Metabolic diseases
Vital metabolic processes take place continuously in every cell of the human body. If something is out of balance, one speaks of a metabolic disorder, which can lead to a metabolic disease if it persists for a long time.
What is a metabolic disease?
Metabolic processes are the basis of all vital body functions. The organism gains energy and regenerates itself through metabolism; metabolism is also the basis for all growth. To do this, a wide variety of nutrients and chemical substances are channeled into the cells and converted there into compounds that are important for the body.
Other metabolic processes serve to break down superfluous, sometimes toxic metabolic products and prepare them for excretion. Any disturbance of the precisely interlinked metabolic processes can cause damage.
Metabolic diseases are often innate and anchored in the genes. Some genetic defects are hereditary, others arise spontaneously. Metabolic diseases can also develop due to unfavorable environmental factors. In many cases, there is a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental influences such as lifestyle.

Metabolic diseases from A to Z
A.- Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency
- Cushing's Syndrome
- Type 1 diabetes
- Type 2 diabetes
- Type 3 diabetes
- Diabetes in children
- Diabetes mellitus
- Diabetic ketoacidosis
- Fructose intolerance
- gout
- Hashimoto's thyroiditis
- Hemochromatosis
- Lactose intolerance
- Metabolic syndrome
- Addison's disease
- Cushing's disease
- Meulengracht's disease
- Wilson disease
- Cystic fibrosis
- Phenylketonuria
- Porphyria
- Rickets and osteomalacia
- Hypothyroidism
- Hyperthyroidism
- Gestational diabetes
- Celiac disease
What are metabolic disorders?
In metabolic processes, various chemical reactions take place in successive steps. Every single metabolic step is controlled by a specific enzyme. If one or more enzymes are defective, if they are not available in sufficient quantities or in too large a quantity, this disrupts the entire process.
Disturbed hormone production is often the trigger for metabolic disorders. The hormones act as messenger substances, which in turn control the enzymes. This is how hormones direct the entire metabolic process. If the body releases too much or too little of certain hormones, the possible consequence is a disturbed metabolism.
effects
Metabolic disorders can have the following effects:
Enrichment of metabolic products: In some metabolic disorders, the organism does not break down certain substances or intermediate products quickly enough. They build up in the body and cause problems.
Deficiency of substances: Other metabolic disorders cause a deficiency of certain metabolic products, which disrupts the body's functions.
Modified metabolic products: Due to disturbed metabolic processes, modified, harmful or non-usable metabolic products or intermediate products can arise.
Types of metabolic disorders
There are different types of metabolic disorders. Among other things, they are divided into four main groups according to the nutrient classes that are processed:
- Disorders of lipid metabolism (e.g. increased cholesterol levels)
- Disorders in carbohydrate metabolism (e.g. diabetes)
- Disturbances in protein metabolism (e.g. maple syrup disease - a severe, congenital genetic defect in which the body cannot break down certain amino acids)
- Disturbances in the mineral balance (e.g. phosphate deficiency)

Cholesterol Levels - What They Mean High cholesterol levels pose a serious threat to the body. Read what cholesterol actually is and what the measured values say! Learn more
Common metabolic diseases
Some metabolic diseases occur very frequently in the Central European population - for example disorders of the thyroid function or the so-called diabetes mellitus. The most important metabolic diseases at a glance:
diabetes
The most common and well-known metabolic disease is diabetes mellitus. There are two main forms of this. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease. The immune system destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. As the blood level of insulin falls, less and less blood sugar reaches the body's cells. The blood sugar level rises, at the same time the body cells “starve”.
Type 2 diabetes has a completely different disease mechanism: there is enough insulin in the blood, but the body cells are becoming increasingly insensitive to it (insulin resistance). You therefore take in less blood sugar - so the values rise here too. The cause of this form of diabetes is a combination of certain genes with an unfavorable lifestyle - mainly characterized by poor diet, lack of exercise and obesity.


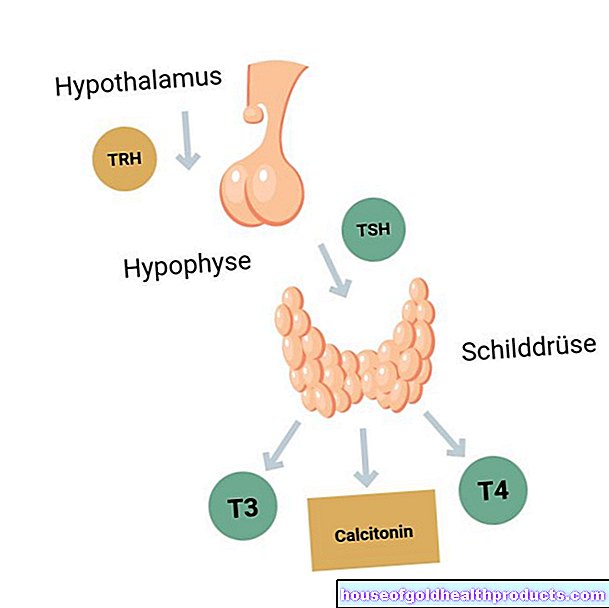
Thyroid dysfunction
The thyroid regulates the body's pace of work through various hormones. Your hormones are therefore of central importance for numerous metabolic processes. For example, they control cardiac activity, energy expenditure, bowel function and muscle strength.
Hypothyroidism: With hypothyroidism, the metabolism slows down. The consequences include weight gain, hair loss, exhaustion and a depressed mood.


