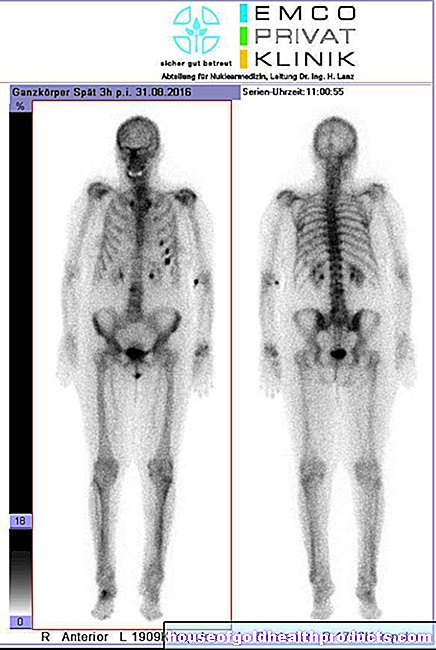
Fumaric acid
Benjamin Clanner-Engelshofen is a freelance writer in the medical department. He studied biochemistry and pharmacy in Munich and Cambridge / Boston (USA) and noticed early on that he particularly enjoyed the interface between medicine and science. That is why he went on to study human medicine.
More about the experts All content is checked by medical journalists.The active ingredient fumaric acid and its derivatives are used in the chronic skin disease psoriasis and multiple sclerosis (MS), a chronic inflammatory disease of the nervous system. Although the active ingredient has been known as a component of some plants such as common ground smoke for almost two centuries, approval for the treatment of nerve diseases is relatively new. Here you can find out why fumaric acid can support MS and psoriasis treatment, as well as other important information about this active ingredient.
This is how fumaric acid works
Fumaric Acid & MS
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an inflammatory disease of the insulating layer around the nerve pathways in the human body. The nerves in the brain and spinal cord are particularly affected. Because the insulation of the nerves is gradually being broken down, the often tightly packed nerve bundles can fail and malfunction - similar to a power cable. Experts assume that the cause of the disease is that in most cases the own immune system attacks the insulating layer and ensures that it is broken down, or that the body has problems building up this very complex protective layer around the nerves. The course of the disease varies from person to person, but it always worsens over the years. There is currently no cure for MS, but modern drugs can achieve a life expectancy that is only five to ten years shorter.
One of these drugs contains the active ingredient fumaric acid, more precisely its derivative dimethyl fumarate, which was developed so that the active ingredient can be better absorbed through the intestine into the blood. It is used in the treatment of a specific form of the disease - relapsing-remitting MS. Here the disease occurs in episodes that regress completely or incompletely.
The mode of action of fumaric acid in this form of disease is not fully understood. However, studies indicate that the substance acts directly on the cells involved in the disease and thus has anti-inflammatory and immune system-modifying properties. It has also been shown that treatment with fumaric acid causes fewer inflammatory messengers to be released by the immune system, which inhibits the progression of the disease.
Fumaric Acid & Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a non-contagious, inflammatory skin disease in which punctiform to palm-sized, strongly scaly, reddened skin changes usually develop on the knees and elbows. Often these areas also itch a lot. The inflammatory process leads to increased formation of new skin, but the skin cells are still too tightly attached to one another to be able to be removed uniformly - this leads to the formation of scales. Experts suspect that an increased number of immune cells can also be found in the affected areas, which is partly responsible for the inflammatory reaction.
Psoriasis cannot be treated causally. You can only limit the extent of the disease with active ingredients such as fumaric acid (or its derivatives such as dimethyl fumarate and ethyl fumarate). Similar to MS, the active ingredient intervenes in the inflammatory process and significantly improves it.
Uptake and degradation of fumaric acid
After ingestion of fumaric acid, it is absorbed into the blood through the intestines. Maximum blood levels are reached around five to six hours after ingestion. The derivatives of fumaric acid are broken down into fumaric acid. This is then metabolized as the cells. About 60 percent of the active ingredient is ultimately exhaled as carbon dioxide. Most of the rest is excreted in the urine via the kidneys.
When is fumaric acid used?
The derivatives of fumaric acid are used to treat:
- adult patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis
The application is long-term due to the anti-inflammatory effect.
This is how fumaric acid is used
Higher doses of fumaric acid are used to treat MS: Start with 120 milligrams of the fumaric acid derivative twice a day. After a week, the dose is increased to 240 milligrams twice a day. If side effects occur temporarily, the dose can be reduced again for a while in consultation with the doctor. The occurrence of side effects can be reduced if the capsules are taken with a meal.
In the treatment of psoriasis, lower doses of fumaric acid are used. There is also a low-dose “starter pack”: To reduce the risk of side effects, the dose is slowly increased from one to three tablets per day over a period of 3 weeks. With the second, stronger pack, the dose is increased by one tablet a week for six weeks. If the full therapeutic effect is achieved earlier, the dose does not have to be increased any further.
What are the side effects of fumaric acid?
The most common fumaric acid side effects (affecting more than one in ten people) are feeling hot and gastrointestinal complaints such as abdominal pain, indigestion and nausea. These can only occur initially, but can also recur for a short time during treatment with fumaric acid.
Other side effects of fumaric acid (in one in ten to one hundred patients) include changes in the blood count, itching, skin rashes and increased protein excretion in the urine (indication of kidney problems).
What should be considered when taking fumaric acid?
Since fumaric acid and its derivatives can negatively affect kidney function, no other active ingredients that have similar side effects should be taken during treatment. These include, for example, methotrexate (rheumatism and cancer drug), retinoids (acne drug) and ciclosporin (immunosuppressant, for example after organ transplantation).
The double use of fumaric acid, for example as a tablet and as a cream, should be avoided.
As there is insufficient experience with the use in children and adolescents under 18 years of age, pregnant and breastfeeding women, the use is not recommended in these cases.
How to get medicines with fumaric acid
All preparations with fumaric acid and its derivatives are approved for serious illnesses, which is why drugs can only be purchased in pharmacies with a doctor's prescription.
Since when has fumaric acid been known?
Fumaric acid was first found in the mushroom Boletus pseudoignarius discovered and could be obtained in pure form from the common earth smoke (a plant from the poppy family) in 1832. The common earth smoke was also used in ancient times as a medicinal plant against cramps in the digestive tract and the gall bladder, against constipation and against skin ailments.
Based on this experience, the doctor Günther Schäfer developed a psoriasis therapy with fumaric acid in the 1970s. However, fumaric acid approval for MS therapy was only granted in 2013 after the active ingredient and its derivatives had proven to be effective in clinical studies.
Tags: Diagnosis parasites alcohol
















.jpg)