Ascites puncture
All content is checked by medical journalists.During an ascites puncture, the doctor draws fluid that has accumulated in the abdominal cavity. Depending on the situation, the puncture should provide diagnostic information or serve as a therapy. Ascites is also popularly known as "ascites". Here you can read everything you need to know about ascites puncture, how it works and what risks you as a patient should be aware of.

What is an ascites puncture?
With an ascites puncture, the doctor uses a hollow needle or cannula to remove fluid that has collected in the abdominal cavity. Since a newly occurring or increasing ascites ("ascites") is usually an expression of a serious illness, the causes must be found as quickly as possible. In addition, ascites can cause such discomfort that relief by draining off larger amounts of fluid is necessary.
When to do an ascites puncture
Ascites can have many causes, for example inflammation of the peritoneum (peritonitis) or cancer. Other conditions that can lead to ascites include:
- Cirrhosis of the liver
- acute liver damage
- Closure of the hepatic vessels
- Functional weakness of the right half of the heart (right heart failure) or the whole heart muscle (global heart failure)
- Inflammation of the pericardium (pericarditis)
- Inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis)
- Albumin deficiency (hypoalbuminemia), for example in the case of malnutrition
- Disorders of lymphatic drainage
Not every ascites has to be punctured, however. Basically, a new accumulation of fluid within the peritoneum should always be punctured in order to find out the cause by analyzing the removed fluid (diagnostic puncture).
A puncture should also be performed in patients with known ascites, whose condition is deteriorating or whose fluid retention is increasing.
What do you do with an ascites puncture?
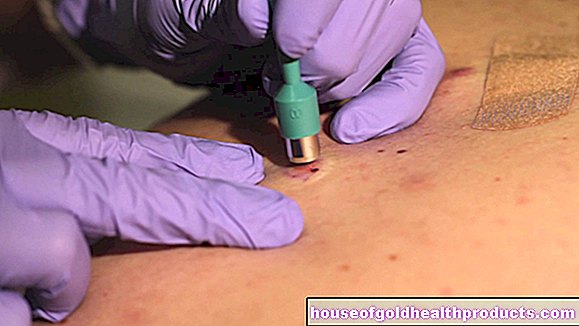
The ascites puncture is usually performed with the patient lying down. So that the doctor finds the optimal and safest puncture site and does not injure any organs or vessels, he searches for it with an ultrasound device and marks it on the patient's body. To reduce the risk of infection, he first disinfects the puncture site. He then injects a topical anesthetic into the tissue so that the patient feels the puncture less painful. The further procedure depends on whether the ascites puncture is performed for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes.
Ascites puncture: implementation for diagnosis
The doctor only needs small amounts to assess the accumulated fluid. With a hollow needle, which he carefully pierces through the abdominal wall, he can draw a sample of the fluid that has accumulated in the abdominal cavity into a syringe. This sample is then examined in the laboratory for color, cell count, protein content, bacteria and many other parameters.
Ascites puncture: performed for therapeutic purposes
The therapeutic ascites puncture is also called paracentesis in medicine. The doctor first uses an ultrasound image to determine the most suitable location for the puncture and then inserts the hollow needle through the abdominal wall. This is connected to a thin tube via a small plastic tube. The liquid can now flow off easily via this. If the ascites is sufficiently relieved, the doctor removes the hollow needle and covers the puncture site with a sterile layer.
What are the risks of an ascites puncture?
A purely diagnostic ascites puncture is a very safe procedure and carries hardly any risks for the patient. Ascites drainage for therapeutic purposes, on the other hand, has a higher complication rate. Possible dangers that the patient should be aware of are:
- Continuous leakage of liquid through the branch canal
- Infections of the peritoneum (peritonitis)
- Abdominal wall abscess
- Bleeding
- Injury to surrounding structures and organs
What should I watch out for after an ascites puncture?
If you have been given a sedative for the ascites puncture, your ability to drive is significantly restricted. Unless you are staying in the hospital anyway, you should arrange for someone to come and meet you in advance.
If you have received a therapeutic ascites puncture in which several liters of fluid were removed, you will then receive an infusion as a protein / fluid replacement.
Tags: vaccinations symptoms anatomy