Finasteride
All content is checked by medical journalists.Finasteride is one of the most important active ingredients in benign prostate enlargement (benign prostatic hyperplasia). The prostate or prostate gland is a ring around the urethra and is benignly enlarged in many older men. In lower doses, finasteride stops hair loss caused by hormones. The active ingredient is generally considered to be well tolerated. In rare cases, it causes side effects such as sexual dysfunction. Here you can read everything you need to know about finasteride.
This is how finasteride works
Mechanism of action
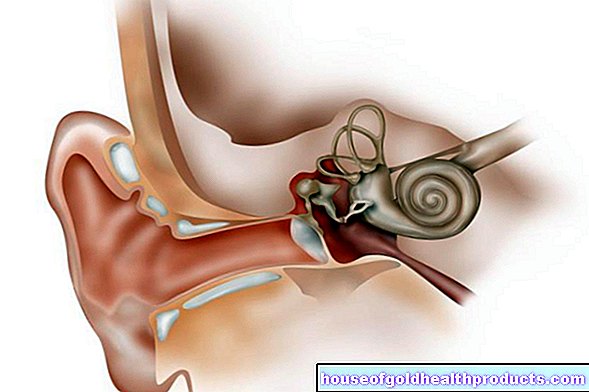
Most older men have a benign enlargement of the prostate gland. In many cases, the pressure of the newly formed tissue on the urethra leads to discomfort when urinating, frequent nocturnal urination, problems emptying the bladder completely, and backflow damage with urinary tract diseases and kidney dysfunction.
The hormone testosterone is primarily responsible for the development of male sexual characteristics and is found everywhere in the human body. If testosterone is converted by a certain enzyme (so-called "5-alpha reductase"), dihydrotestosterone is created, which binds very specifically to certain docking sites. A signal is then transmitted which, in sensitive men, can lead, among other things, to an increase in tissue in the prostate gland and to hair loss.
The active ingredient finasteride inhibits this enzyme, so it is a so-called "5-alpha reductase inhibitor". This reduces the concentration of dihydrotestosterone. As a result, the size of the prostate decreases and hormonal hair loss is stopped.
Uptake, degradation and excretion of finasteride
Almost all of the active ingredient (80 percent) is absorbed from the intestine into the blood. It takes about two hours to take effect. Finasteride is then broken down in the liver and excreted in the urine and stool.
When is finasteride used?
The most important areas of application (indications) of finasteride include:
- Benign tissue proliferation of the prostate gland (benign prostatic hyperplasia)
This is how finasteride is used
The most commonly used drug form is the film-coated tablet: The active ingredient is located in the core of the tablet and is surrounded by a protective jacket. This prevents the active ingredient from being absorbed through the skin when the tablet is touched.
The finasteride dosage in men with benign prostate enlargement is five milligrams per day. When treating hair loss caused by hormones, only one milligram is taken daily. Patients who suffer from impaired liver function receive a reduced dose.
The tablet is taken with sufficient liquid (preferably a large glass of tap water) regardless of a meal.
In the case of benign prostate enlargement, finasteride is often administered in combination with a so-called "alpha-1 adrenoceptor blocker" (such as tamsulosin): The different mechanisms of action make it possible to combat symptoms and causes at the same time very effectively.
What side effects does finasteride have?
Often (that is, in one to ten percent of those treated) finasteride causes side effects such as decreased libido and sexual dysfunction. Rarely (that is, in less than one percent of those treated) there is a feeling of tension in the chest. Ingestion leads to lumps in the breast or fluid excretion from the mammary gland.
In fetuses, finasteride leads to malformations of the external sexual characteristics. Therefore, pregnant women and women who could become pregnant must not come into contact with the drug.
What should be considered when taking finasteride?
Warnings and Precautions
The active substance finasteride can change a certain laboratory value that is used to identify a malignant change in the prostate tissue (tumor). The doctor treating you must therefore rule out the possibility of a tumor prior to treatment.
Breast cancer very rarely develops in men during treatment with finasteride. Regular checks of the breast tissue by the doctor must therefore be ensured. If there are nodular changes, pain or secretions from the mammary gland while taking finasteride, a doctor should be consulted immediately.
Contraindications
Pregnant women and women who can become pregnant must not take medication containing finasteride, nor should they split or mortar the tablets.
Interactions
So far, no clinically relevant interactions with other drugs are known.
pregnancy and breast feeding period
Finasteride is not intended for use in women.
Men who take finasteride should take care that the woman does not come into contact with the semen (for example by using a condom) when having sex with pregnant women. The reason: Finasteride can also be detected in semen. If the active ingredient reaches the unborn child, malformations of the external sexual characteristics can occur.
How to get medication with finasteride
Finasteride requires a prescription and is therefore only available with a prescription from a doctor in the pharmacy.
More interesting facts about finasteride
Until recently, the active ingredient finasteride was still known as a doping agent. The aim of the athletes was to mask the use of the forbidden doping agent testosterone (which leads to increased muscle building and general increase in performance). In the meantime, however, doping tests have become so sensitive that unnaturally elevated levels of testosterone can be detected despite taking finasteride. Finasteride has thus lost its importance as a doping agent today.
Tags: hospital prevention stress






.jpg)