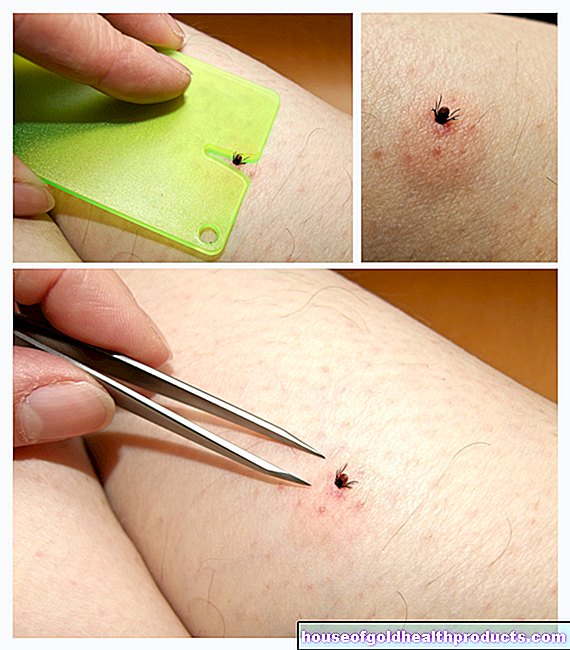
Subluxation
Marian Grosser studied human medicine in Munich. In addition, the doctor, who was interested in many things, dared to make some exciting detours: studying philosophy and art history, working on the radio and, finally, also for a Netdoctor.
More about the experts All content is checked by medical journalists.Subluxation is a dislocation in which the bones of a joint have shifted against each other. However, the joint surfaces are still partly against one another. However, subluxations can be very painful and severely impair the function of the joint. Here you can read all about the different forms of subluxation and their possible symptoms.
ICD codes for this disease: ICD codes are internationally recognized codes for medical diagnoses. They can be found, for example, in doctor's letters or on certificates of incapacity for work. M24
What happens with the subluxation?
A joint on the body is the area in which bones are more or less flexibly connected to one another. The parts of the bones that lie against each other are called the articular surfaces. They are covered with a smooth layer of cartilage. Ligaments, a joint capsule, and muscles almost always hold the bones of the joint in place.
Due to external force, however, it can happen that their stabilizing function is insufficient and the joint surfaces shift against each other. If this does not happen completely, but they are still partially in contact with each other, one speaks of a subluxation.
Which joints are affected?
In principle, a subluxation can occur in any joint. Just like dislocation, however, it mainly affects those joints that are particularly prone to injury due to their anatomy or position on the body (shoulder, elbow, hip). In certain joints, the bone parts almost never slip completely, so that subluxation is much more common here. One example is the dislocation of vertebral bodies.
Chassaignac palsy (Pronatio dolorosa)
A special form of subluxation that only occurs in children is Chassaignac's palsy. It is a special case among subluxations, as it only occurs in children up to the age of six. Chassaignac's palsy is named after the French surgeon Charles Chassaignac and is one of the most common injuries at this age. Because the affected children can hardly and do not want to move their forearms, one speaks of paralysis - medically not very precisely.
What causes Chassaignac palsy?
The (bony) arm consists of the humerus and the two forearm bones ulna and radius. These three bones create three joints on the elbow: The ulna forms a hinge joint with the humerus and enables the forearm to bend and straighten. The spoke forms a joint with the ulna and a ball joint with the humerus. In this way, the forearm can be turned in and out of the upper arm.
A typical mechanism for the development of Chassaignac paralysis is this: the child is standing on the street with an adult by the hand and suddenly starts running, the adult suddenly pulls the child back by the hand because a car is coming. The resulting forces can lead to the dislocation of the head of the spoke. Because in smaller children, the ligament that holds the head of the spoke in its two joints is not yet very stable. This allows the head of the spoke to slip out of the ball joint with the humerus. Even with the popular “angel flying”, an unfavorable force is exerted on the elbow joint.
The children then hold their arm slightly bent and turned inwards. In this relieving position, you hardly have any pain.
