Allergy test
and Martina Feichter, medical editor and biologist Updated onDr. med. Philipp Nicol is a freelance writer for the medical editorial team.
More about the expertsMartina Feichter studied biology with an elective subject pharmacy in Innsbruck and also immersed herself in the world of medicinal plants. From there it was not far to other medical topics that still captivate her to this day. She trained as a journalist at the Axel Springer Academy in Hamburg and has been working for since 2007 - first as an editor and since 2012 as a freelance writer.
More about the experts All content is checked by medical journalists.
The term allergy test describes various methods that the dermatologist can use to determine an allergy. For example, he confronts the patient with various possible allergy triggers (allergens). The patient's physical reaction to this indicates whether they are hypersensitive. Read more about allergy tests, when they are carried out and the risks here.

What is an allergy test?
Before the actual allergy test, the doctor collects the patient's medical history (anamnesis) in conversation. In addition, he asks about the living conditions, eating habits and the professional environment of the patient, among other things. The exact description of the complaints is also particularly important. The doctor asks the patient, for example, whether the symptoms only occur at certain times of the year or in certain situations and, if so, which ones.
This anamnesis interview is followed by skin tests, blood tests and a follow-up history (e.g. checking whether symptoms and test results match). Sometimes a so-called provocation test is also useful. The doctor confronts the patient directly with the (potential) allergy trigger.
Background knowledge: allergy
In the case of an allergy, the immune system reacts to actually harmless substances (pollen, grass, certain foods, etc.), more precisely: to certain ingredients (mostly proteins) of these substances. It wrongly classifies these allergens as dangerous at the first contact and produces suitable antibodies against them (sensitization of the immune system). Upon renewed contact with the allergen, an increased immune reaction sets in, which can be accompanied by symptoms such as reddened eyes, runny nose (allergic rhinitis, allergic runny nose), cough, shortness of breath and / or a rash.
When do you do an allergy test?
The triggering allergen is often unknown and only symptoms such as reddened eyes, difficulty breathing, itching or a rash are noticed at first. It therefore makes sense for those affected to keep an allergy diary. In it they enter, for example, the type, severity and duration of the complaints, the time of day at which they occur, as well as medication intake, diet, activities and environmental influences. These records, in combination with the subsequent allergy tests, help the doctor to more easily identify the triggering allergen.
In certain circumstances, skin and provocation tests should not be performed. These include:
- high risk of an allergic reaction from the test
- Skin diseases in the test field
- pregnancy
- Treatment with beta blockers (certain cardiovascular drugs)
Allergy test in children
If there is a justified suspicion of an allergy, allergy tests can also be carried out on children. However, the results cannot be assessed as clearly as with adults. A positive test result does not necessarily mean that the child really has an allergy, but only that the immune system reacted to the contact with the test substance.
What do you do with an allergy test?
If the doctor has any suspicions based on the preliminary examinations, he will carry out an allergy test for the relevant allergen.
Allergy blood test
The blood test is a common laboratory test for people who have an allergy. Blood is examined for certain substances that can provide information about an allergy.
- Measurement of antibodies of the IgE type: The RAST test (Radio Allergo Sorbent Test) shows how many specific, allergy-causing antibodies (IgE) are present in the blood. However, allergy symptoms may be absent despite increased IgE values.
- Lymphocyte transformation test: Certain allergies (e.g. to nickel) are not mediated via IgE antibodies, but via special immune cells (lymphocytes). The lymphocyte transformation test (LTT) is used to diagnose these allergies. However, this test is not a standard procedure and should be backed up by further clinical findings and allergy tests. The LTT should only be carried out by specialized and certified laboratories.
- Measurement of antibodies of the IgG type: The determination of IgG antibodies is also used in allergy tests. It can be used to detect food or related allergies. However, the test is not very meaningful. It is therefore not recommended by medical societies.
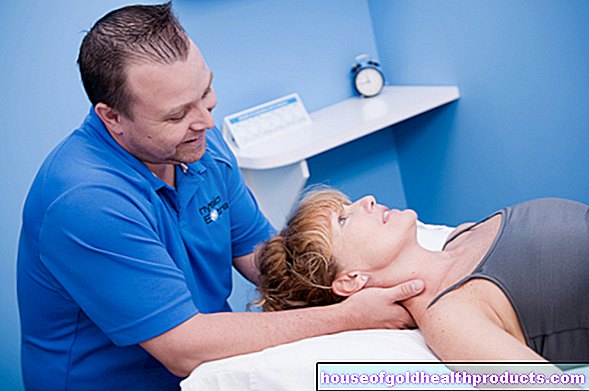
Skin test
The allergy test on the skin is a simple and quick procedure. The doctor applies the allergens to be tested to or into the patient's skin. He then observes any skin reactions such as redness, swelling or blistering. Frequently used skin tests for suspected allergies are the patch test, the prick test and the intracutaneous test.
Patch test
When the doctor carries out a patch test, how it works and what needs to be taken into account, you can read in the article Patch test.
Prick test
When a prick test is used, how it works and what you have to consider in the article Prick test.
Intracutaneous test
The intracutaneous test is similar to the prick test. Because of its sensitivity, it can be used to detect so-called "weak" allergens such as house dust mites. To do this, the doctor injects allergen extracts directly under the skin on the patient's back with a special needle until a vesicle about one to two millimeters in size forms. If there is an allergy, the skin around the puncture site will redden and swell after about 20 to 30 minutes.
Provocation test
In a provocation test, the patient is brought into direct contact with the suspected allergen in order to see whether this actually causes the expected allergic reaction. Such a test to confirm a specific suspicion of allergies can be carried out by a doctor in the case of questionable respiratory allergies (e.g. hay fever, house dust allergy, cat allergy), food allergies and drug allergies.
There are different forms of provocation test. Some examples:
If hay fever is suspected, a nasal provocation test can be helpful. The doctor injects a test solution with the suspected pollen directly into the patient's nose. If symptoms such as runny nose or swelling of the nasal mucous membrane occur, this confirms the suspected diagnosis.
For patients with allergic conjunctivitis (conjunctivitis), the conjunctival provocation test is ideal: The doctor instills the suspected allergy trigger in the form of a test solution into the lower conjunctival sac of the eye. After about ten minutes, he will assess possible reactions such as tearing, itching and increasing reddening of the eyes.
In the inhalation provocation test, the patient inhales a small dose of the suspect allergen. Whether the deep airways (bronchi) are over-sensitive to this can be determined by means of a lung function test (such as spirometry or body plethysmography).
The food challenge test is used to confirm a suspected food allergy: the patient must ingest the food to be tested by mouth. The doctor starts the test with a very low dose and then increases it gradually. During the whole time he watches out for hypersensitivity reactions in the patient.
So that expectations or assumptions of the patient and / or the doctor cannot influence the test result, a placebo-controlled and double-blind food challenge test should be carried out: Neither doctor nor patient should know whether a dose of the allergen or an allergen-free test preparation is being administered.
What are the risks of an allergy test?
In an allergy test, the patient is exposed to small amounts of the allergenic substance. This can lead to significant allergic reactions such as palpitations, shortness of breath, itching or malaise. In rare cases, allergic shock (anaphylactic shock) with cardiac and circulatory arrest can develop. For this reason, an allergy test - especially a provocation test for food or medication - should be carried out under the supervision of a doctor so that he can quickly administer emergency medication to the patient in an emergency.
What do I have to consider after an allergy test?
In order to be able to recognize late complications of the allergy test, you should remain under observation for about half an hour after the allergy test.
Tags: desire to have children book tip symptoms