Diabetes: 1,000 steps after eating
Dr. Andrea Bannert has been with since 2013. The doctor of biology and medicine editor initially carried out research in microbiology and is the team's expert on the tiny things: bacteria, viruses, molecules and genes. She also works as a freelancer for Bayerischer Rundfunk and various science magazines and writes fantasy novels and children's stories.
More about the experts All content is checked by medical journalists.Physical exercise is one of the most important therapy modules for type 2 diabetics. Because training activates the circulation and metabolism and reduces insulin resistance. This lowers the blood sugar level. How effective the physical training is depends on the right time.
Be active for at least 150 minutes a week - this is what the guidelines recommend for type 2 diabetics. Even moderate exercise such as walking, cycling or climbing stairs have a positive effect on blood sugar levels. Keeping this under control, i.e. making sure that it remains as constant and low as possible, is important in order to avoid serious secondary diseases.
Meals drive blood sugar up
The best time of day to do sport has not yet been recommended. "But that could be exactly what matters," says Andrew N. Reynolds of the University of Dunedin, New Zealand. Because the blood sugar level increases particularly strongly after meals.
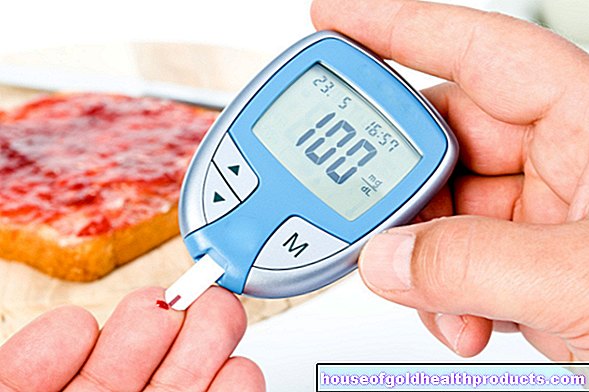
Reynolds and his team have therefore investigated whether the famous 1,000 steps directly after a meal are more beneficial for diabetics than exercising without eating. To this end, he divided 41 type 2 diabetics with an average age of 60 years into two groups: group one went for a half-hour walk once a day, group two for ten minutes each immediately after meals.
The doctors used a pedometer to check whether the study participants really followed the guidelines. The blood sugar level was measured continuously. After two weeks there was a break of 30 days, then the groups were swapped.
Running after dinner
The result: exercise after eating had a more positive effect on blood sugar levels than exercise in one go. The blood sugar after the main meals was then on average twelve percent lower. The scientists observed the greatest effect after dinner - the blood sugar level was 22 percent lower as a result. Probably because a particularly large number of carbohydrates were eaten here or the patients normally preferred to lie down on the couch without being required to exercise, the researchers speculate.
“Type 2 diabetics should be active after eating. Especially if you have eaten a lot of carbohydrates, ”is the clear recommendation of Reynolds and his colleagues. With the right timing, physical exercise can save insulin. In a further study, the scientists want to test whether walks after eating also have a long-term positive effect on blood sugar levels and whether longer exercise intervals after meals that are particularly rich in carbohydrates have a stronger effect.
Disturbed sugar balance
Diabetes is a pathological disorder of the sugar metabolism. In type 2 diabetes, the cells' sensitivity to insulin decreases. However, this hormone is important to transport sugar from the blood into the cells. If the sugar remains in the blood, it can cause some damage there, especially in areas with fine vessels such as the eyes, the kidneys or the nerves. In addition to exercise, weight reduction is the most important measure to increase the body's cells' readiness to absorb sugar again.
Source: Reynolds A. n et al .: Advice to walk after meals is more effective for lowering postprandial glycaemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus than advice that does not specify timing: a randomized crossover study, Diabetologia 2016.
Tags: baby toddler interview anatomy