Esophageal Cancer Symptoms
Ricarda Schwarz studied medicine in Würzburg, where she also completed her doctorate. After a wide range of tasks in practical medical training (PJ) in Flensburg, Hamburg and New Zealand, she is now working in neuroradiology and radiology at the Tübingen University Hospital.
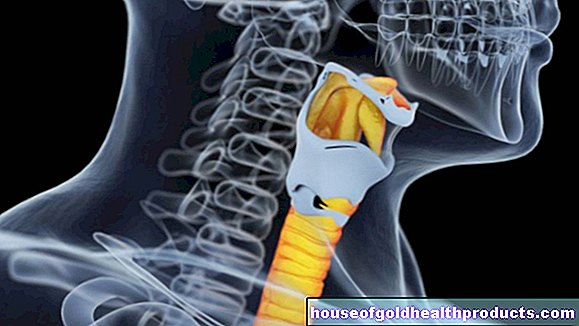
More about the experts All content is checked by medical journalists.Esophageal cancer symptoms usually only appear when the disease has progressed further ("silent cancer"). In the first stages of the disease, the patients do not notice any changes. It is only later that signs of esophageal cancer such as difficulty swallowing and weight loss appear - although not necessarily in all those affected.Depending on how the tumor grows, other symptoms may arise. Here you can read everything you need to know about esophageal cancer symptoms.
ICD codes for this disease: ICD codes are internationally recognized codes for medical diagnoses. They can be found, for example, in doctor's letters or on certificates of incapacity for work. C15

Esophageal cancer symptoms: general
Most people with esophageal cancer do not have symptoms until very late in the course of the disease. Esophageal cancer usually only causes symptoms when the tumor is so large that it significantly narrows the esophagus or affects other organs such as the bones or the lungs. In addition, the esophageal cancer symptoms are very unspecific. This means that they can also occur in many other diseases. They are therefore often not taken seriously by those affected - which is fatal, since a late diagnosis considerably reduces the chances of recovery.
Because esophageal carcinoma is a malignant tumor, it is often associated with general signs of cancer such as weight loss, fever, night sweats, weakness, tiredness, or a drop in performance.
The different signs of esophageal cancer, in order of frequency, are:
Esophageal cancer symptoms: difficulty swallowing
Swallowing difficulties are also referred to by doctors as dysphagia (Greek "dys" - not and "phagein" - to eat). They occur when the tumor narrows the esophagus by at least 50 percent. Difficulty swallowing is the most common and typical esophageal cancer symptom. About 87 percent of those affected suffer from dysphagia in the course of their illness. That is why this sign of the disease is also considered to be the leading symptom of esophageal cancer. Difficulty swallowing occurs especially when eating dry food.
Of course, not everyone with swallowing disorders suffers from esophageal cancer. There are numerous other diseases that cause similar ailments. In people under 45 years of age, difficulty swallowing occurs most often when stomach acid runs back into the esophagus and inflames the mucous membrane there (reflux esophagitis). In this age group, swallowing difficulties develop more often if the muscles of the esophagus do not contract properly. Then the transport of the food into the stomach is more difficult. Another disorder that causes difficulty swallowing is what is known as achalasia. In this disease, the lower esophageal sphincter (esophageal sphincter) is constantly tense. In this rare disease, it is increasingly difficult for the food pulp to reach the stomach and ultimately not at all.
People over the age of 45 who suffer from steadily increasing, painless swallowing difficulties are more likely to develop esophageal cancer. Of course, diseases of the central nervous system such as a stroke, Parkinson's disease or a traumatic brain injury can also cause similar symptoms. In any case, all people of this age with increasing difficulty swallowing are recommended to see a doctor as soon as possible. This can rule out a malignant tumor or, if necessary, initiate treatment quickly.
Esophageal cancer symptoms: weight loss
In some cases, esophageal carcinoma narrows the esophagus so severely that people can eat little or no solid foods. You then often lose a lot of body weight in a few weeks. In the case of older people in particular, unwanted weight loss should always be clarified by a doctor. Esophageal cancer is associated with significant weight loss in around 70 percent of cases. But many other cancers also cause those affected to lose a relatively large amount of weight in a short period of time.
Esophageal Cancer Symptoms: Pain
About 46 percent of esophageal cancer patients experience pain behind the sternum. They mainly occur when people swallow. Once the tumor has reached a certain size, it presses on nerve fibers that transmit the information "pain" to the brain. When you swallow, the muscle tension builds up even greater pressure on these nerves. This is why some people only feel pain when they swallow something. Pain behind the sternum can also occur in connection with other diseases of the esophagus, but also with a heart attack.
Esophageal cancer symptoms: regurgitation
About 30 percent of patients with esophageal cancer report that they often choke the pulp from the esophagus back into their mouth (regurgitation). Solid food in particular cannot easily pass through the esophagus if it is narrowed and is therefore transported back upwards. In contrast to vomiting, regurgitation in esophageal cancer is not preceded by nausea, as it is not caused by the vomiting center in the brain but by the mechanical obstacle to passage in the esophagus. In other diseases such as reflux disease or muscular bulging of the esophagus, similar symptoms are sometimes observed.
Esophageal cancer symptoms: salivation
Some patients with esophageal cancer suffer from increased salivation (hypersalivation). It occurs when the body perceives the tumor in the esophagus as a foreign body or food particles. The salivary glands then produce more secretions to flush them down.
Esophageal cancer symptoms: cough and hoarseness
If esophageal carcinoma occurs in the upper part of the esophagus, it can cause an urge to cough. It is based on a body reflex that normally prevents food residues or foreign objects from remaining in the windpipe or bronchi.
If tumors or lymph nodes affected by it in the neck area press on the larynx and vocal cords, esophageal cancer causes a hoarse voice. Of course, coughs and hoarseness also occur with harmless illnesses such as a cold. Only when other esophageal cancer symptoms listed here appear at the same time or persist for a long time is it time to rule out esophageal cancer.
Esophageal cancer symptoms: palpable lumps
When the esophageal cancer is advanced, enlarged nodules along the esophagus can sometimes be felt. This can be the original malignant tumor itself. But it can also be enlarged lymph nodes. They can be enlarged due to the general disease process when malignant cells have spread into these lymph nodes and are growing there.
Esophageal Cancer Symptoms: See a Doctor
Most esophageal cancer symptoms are very non-specific. They can have many other causes as well. You should always consult a doctor if you have persistent swallowing difficulties or a combination of several potential esophageal cancer symptoms. This is especially true for people over 45 years of age who have difficulty swallowing. Unfortunately, esophageal cancer is often diagnosed late. As a result, therapeutic measures are often very extensive and the prognosis is poor. The chances of recovery are significantly better if the esophageal cancer symptoms are correctly interpreted at an early stage of the disease.
Tags: anatomy alternative medicine pregnancy birth