tea made from chamomile, calendula or sage. Leave the cool compress on your eyes as long as you are comfortable.
Instead of damp cotton cloths, you can also place a grain pillow (e.g. cherry stone pillow) that you have chilled in the freezer compartment on your eyes. Or you can use cool packs. Do not put these directly on the reddened eyes, but first wrap them in a cotton cloth.
Tags: diet hair alternative medicine