Biopharmaceuticals & Biosimilars
All content is checked by medical journalists.
Biopharmaceuticals: Living Producers
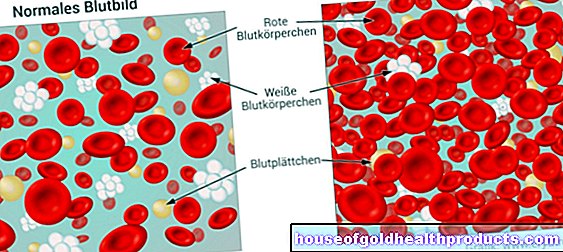
Nowadays, drugs are not only manufactured in chemical laboratories, but also with the help of living cells, i.e. biotechnologically - so-called biopharmaceuticals. Animal cells as well as yeast or bacterial cultures and - very rarely - plant cells are used.
In contrast to chemical synthesis, biotechnology can also be used to obtain highly complex active ingredients (such as insulin, beta-interferon) and treat diseases that were previously impossible or difficult to treat. However, the production process for biopharmaceuticals is not only more expensive, it is also much more complex and lengthy than for active ingredients that come from the chemistry laboratory - chemical synthesis is only suitable for active ingredients with a simpler chemical structure.
Biopharmaceuticals represent one of the fastest growing areas of the pharmaceutical market. In Germany, more than 140 biopharmaceuticals are currently approved. They are based on 108 genetically engineered active ingredients. Numerous other biopharmaceuticals are being worked on.
Biosimilars: Counterfeit biopharmaceuticals
Imitation products can also be produced from biopharmaceuticals after patent protection has expired. These so-called biosimilars are - in contrast to generics - not a copy of the original active ingredient, but only similar to it (therefore the synonym "biogenerics" is not correct). The reason lies in the production with the help of living, genetically modified cell lines:
The original cell line is only available to the original manufacturer. While other pharmaceutical companies may use a related cell line, it will never be the same as the original manufacturer's. However, even the smallest deviations in the manufacturing process can significantly affect the effectiveness and harmlessness of the drug. In contrast to generics, biosimilars therefore have to prove both properties in extensive studies on cell cultures, animals and humans.
14 biosimilars are currently approved in Europe. These include preparations against anemia, the blood formation disorder neutropenia and short stature.
Tags: skin care travel medicine alternative medicine