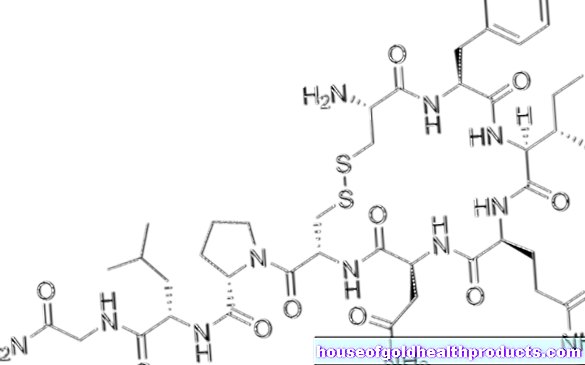
Oxytocin
Benjamin Clanner-Engelshofen is a freelance writer in the medical department. He studied biochemistry and pharmacy in Munich and Cambridge / Boston (USA) and noticed early on that he particularly enjoyed the interface between medicine and science. That is why he went on to study human medicine.
More about the experts All content is checked by medical journalists.The active ingredient oxytocin is a hormone that is produced in the brain, more precisely by the hypothalamus. It occurs naturally in the body of mammals and plays a role in couple bonding, orgasms, maternal bonding, group and fear behavior, among other things. Officially, the hormone is only used medically in connection with pregnancy and childbirth. Here you can read everything you need to know about the active ingredient oxytocin, side effects and use.
This is how oxytocin works
The hormone oxytocin is formed in the hypothalamus and released by the pituitary gland (pituitary gland). It works both in the brain and in the rest of the body, where it gets from the brain through the blood system.
According to scientific studies, oxytocin causes, among other things, sexual arousal, attachment behavior and (after birth) maternal care for the newborn in the brain.
When released into the bloodstream, oxytocin has a number of effects, often related to childbirth. It triggers contractions in the uterine muscles - also known as "labor" during childbirth. In order to induce an overdue birth or to intensify weak contractions, the hormone can therefore be administered from the outside as a drug.
After birth, oxytocin prevents increased bleeding and promotes the detachment of the placenta from the uterus. During breastfeeding, it causes the milk glands to contract by contracting the milk in the direction of the nipple (milk ejection reflex).
In addition, oxytocin - especially in high doses - can reduce the amount of urine. Because the hormone is broken down very quickly, this effect is of little importance in practice. The time in which the original amount of hormone is broken down by half and thus inactivated is about three to twenty minutes.
When is oxytocin used?
The active ingredient oxytocin is approved for use in pregnant women to induce childbirth and during childbirth to intensify or stimulate labor. After the birth, the hormone is given to prevent bleeding (bleeding prophylaxis) and to accelerate the expulsion of the placenta.
Outside of the officially approved areas of application (ie "off-label"), oxytocin is sometimes administered for autism or other behavioral disorders.
Duration of use
Within the approved areas of application, oxytocin is only used briefly for a few minutes to hours. The "off-label" application can also take place over a longer period, depending on the doctor's prescription.
This is how oxytocin is used
Oxytocin is mostly given as an infusion. Because the active ingredient is inactivated so quickly in the body (especially in pregnant women), constant administration is necessary to maintain the effect. The oxytocin circulating in the blood cannot get into the brain because it cannot cross the blood-brain barrier.
An oxytocin nasal spray is used especially outside of the approved areas of application, as this is more practical than an infusion, especially when used several times a day over longer periods of time. In contrast to an infusion, some of the hormone can get into the brain with an oxytocin spray.
What are the side effects of oxytocin?
Common oxytocin side effects - side effects that occur in every tenth to one hundredth patient - are cardiac arrhythmias, too fast or too slow heartbeat, rise in blood pressure, headache, nausea and vomiting.
Occasionally (in every hundredth to one thousandth patient) allergic reactions and permanent contractions of the uterus occur.
What should be considered when using oxytocin?
Since the active ingredient is a natural hormone, there are seldom interactions with other drugs. Above all, drugs should be mentioned that cause a QT time lengthening, i.e. a special form of cardiac rhythm change. These include some antidepressants (amitriptyline, venlafaxine, sertraline), asthma drugs (salbutamol, terbutaline), antibiotics (erythromycin, ciprofloxacin, azithromycin) and antifungal agents (fluconazole, ketoconazole).
Prostaglandins should not be given before oxytocin administration, because otherwise the uterine muscles will react much more strongly to the active ingredient.
Caution is advised when using drugs that affect blood pressure (such as high blood pressure drugs) at the same time.
The application area according to the approval only includes pregnant women and women immediately after birth. It has not yet been sufficiently clarified how great the benefits and risks of using the hormone in the “off-label” area in children and adults, mostly with mental illnesses. An “off-label” application is therefore decided individually by the attending physician.
How to get medication with oxytocin
The active ingredient oxytocin is usually applied personally by the doctor (usually as an infusion).
The oxytocin nasal spray as a finished drug has not been on the market in Germany since 2008, but can be produced as an individual prescription in the pharmacy - but only after a doctor's prescription.
Since when has oxytocin been known?
The hormone oxytocin was discovered at the beginning of the last century. In 1906, its effect on the uterus was first described by the British biochemist Henry Hallett Dale; The hormone got its name (from the Greek "okytokos": easily giving birth) in 1927. The structural structure of the hormone was not deciphered until 1953, which was the basis for the production of the active ingredient in relevant quantities. Oxytocin was the first polypeptide hormone to be produced synthetically.
Tags: travel medicine hospital fitness