Leukocytosis
and Martina Feichter, medical editor and biologistDr. med. Andrea Reiter is a freelance writer for the medical editorial team.
More about the expertsMartina Feichter studied biology with an elective subject pharmacy in Innsbruck and also immersed herself in the world of medicinal plants. From there it was not far to other medical topics that still captivate her to this day. She trained as a journalist at the Axel Springer Academy in Hamburg and has been working for since 2007 - first as an editor and since 2012 as a freelance writer.
More about the experts All content is checked by medical journalists.
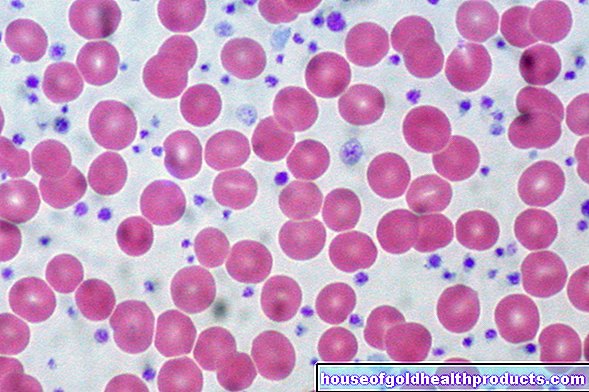
With leukocytosis, the number of white blood cells (leukocytes) is increased. In most cases, infections cause leukocytosis. But other diseases such as rheumatism or blood cancer are also possible causes. Read everything you need to know about the blood count, which diseases the leukocytosis indicates and when it is dangerous.
Leukocytosis: what is it?
With leukocytosis, the number of leukocytes in the blood is increased. Mostly it is an expression of an infection or an inflammatory disease. This is because leukocytosis occurs primarily when the bone marrow has been stimulated by the immune system to produce and release white blood cells. This is done in order to have enough cells available for immune defense.
Sometimes, due to a DNA defect, the bone marrow receives incorrect information and freely produces white blood cells without causing inflammation. In this case one speaks of blood cancer or of so-called "myeloproliferative neoplasias". If the number of blood cells exceeds a certain limit, there is an increased risk of thrombosis and strokes.
Too many white blood cells: cause
If the number of leukocytes is too high, this can have the following causes, among others:
- Infections
- Leukemia and myeloproliferative neoplasms (too many immature cells that are not fully functional are then produced and released in the bone marrow)
- Tumors
- Autoimmune diseases
- Nicotine use
- Medication
- a spleen removal (as the leukocytes are then insufficiently broken down)
- pregnancy
- Heart attack
Bacterial infections often lead to severe leukocytosis. In viral infections, the number of leukocytes is usually only slightly increased, and sometimes it even decreases.
Myeloproliferative neoplasms do not only affect the white blood cells: elevated leukocytes and erythrocytes in the blood, for example, are an expression of what is known as polycythemia vera, in which the bone marrow incorrectly produces too many blood cells of all types.
Too Many White Blood Cells: What To Do?
An increased white blood cell count does not reveal anything about an underlying disease. Nevertheless, if there are too many white blood cells in the blood sample, the first point is that there are inflammatory processes in the body. In such cases, the white blood cell count regulates itself when the inflammation has subsided. A little more blood is therefore drawn at intervals to determine the leukocyte count. This is how the course of the infection can be controlled.
However, if the number of leukocytes remains too high, further examinations must follow in order to find the cause of the leukocytosis. Occasionally the white blood cell count is slightly increased without a cause being found. In this case, one speaks of idiopathic leukocytosis.
Tags: nourishment sleep alternative medicine