Loratadine
Updated on All content is checked by medical journalists.Loratadine is one of the most important remedies against allergies, more precisely one of the second generation antihistamines. It is just as effective as the first generation antihistamines, but unlike them, it practically does not make you tired. Due to its good tolerability, the active ingredient is also considered to be the agent of choice for the treatment of allergic reactions by pregnant and breastfeeding women. Here you can read everything you need to know about loratadine.
This is how loratadine works
Loratadine blocks the effects of the messenger substance histamine and thus alleviates the symptoms of an allergic reaction:
An allergic reaction is a hypersensitivity reaction of the immune system. Upon contact with an actually harmless allergy trigger (allergen such as pollen, house dust or animal hair), there is suddenly an excessive release of the messenger substance histamine in order to transfer the allergen recognized by the body as "foreign" fight.
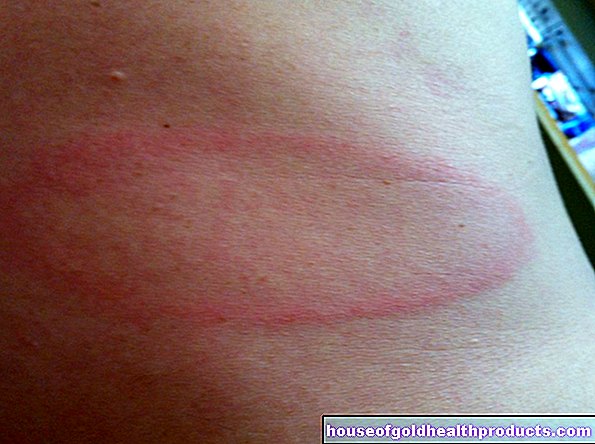
If histamine subsequently binds to its docking point (receptor), the typical symptoms of an allergy such as increased blood flow to the tissue (redness, swelling, wheals), itching, watery eyes, runny nose and cramping of the airways muscles (bronchospasm) occur ).
As a selective inhibitor of the histamine receptor (H1 receptor), loratadine can prevent these histamine effects and thus help against allergic symptoms. In contrast to antihistamines of the first generation, loratadine does not cross the blood-brain barrier and accordingly makes you tired much less often.
Uptake, breakdown and excretion
After ingestion via the mouth (orally), the active ingredient is quickly and completely absorbed from the intestine into the blood and converted into its active form by the enzymes CYP3A4 and CYP2D6.
It is then distributed in the body and is then broken down in the liver. The breakdown products are then excreted through the kidneys.
When is loratadine used?
The areas of application (indications) for loratadine include:
- allergic rhinitis such as hay fever
- Hives (urticaria)
This is how loratadine is used
Loratadine is usually given in the form of tablets. The dosage is usually ten milligrams a day. Small children weighing less than 30 kilograms and people with liver problems receive a reduced dose.
The tablets can be taken with or without food, preferably with a large glass of tap water.
What are the side effects of loratadine?
Loratadine often causes side effects such as tiredness and headaches, i.e. in one to ten percent of those treated.
Rarely does the ingestion of the active ingredient lead to an increase in appetite and gastrointestinal complaints.
What should be considered when taking loratadine?
Interactions
In contrast to other allergy drugs, there is no known increase in effectiveness when taken at the same time as alcohol.
An interaction with other drugs that leads to increased side effects is also not known. Theoretically, however, drugs that inhibit or induce the activating enzymes CYP3A4 and CYP2D6 can increase or weaken the effect of loratadine accordingly.
Driving and using machines
In rare cases, loratadine can cause tiredness as a side effect. Therefore, at the beginning of a treatment, attention should be paid to the individual reaction to the active ingredient.
In case of uncertainty, patients should decide together with their doctor whether active participation in road traffic and operating heavy machinery is advisable.
Age restrictions
The active ingredient loratadine may be used from the age of two years (or from a body weight of 30 kilograms). Children who are younger or lighter should always see a doctor if they have an allergic reaction.
pregnancy and breast feeding period
The effects of loratadine during pregnancy and breastfeeding have been very well studied. So far, no harmful effects have been found in the child when it is taken, although the active ingredient is excreted in breast milk in breastfeeding women.
Medicines containing loratadine are therefore the means of choice for allergic reactions in pregnant and breastfeeding women.
How to get medication with loratadine
Medicines containing loratadine are very well tolerated and are therefore suitable for self-medication. For this reason, they are available over the counter in pharmacies in Germany, Austria and Switzerland.
How long has loratadine been known?
Loratadine is a relatively new active ingredient. As a so-called second-generation antihistamine, its mode of action is much more selective than that of its predecessors and has significantly fewer side effects with the same effectiveness.
In contrast to other allergy medications, loratadine practically does not make you tired, which is a clear advantage over the other representatives of this class of active ingredients.
More interesting facts about loratadine
Medicines containing loratadine also suppress skin allergic reactions. Therefore, they should always be discontinued at least two days before an allergy skin test.
This is a test in which allergens are applied directly to the skin to find out which allergen the person being treated is hypersensitive to (certain pollen, house dust, animal hair, etc.). If you did not stop taking the allergy tablets beforehand, it could be that an actually positive test turns out wrongly negative, i.e. an existing allergy is not recognized.
Tags: unfulfilled wish to have children anatomy travel medicine












.jpg)