Liver biopsy
All content is checked by medical journalists.In a liver biopsy, the doctor takes a tissue sample from the liver through the abdominal skin with a hollow needle. The method is used in particular for the diagnosis and follow-up of chronic liver diseases such as hepatitis or liver damage caused by alcohol and cancer. Read here how the liver biopsy works and what you should pay attention to afterwards.
How does the liver biopsy work?
Before the liver biopsy, the doctor will give the patient a light sedative if desired. The doctor carefully disinfects the skin of the abdomen and injects a local anesthetic, as the liver biopsy can be painful. The puncture site is determined by means of ultrasound. The patient now exhales and then holds the breath, which pushes the liver downwards from the diaphragm.
The doctor pushes a thin, approximately one to two millimeter thick hollow needle through between two costal arches into the liver and removes a small cylinder of tissue from the liver. The hollow needle is immediately withdrawn from the liver. The puncture therefore takes a second at most.
In some cases, a tissue sample from the liver is also taken laparoscopically - via a laparoscopy.
What are the risks of a liver biopsy?
Liver biopsy is a relatively safe procedure. Bleeding during or after the procedure is the most common complication of the biopsy, as liver tissue is very well supplied with blood. After the procedure, large bruises may form in the liver, which may have to be surgically removed. Patients who have a severe bleeding disorder may not be biopsied!
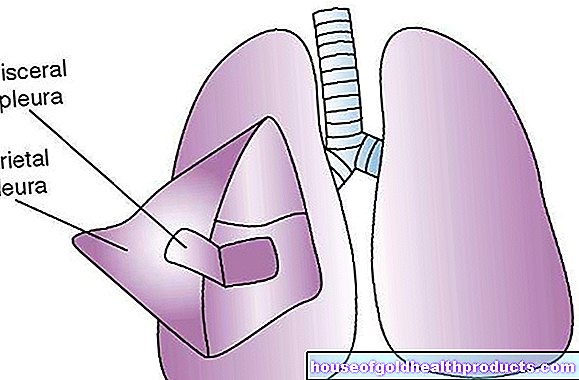
Rarely, inflammation of the peritoneum (peritonitis), infection or injury to neighboring organs such as the lungs or gallbladder occurs. If the lungs are punctured, air or blood can build up in the chest cavity in what is known as a pneumothorax or hemothorax and needs to be treated quickly. This causes the lungs to collapse and impair the function of the lungs.
What do I have to consider after the liver biopsy?
Most complications occur in the first 24 hours after the biopsy. Therefore, you should stay in the clinic for monitoring until the next morning. The pulse and blood pressure are measured regularly in order to be able to determine and treat secondary bleeding from the puncture canal in good time. A bed rest for six to eight hours is recommended after a liver biopsy.
Tags: womenshealth parasites tcm