Calcium deficiency
and Martina Feichter, medical editor and biologistDr. med. Andrea Reiter is a freelance writer for the medical editorial team.
More about the expertsMartina Feichter studied biology with an elective subject pharmacy in Innsbruck and also immersed herself in the world of medicinal plants. From there it was not far to other medical topics that still captivate her to this day. She trained as a journalist at the Axel Springer Academy in Hamburg and has been working for since 2007 - first as an editor and since 2012 as a freelance writer.
More about the experts All content is checked by medical journalists.
A calcium deficiency (calcium deficiency, hypocalcemia) can be life-threatening. It arises from a reduced calcium intake from food, kidney diseases or hormone imbalances, more rarely from an increased calcium loss or need. A typical symptom is muscle cramps in the hands. Read more about calcium deficiency here!
What is calcium deficiency?
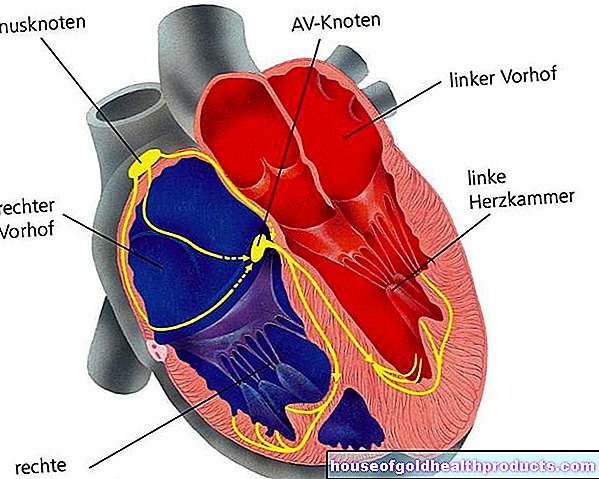
In the human body, up to 1.5 kilograms of calcium are stored in the bones. Only a small part of the calcium ingested through food circulates in the blood or is present in the body cells. However, there it is involved in a large number of metabolic processes. In the case of muscle cells (including heart muscle cells), for example, only the influx of calcium leads to muscle contraction.
The calcium level in the blood is influenced by hormones, vitamin D, the phosphate metabolism and finally also by food intake. Various factors can cause the level to drop below the normal range. Then a calcium deficiency (hypocalcaemia) occurs. Possible causes are, for example:
- Hypoalbuminemia = lack of albumin (an important protein in the blood plasma), for example in liver cirrhosis
- impaired absorption of vitamin D or calcium, for example in celiac disease or rickets
- Kidney failure (renal failure)
- Underactive parathyroid glands (hypoparathyroidism)
- acute inflammation of the pancreas (acute pancreatitis)
- certain medications (anti-epileptics, some diuretics, cortisone)
Calcium deficiency: symptoms
A calcium deficiency often has no symptoms at first. Sometimes a tingling sensation occurs around the mouth, hands and feet. If the doctor examines the reflexes, they are often increased. This means that the muscles twitch more violently when the doctor taps certain areas with the reflex hammer.
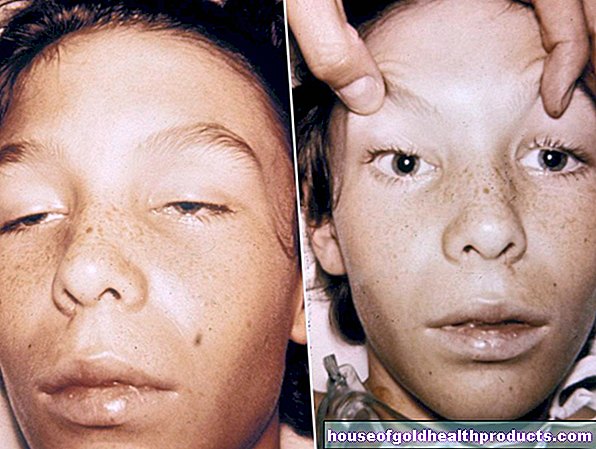
Sometimes the heartbeat becomes slower, in extreme cases the heart can weaken or even stop. Depression and anxiety can occur. A very typical sign of severe calcium deficiency is what is known as tetany. These are cramps or spasms in the hands and feet. The hands assume a so-called paw position, the feet are in an equinus position, that is, the toes point to the ground when sitting.
Calcium Deficiency: What To Do?
If you have mild hypocalcaemia, you can try to increase the calcium level by eating calcium-rich foods. If necessary, calcium-containing preparations such as effervescent tablets, powders or juices must be taken. If the calcium deficiency is pronounced, the person concerned must be treated in a hospital because of the risk of cardiac arrest. There, the calcium deficiency is often treated with infusions. If a disease is responsible for the calcium deficiency, it must be treated as well.
Tags: skin healthy feet symptoms