Immunoglobulin E.
and Eva Rudolf-Müller, doctorEva Rudolf-Müller is a freelance writer in the medical team. She studied human medicine and newspaper sciences and has repeatedly worked in both areas - as a doctor in the clinic, as a reviewer, and as a medical journalist for various specialist journals. She is currently working in online journalism, where a wide range of medicine is offered to everyone.
More about the experts All content is checked by medical journalists.Immunoglobulin E (IgE) is an antibody that is primarily responsible for defending against parasites. This class of antibodies also plays a key role in type I allergic reactions such as hay fever or allergic asthma. Read here about the exact function of immunoglobulin E in the body and how the IgE level can be increased or decreased.
What is immunoglobulin E?
Immunoglobulin E (IgE) is a specific group of antibodies. IgE antibodies are mainly found bound to the surface of certain immune cells (such as mast cells, eosinophilic granulocytes, etc.). Only a very small amount of free immunoglobulin E.
What are the tasks of immunoglobulin E?
The immunoglobulin E is mainly involved in the fight against parasites such as worms or protozoa. It also activates cells that initiate immediate-type allergies (type I allergy). These include, for example, allergies to:
- Medications like penicillin
- Food (nuts, shellfish, citrus fruits, etc.)
- Bee or wasp poisons
- Pollen (hay fever)
- latex
- Contrast media
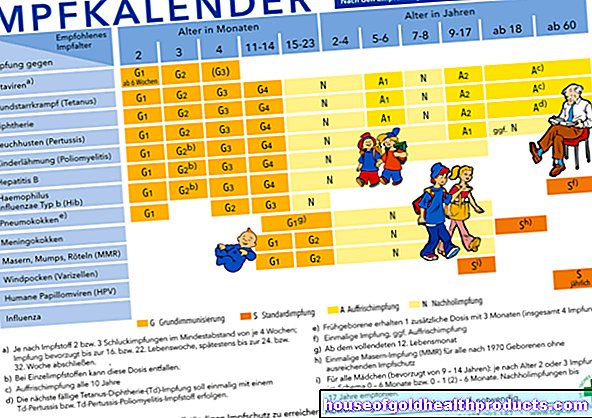
Normal values for immunoglobulin E.
The IgE values are determined in the blood serum. The normal range for adults is up to 100 IU / ml. The unit IU stands for "international units".
In allergy tests, the IgE values are given in the unit kU / l (kilo units per liter) and divided into different RAST classes:
|
RAST class |
kU / l |
|
0 |
0,00 - 0,34 |
|
1 |
0,35 - 0,69 |
|
2 |
0,70 - 3,49 |
|
3 |
3,50 - 17,49 |
|
4 |
17,50 - 49,99 |
|
5 |
50,00 - 99,99 |
|
6 |
≥ 100 |
For example, if someone achieves a RAST class 0 result in an allergy test for bee venom, this means that there are no allergen-specific IgE antibodies circulating in their blood.
When is the immunoglobulin E low?
The IgE blood level is low in so-called agammaglobulinaemia. There is a deficiency in all immunoglobulins, including immunoglobulin A and M, for example. Agammaglobulinemia can be congenital or acquired.
Isolated IgE deficiency is rare.
When is IgE elevated?
The immunoglobulin E is increased in the following diseases:
- Atopic diseases such as neurodermatitis, allergic rhinitis (allergic rhinoconjunctivitis) and allergic asthma
- Cancers
- Worm infestation (helminthiasis, e.g. infections with roundworms, tapeworms or roundworms)
- Protozoal infection (e.g. leishmaniasis or plasmodia infection)
- special immunodeficiency syndromes such as hyper-IgE syndrome or Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
In addition, the immunoglobulin E increases in the so-called graft-versus-host reaction: After a transplantation of foreign stem cells, the donor's immune cells fight the tissue of the organ recipient.
Tags: foot care womenshealth news