Asthma attack
Carola Felchner is a freelance writer in the medical department and a certified training and nutrition advisor. She worked for various specialist magazines and online portals before becoming a freelance journalist in 2015. Before starting her internship, she studied translation and interpreting in Kempten and Munich.
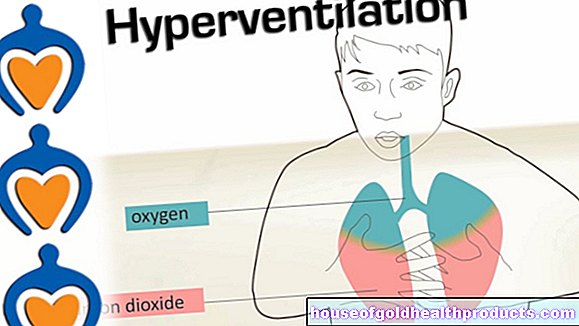
More about the experts All content is checked by medical journalists.In the event of an acute asthma attack, those affected suffer from sudden breathlessness and coughing. They also feel an acute tightness in the chest. An asthma attack is an acute worsening of the underlying disease asthma (bronchial asthma, bronchial asthma) - a chronic disease of the lungs. Find out here how to provide first aid in the event of an acute asthma attack!

Brief overview: asthma attack
- What to do if you have an asthma attack Calm the patient down and bring him into a position in which he can breathe easily (usually with the upper body slightly bent), possibly encouraging the person affected to take certain breathing techniques, giving asthma medication or supporting the patient in using the preparations
- Asthma attack symptoms: acute shortness of breath, coughing, tightness in the chest, fear and restlessness, racing heart, in severe cases insufficient oxygen supply (recognizable by bluish discolored lips, for example) up to death
- When to the doctor In the case of severe asthma attacks, as life-threatening complications can then occur.
Caution!
- Only give one stroke at a time from the inhaler, wait a few minutes before the next.
- If, during acute asthma attacks, rapid heartbeat and severe shortness of breath occur and the skin and lips turn bluish, you must call an emergency doctor immediately!
- Asthma attacks can recur at any time even after a (longer) symptom-free period.
Asthma attack: what to do?
In the event of an asthma attack, you should quickly provide first aid to ensure the patient is supplied with oxygen. Here's what you should do:
- Rest: Anxiety can aggravate shortness of breath. Therefore, you should definitely reassure the patient.
- Correct position: certain postures make it easier to breathe, e. B. Coachman's seat (while sitting, support your hands or forearms on your knees, tilt your upper body slightly forward), rider's seat (sit astride a chair, rest your arms on the backrest) or goalkeeper's posture (stand with your legs apart, bend your knees slightly, upper body forward bend, put your hands on your knees). Ask the patient what position they are most comfortable in.
- Breathing techniques: Asthmatics have often learned certain breathing techniques in order to be able to breathe more effectively when there is a shortage of air, such as the brake lip (when exhaling, place your lips loosely on top of each other so that the air escapes with a slight noise). So the patient should exhale slower and longer. Try to get him to use learned breathing techniques despite fear.
- Medication: If necessary, you should help the patient use emergency medication (e.g. inhalation spray).
- Emergency doctor: In the event of a severe asthma attack (normal speech no longer possible, shallow breathing, blue discoloration of lips and fingernails, etc.) you should call the emergency doctor as soon as possible!
Many asthma patients are well prepared for an asthma attack thanks to education. You have discussed with your doctor how you should react in an emergency (stay calm, measure the peak flow value, use reliever and emergency medication - possibly by adjusting the dose, using breathing techniques, etc.). Support a patient in implementing their personal emergency plan!
Asthma attack: symptoms and risks
As threatening as symptoms like breathing difficulties and tightness in the chest feel - an acute asthma attack usually goes away on its own. However, it can also get worse and become dangerous with symptoms such as:
- severe shortness of breath
- rapid but superficial breathing
- Racing heart
- bluish discoloration of the lips and fingernails
- Restlessness
- Inability to say longer sentences
- Disturbances in consciousness such as confusion or even loss of consciousness
In the event of such signs of a severe asthma attack, you must call an emergency doctor immediately!
The status asthmaticus is a life-threatening complication. This is a very severe asthma attack that cannot be stopped despite the use of the usual medications (such as cortisone, beta-2 sympathomimetics) and lasts for more than 24 hours. Gas exchange in the lungs can then fail, which can ultimately lead to impaired consciousness and respiratory failure.
A severe asthma attack can also lead to acute overinflation of the lungs. With each breath, a little more air remains in the lungs than normal.
Asthma attack: when to see a doctor?
Patients with a very severe asthma attack should be hospitalized by an emergency doctor. Due to the very difficult breathing, the body can be dangerously undersupplied with oxygen. The brain is particularly sensitive to a lack of oxygen. There is also the risk of life-threatening complications of the cardiovascular system.
Asthma attack: treatment by the doctor
The doctor (emergency doctor) will give the patient the necessary asthma medication - active ingredients that the patient himself uses as emergency medication. These include, for example, beta sympathomimetics for inhalation or as an infusion. They relax and widen the airways. Cortisone, which is administered as a tablet or injection, is also important. It inhibits the inflammatory response in the bronchi.
If necessary, the patient is also given oxygen via a nasogastric tube.
In the event of a very severe asthma attack, patients must be treated immediately in the intensive care unit.
Prevent asthma attacks
There are several things you can do to reduce the risk of an asthma attack:
- Avoid triggers: If possible, you should avoid known triggers for an asthma attack, e.g. cold air, house dust, stress, certain foods.
- No nicotine: You shouldn't smoke (even passively). The smoke also irritates the lungs and intensifies the inflammatory processes there.
- Exercise: Regular exercise at an appropriate intensity can reduce the frequency and severity of asthma attacks. Endurance sports like swimming are best. Do not overexert yourself during training and start with light training units first. Do not exercise in very cold or very dry air, outdoors with high ozone or pollen levels or without warming up. Always take your emergency medication with you to exercise.
It also makes sense to take part in a special training program (disease management program, DMP) for asthmatics. There you will learn important things about asthma and get tips on how to better deal with the chronic disease. For example, you will learn breathing techniques that will help you breathe better in the event of an asthma attack.
Tags: magazine alcohol dental care