Overactive thyroid: The so-called thyroid autonomy is the most common cause of overactive. Parts of the thyroid produce hormones in an uncontrolled manner. Complaints are cardiac arrhythmias, high blood pressure, nervousness, weight loss.


gout
In gout, the uric acid metabolism is disturbed: the level of uric acid is so high that it crystallizes out. The crystals settle in organs and joints and provoke inflammatory reactions there.
The cause of gout is usually a congenital disorder of the purine metabolism due to various genetic defects. Another possible cause is that the kidneys are not excreting enough uric acid. There are various causes for this, such as kidney disease or excessive alcohol consumption.


Cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis is caused by various genetic defects. They cause a certain transport mechanism for salts, the so-called ion channels, to not work properly.
Too much salt remains in the cells of cystic fibrosis patients. As the body strives for a balanced salt concentration, more fluid flows into the cells, while the secretions in the lungs and other organs, for example, become very viscous, which causes massive breathing problems and digestive disorders.

Risk factors for metabolic diseases
Many metabolic diseases develop solely due to genetic defects. For others, however, the so-called lifestyle factors play a role, which only allow a predisposition to a metabolic disease to break through. Factors that affect many metabolic processes are:
Diet: Too much sugar, animal fats and highly processed foods favor the metabolic disease type 2 diabetes, among other things.
Obesity: Body fat is not a passive storage tissue. It produces numerous hormones that also affect metabolic processes. The result can then be, for example, a metabolic syndrome with high blood pressure, high blood lipid levels and insulin resistance.
Smoking: Tobacco smoke contains over a hundred pollutants. These also seem to include those that influence metabolic processes. How exactly this works is still unclear. However, studies show that, among other things, smokers are about twice as likely to develop diabetes as non-smokers.
Alcohol abuse: With heavy alcohol consumption, for example, the body produces larger amounts of certain blood lipids (triglycerides) and the liver stores more fat. In addition, the formation of new glucose is suppressed, which can cause hypoglycaemia when the sugar stores are empty. Uric acid levels in the blood also rise with high alcohol consumption. Possible consequences are gout attacks.
Shift work: People who work shifts have a higher risk of obesity, diabetes mellitus and other metabolic diseases. One possible reason: Shift work disrupts the internal clock, which also regulates the metabolism at different times of the day and night.
Family risk: A family with type 2 diabetes and gout, for example, is more likely to have a genetic predisposition to these metabolic diseases. A healthy lifestyle can then prevent the diseases from breaking out despite unfavorable genetic makeup.



Symptoms associated with metabolic diseases
The body functions are based on innumerable metabolic processes. Metabolic disorders make themselves felt in a correspondingly diverse manner. These include:
- Weight loss
- Weight gain
- Hair loss
- exhaustion
- stomach pain
- nausea
- stomach pain
- Skin problems


Diagnosis of metabolic diseases
The symptoms that come from metabolic disorders also occur in other diseases. So you are unspecific. Because of this, some metabolic diseases are not easy to recognize. At the beginning of the diagnosis there is usually an exclusion process for other diseases, so the doctor first checks for other possible causes of the symptoms. If they are not present, a metabolic disease becomes more likely.
Since many metabolic disorders are inherited, or at least have a genetic implication, knowledge of the family history can put doctors on the right track.
How are metabolic diseases diagnosed?
In particular, the determination of hormone levels and other blood tests can provide indications of metabolic diseases. Noticeable changes in thyroid hormone levels explain, for example, fatigue and weight changes with an unchanged lifestyle. High blood sugar levels in the urine indicate diabetes. Elevated uric acid levels indicate gout and can be the cause of inflamed and sore joints.
If the metabolic disorder can be traced back to a genetic cause, this can be clarified using genetic tests. In newborn screening, doctors examine all newborns for the most important disorders. Treatment that starts early can prevent or at least alleviate consequential damage in some diseases.


What are the treatment options for metabolic diseases?
The treatment of metabolic disorders depends on the type of disease and the severity of the symptoms. However, the treatment options for severe, and especially less common, inherited metabolic diseases are often still limited. Read more about the therapy options in the individual disease descriptions.
Medication: Many metabolic diseases can be treated well with medication. This applies, for example, to gout and diabetes or many disorders of lipid metabolism and disorders of thyroid function.
Diet change: Some metabolic disorders can be improved by omitting certain foods. In the case of certain hereditary metabolic disorders, this is even the most important therapeutic measure. Many patients with metabolic disorders also benefit from weight loss.
Physiotherapy: Some symptoms of metabolic disorders can be alleviated through physiotherapeutic measures. In the case of cystic fibrosis, for example, daily inhalations are necessary to relieve breathing problems and to help the sick to cough up the thick mucus from the bronchi.