Bromhexine
Benjamin Clanner-Engelshofen is a freelance writer in the medical department. He studied biochemistry and pharmacy in Munich and Cambridge / Boston (USA) and noticed early on that he particularly enjoyed the interface between medicine and science. That is why he went on to study human medicine.
More about the experts All content is checked by medical journalists.The active ingredient bromhexine is a cough remover and is used for coughs with thick phlegm. It is taken in the form of drops, juice or tablets and converted in the body into the active ingredient ambroxol, which is also used as a cough reliever. Here you can find out everything you need to know about bromhexine: use, effects and possible interactions and side effects.
This is how bromhexine works
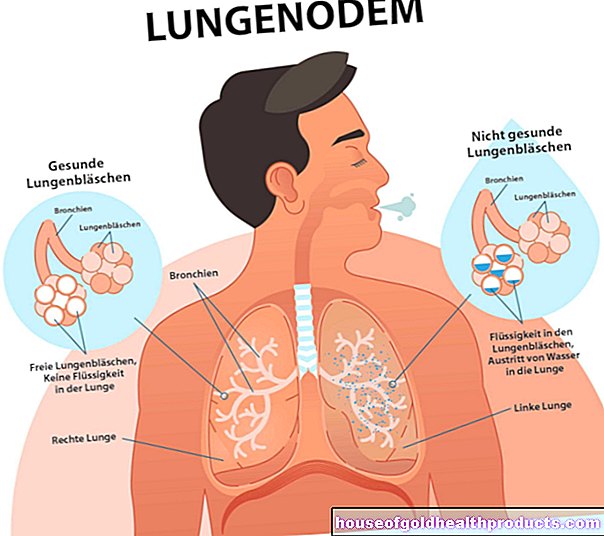
The cough remover bromhexine promotes the expulsion of bronchial secretions: It makes the secretion thinner (secretolytic effect) and makes the cilia of the lung mucous membrane beat faster (secretomotor effect).
The secretion of the lungs is increased especially in the case of infections of the respiratory tract. It should both fight the invading pathogens and ensure that they are transported to the mouth and nose. The glands of the body are roughly divided according to their function into serous (with watery, protein-containing secretions) and mucous (with tough secretions) glands. The former can contain antibodies, whereas mucous glands with their thick mucus mechanically prevent the invading bacteria from advancing.
If the balance between serous and mucosal secretion is shifted too much in the direction of mucus production, mucus is produced so tough that it can hardly be coughed up or not at all.
Secretolytic agents such as bromhexine increase the release of serous secretion and thereby make the mucus thinner. In addition, bromhexine also stimulates the movement of the cilia, which lie on the surface of the lining of the lungs. This allows the mucus to be removed more efficiently.
Uptake, breakdown and excretion of bromhexine
After taking bromhexine drops, juice or tablets, the cough reliever enters the blood through the intestines. The highest levels are reached there after about an hour. Shortly after ingestion, four fifths of the active ingredient is converted in the liver into metabolic products such as ambroxol, which are also effective against thick mucus. The breakdown products are excreted in the urine via the kidneys.
When is bromhexine used?
The cough remover is approved for the treatment of acute and chronic lung and bronchial diseases in which the formation and transport of mucus are disturbed.
It can therefore be used for colds as well as for more serious diseases such as asthma, COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease) and cystic fibrosis.
Bromhexine can be used for both the short and long term, but in the latter case the liver function should be checked regularly.
This is how bromhexine is used
The cough remover is taken in the form of tablets or as a liquid (bromhexine drops, juice). Adults and adolescents from 14 years of age should take 8 to 16 milligrams of bromhexine three times a day, whereby the total daily dose should not exceed 48 milligrams. Children from two years of age can be treated with bromhexine in a correspondingly lower dose. Care should be taken to drink enough fluids during treatment.
According to a doctor's prescription, infants and toddlers under two years of age can also be treated with liquid bromhexine preparations. However, the medicine must not contain mint oil, as this can lead to larynx cramps and suffocation in young children.
What are the side effects of bromhexine?
Bromhexine generally has a good spectrum of side effects. It can occasionally lead to fever, nausea, abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea and allergic reactions (rash, itching, shortness of breath). If allergic reactions occur, the intake should be discontinued and a doctor should be consulted.
Bronchospasm, a spasm of the bronchi, which manifests itself as an asthma attack, can rarely occur.
What should be considered when taking bromhexine?
During treatment with bromhexine, no cough-relieving agents (such as dextromethorphan / DXM, codeine) should be taken permanently, as this can lead to a build-up of secretion in the lungs with shortness of breath or even asphyxiation. Taking cough suppressants only at night in order to ensure a peaceful sleep can be useful after consultation with a doctor.
The use of bromhexine during pregnancy and breastfeeding is not recommended because the data are insufficient and the active ingredient is excreted in breast milk.
Patients with liver and kidney dysfunction should only use bromhexine-containing medicinal products with caution and after consulting a doctor.
How to get medicines with bromhexine
All preparations containing the cough remover bromhexine require a pharmacy, but not a prescription. They can therefore be bought without a prescription in any German pharmacy.
Since when is bromhexine known?
Bromhexine was chemically produced using a natural substance in Indian lungwort (vasicine). Due to the structural change, bromhexine, unlike vasicine, does not have a heart-suppressing effect or stimulate the uterus muscles, but primarily acts on the lungs. Medicines with the active ingredient bromhexine were first approved in Europe in 1966 at the request of the pharmaceutical company Boehringer Ingelheim.
Tags: book tip symptoms news









-kastanienmnnchen-und-perlenschweine.jpg)