Hypothyroidism - desire to have children
Martina Feichter studied biology with an elective subject pharmacy in Innsbruck and also immersed herself in the world of medicinal plants. From there it was not far to other medical topics that still captivate her to this day. She trained as a journalist at the Axel Springer Academy in Hamburg and has been working for since 2007 - first as an editor and since 2012 as a freelance writer.
More about the experts All content is checked by medical journalists.
About ten percent of all cases of unfulfilled desire to have children in women can be traced back to a thyroid disorder. Mostly it is an underactive thyroid. Here you can find out what you can do to still get pregnant and what is important during pregnancy.
ICD codes for this disease: ICD codes are internationally recognized codes for medical diagnoses. They can be found, for example, in doctor's letters or on certificates of incapacity for work. E89E06E03E00
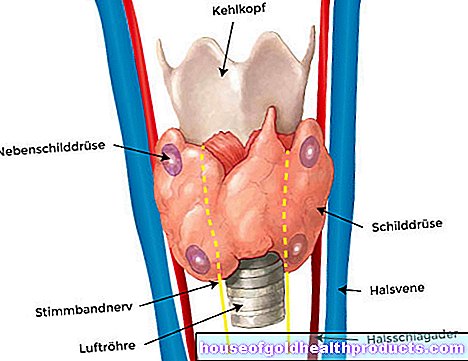
Thyroid hormone imbalance
In addition to numerous metabolic processes, the thyroid hormones also control fertility and reproduction. A hormonal imbalance - be it due to an underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism) or an overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism) - affects egg maturation and the menstrual cycle. Menstrual cycle disorders and infertility can be the consequences.
Latent hypothyroidism: desire to have children is also often unfulfilled
Many women have high levels of TSH in their blood, but their blood levels of thyroid hormones are (still) normal. Doctors call this a latent hypothyroidism. Problems with the desire to have children can also arise and not only when a deficiency in thyroid hormones can be demonstrated.
Hormone measurements and looking for antibodies
The measurement of the thyroid values is part of the basic diagnosis for every patient who cannot become pregnant. The basal TSH value and the blood level of the free thyroid hormones thyroxine (fT4) and triiodothyronine (fT3) are determined.
The doctor can also test the blood for antibodies to the thyroid gland. The detection of such thyroid autoantibodies (TPO antibodies or TAK) suggests Hashimoto's thyroiditis. This autoimmune disease causes chronic inflammation of the thyroid gland and is the leading cause of acquired hypothyroidism.
The test results show the doctor whether and which thyroid disorder is a possible cause of unwanted childlessness. If the thyroid is underactive, he will initiate substitution therapy: The deficiency of thyroid hormones is compensated by taking hormone tablets daily. If the hypothyroidism is adequately substituted, women with an underactive thyroid can also become pregnant.
Hypothyroidism: monitor pregnancy carefully!
Doctors pay particular attention to careful monitoring of thyroid levels in expectant mothers with hypothyroidism. Pregnancy (and breastfeeding) result in an increased need for thyroid hormones. Pregnant and breastfeeding women must therefore take a higher dose of hormone tablets. Otherwise, the hormone deficiency increases the risk of complications. This includes
- Preeclampsia (late pregnancy poisoning)
- child malformations
- delayed lung maturation
- overall delayed development of the child
- Miscarriage, premature birth and still birth
Women with latent hypothyroidism must also take thyroid hormones during pregnancy because the hormone requirements increase during pregnancy. A deficiency in the child could, among other things, result in significant neuropsychological developmental damage and a permanently reduced intelligence quotient in the child.
Hypothyroidism: Men’s desire to have children
In the stronger sex, decreased sexual desire (libido) and impotence are among the possible consequences of an underactive thyroid. Problems with the desire to have children can often be solved in men by substituting the hormone deficiency.
Tags: nourishment therapies healthy workplace