Arrhythmias - Symptoms
Clemens Gödel is a freelancer for the medical team.
More about the experts All content is checked by medical journalists.Many people suffer from irregular heartbeat. Symptoms and causes are very different. Some people suffer from severe symptoms, while others hardly feel the arrhythmia or not at all. Read everything about possible symptoms of cardiac arrhythmias here.
ICD codes for this disease: ICD codes are internationally recognized codes for medical diagnoses. They can be found, for example, in doctor's letters or on certificates of incapacity for work. R01I48I46I47I49I45I44
How do cardiac arrhythmias express themselves?
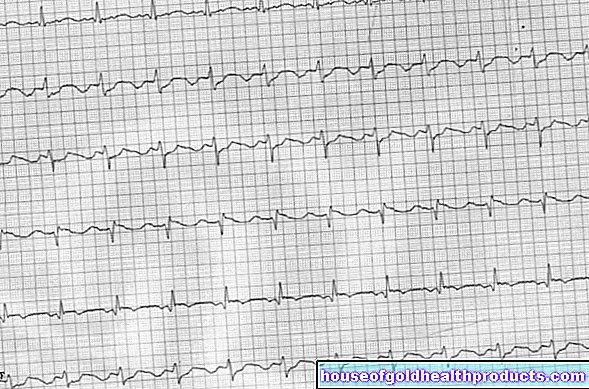
The symptoms of an arrhythmia mainly depend on whether the heart is beating too fast or too slowly and in which area of the heart the arrhythmia developed. The physical condition also has a decisive influence.
Arrhythmias: Symptoms of a slow heartbeat
If the heartbeat is too slow, the heart continues to pump too little blood per minute. As a result, less oxygen arrives in the body's circulation, which the brain urgently needs, above all. Affected person feels nauseous and dizzy. Sweating can also occur. Other complaints are fatigue, poor performance, drowsiness or even fainting. The eye also reacts to the reduced blood supply. Those affected therefore often suffer from visual disturbances. The slow heartbeat can also be irregular (e.g. bradycardial atrial fibrillation).
Cardiac arrhythmias: symptoms of too fast heartbeat
Fast "heart pounding" to "racing heart" and restlessness are the most common symptoms. Cardiac arrhythmias with a heartbeat that is too fast are often associated with an irregular pulse. But there are also forms in which the pulse feels like a quick "hammer blow". Often those affected also notice a "heart stumbling". Doctors call the palpitations and palpitations.
Difficulty breathing, chest pain, dizziness, drowsiness, confusion or loss of consciousness may also occur. The racing heart is often accompanied by fear and nervousness. In some cases, people pass urine during or after a rapid heartbeat attack.
Consequences of the arrhythmia
Both persistently (or frequently recurring) and slow cardiac arrhythmias can lead to chronic cardiac insufficiency over the long term, especially if the rhythm is irregular.
There is also the risk that the blood will swirl at certain points in the heart instead of being pumped out. As a result, the blood "stalls" at some point and a blood clot (thrombus) develops. If it comes off, it can get into the lungs or the brain with the blood, for example. The blood clot can close a vessel there, leading to a pulmonary embolism or a stroke.
Arrhythmias arise in the atrium or the ventricle
Rhythm disorders that arise in the so-called atrium of the heart are uncomfortable, but usually not acutely life-threatening. However, some arrhythmias originate in the heart chambers (ventricular arrhythmia). Ventricular fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia are examples. You are life threatening.
With ventricular arrhythmias, those affected often suffer from shortness of breath, chest pain, dizziness and paleness, but the symptoms can worsen within minutes. With ventricular fibrillation, the body's circulatory system breaks down quickly. It is therefore the most dangerous type of cardiac arrhythmia. It leads to a lack of pulse, fainting and respiratory failure. In the case of ventricular fibrillation, resuscitation must be carried out immediately, otherwise death will only occur in a short time.
Cardiac arrhythmias of the atrium (supraventricular cardiac arrhythmias) usually do not have such a dramatic course. This is because the heart skeleton acts as electrical insulation between the atria and the heart chambers. If the atrial rhythm is too fast, not all beats are often passed on to the ventricles. Atrial fibrillation does not lead to rapid death, but it also causes palpitations and palpitations.
In infants, cardiac arrhythmias often manifest themselves as tearfulness, restlessness, paleness and poor drinking.
Cardiac arrhythmias: What are the symptoms to see a doctor?
Sometimes you feel a "heart stumbling" while exercising or in a stressful situation, but sometimes also when you are at rest. This is not unusual and does not need further investigation. Doctors call these occasional extra beats extrasystoles. If the heart stumbling occurs frequently, in quick succession, or if it is accompanied by persistent palpitations, chest pain, sweating, shortness of breath, dizziness or nausea, a doctor should be consulted quickly. Even if you feel an irregular pulse, you should consult a doctor.
If cardiac arrhythmias are causing symptoms in children, it is especially important to act quickly and see a doctor.
Tags: drugs skin healthy workplace