Dependency - the causes
All content is checked by medical journalists.According to the law, there is a need for care if someone is unable to carry out everyday tasks, activities and obligations for at least six months due to physical or psychological problems or limitations, and needs help to do so. Chronic illnesses (e.g. heart failure, rheumatism, dementia) and sudden events such as a stroke or fall are common reasons for the need for care.

Six disease groups
There are six major groups of illnesses that are responsible for the majority of all care cases:
- Circulatory system diseases
- Mental and behavioral disorders
- Nervous system diseases
- Musculoskeletal disorders
- Cancers
- Senility and Other Nonspecific Symptoms
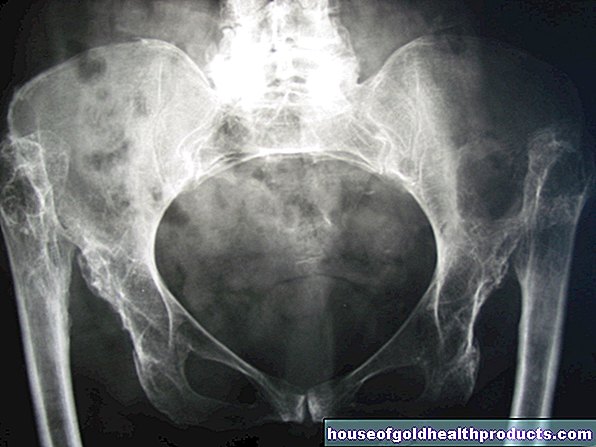
Circulatory system diseases
Diseases of the circulatory system are a very common reason for applying for care benefits in both men and women. Heart failure (heart failure) and stroke are the most common triggers for the need for care.The reason: the heart and brain are very sensitive organs that react fastest and most sensitively to changes in the supplying blood vessels (such as arteriosclerosis).
stroke
A stroke occurs either as a result of acute reduced blood flow in the brain (ischemic stroke) or due to cerebral hemorrhage (hemorrhagic stroke). The consequences can include unsteady gait, paralysis, speech disorders, clumsiness in handling cutlery and tools, and reduced mental performance. If there are permanent restrictions after the stroke has healed, the sick person needs certain help. These can be simple aids such as thicker cutlery handles or a non-slip cutting board. However, the stroke can also make you bedridden and require all-round care.
Heart failure
After a heart attack, inflammation of the myocardium or long-term alcohol consumption, the pumping capacity of the heart muscle can be so severely restricted that many physical activities are no longer possible. This weakness of the heart muscle means that various body tissues no longer receive sufficient blood - and thus oxygen and nutrients. Even with the slightest physical exertion, this manifests itself in shortness of breath and muscle weakness. People with severe heart failure need help even with normal activities such as shaving or walking into the living room.
Mental and behavioral disorders
Slowly progressing degradation processes in the brain are mainly responsible for the need for care in old age, largely summarized under the term dementia. Alzheimer's disease is the most common, followed by vascular dementia. Both are - just like frontotemporal dementia (Pick's disease) - independent diseases (primary dementias).
Dementia is rarely the result of other diseases or health disorders, such as Parkinson's, HIV or chronic alcohol abuse. One then speaks of secondary dementia.
Since the introduction of the new definition of long-term care in 2017, people with dementia have access to all long-term care insurance benefits as well as people with physical limitations.
Nervous system diseases
Inflammation and breakdown processes in the nervous system can limit the range of motion so much that the chronically ill are completely dependent on the help of others. Mental impairments do not have to be present.
Multiple sclerosis is an example of such a neurological condition leading to dependency. It can lead to disabilities at a young age. In older people, it is Parkinson's disease in particular that leads to restrictions in everyday life. The neurological consequences of diabetes are on the advance, especially diabetic polyneuropathy: At first toes and feet become numb and numb, later the gait becomes more and more unsteady. Finally, paralysis occurs, so that patients can no longer move without assistance.
Musculoskeletal disorders
Joint wear and tear (osteoarthritis) and rheumatic diseases cause pain and unsteady gait. There is a risk of falls, in which those affected can injure themselves, so that they are often further restricted as a result. If hands and fingers are also affected, this can massively impair dexterity in general and the performance of everyday activities - such as tying shoelaces, holding on to a banister or eating.
Cancers
Often it is not the cancer itself that leads to comprehensive helplessness, but rather the consequences of the tumor. Severe pain, unstable bones due to secondary tumors (metastases), severe digestive disorders or impairment of brain function in brain tumors are the causes of the increased need for help in the last phase of the disease.
Senility and Other Nonspecific Symptoms
Diseases in which mental abilities and physical resilience decline are possible causes of need for care.
Tags: womenshealth dental care first aid











.jpg)