Therapy for Chaissaignac's palsy
This type of subluxation is well treatable. With a targeted movement of the doctor, the spoke head ideally jumps back into the ring-shaped retaining strap and the pain and the restriction of movement are eliminated just as quickly as they occurred. After the re-straightening, the arm usually does not need to be particularly spared.
Complications of Chaissaignac Palsy
Pronatio dolorosa is very painful for the child, but is rarely associated with accompanying injuries. As soon as the spoke head is back in position, the symptoms abruptly subside and the arm can move freely again. However, if the elbow joint is not adjusted quickly, it usually takes a few days after the adjustment before the child can move the arm pain-free again.
As with any subluxation and dislocation, there is an increased risk of re-dislocation after an injury of this type. If the spoke head slips out of the ring ligament shortly after the reduction, an upper arm cast can help. This is applied for about two weeks and holds the arm in an outwardly rotated position. In this way, a new subluxation is prevented.
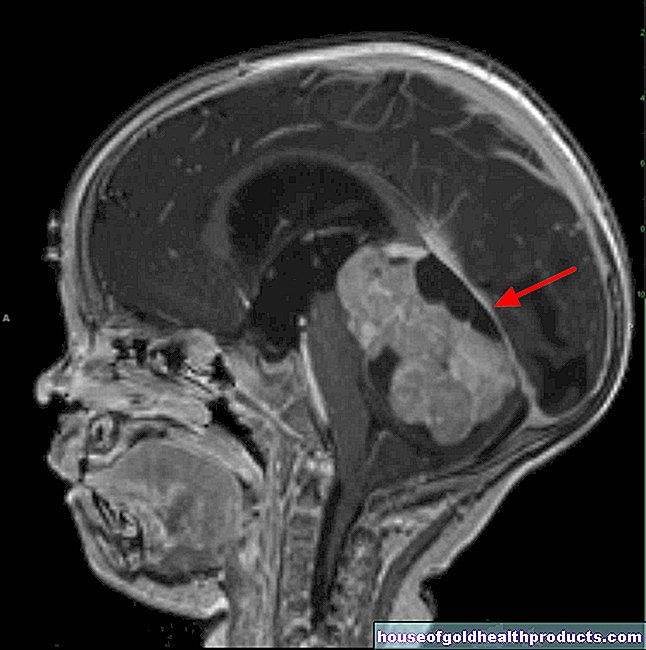
Subluxation on the vertebral bodies
If the first (top) cervical vertebra slips in relation to the second cervical vertebra, it is called an atlanto-axial subluxation. Neurological symptoms up to paraplegia can be the result.
How does an atlanto-axial subluxation arise?
The first cervical vertebra has the structure of a ring on which the head rests. A bony protrusion (dens axis) grows from below through this ring from the second cervical vertebra. In this way, the first and second cervical vertebrae form the atlanto-axial joint, which enables the head to rotate sideways.
The atlanto-axial joint can become dislocated in the case of malformations, such as an incorrectly grown bony protrusion or weak connective tissue. Chronic inflammation of the atlanto-axial joint, as it occurs in the context of polyarthritis, also represents a risk of subluxation. In the event of external violence, for example in a traffic accident, the bony protrusion can even break off and thus cause a subluxation.
Symptoms and treatment of atlanto-axial subluxation
The greatest danger with an atlanto-axial subluxation is that the spinal cord, which also runs through the cervical ring, is damaged. In addition to pain in the neck area, especially when bending the neck, motor or sensory disorders can occur in the limbs. In severe cases, all limbs can be paralyzed ("high paraplegia", tetraplegia).
In the case of a subluxation due to malformations, the symptoms usually appear insidiously in the first months of life, whereas in an acute subluxation they appear very suddenly. An atlanto-axial subluxation must be confirmed by imaging. If the spinal cord is damaged, an operation is usually unavoidable.
Subluxation in Chiropractic
Subluxation plays a relatively large role in chiropractic treatment, and here it exclusively refers to the displacement of two vertebrae with respect to one another. It is assumed that not only accidents and other injuries can displace the vertebrae, but also everyday improper stress and even psychological stress can be the cause of subluxations. The subluxation of the vertebrae irritates the exiting nerves, which not only leads to nerve damage, but can also cause malfunctions in the organs.
Tags: fitness healthy feet menshealth