Smoking promotes chronic back pain
All content is checked by medical journalists.MunichSmokers are up to three times more likely to pinch their backs than non-smokers. The reason for this lies in the pain center in the brain. The good news: this can affect smokers.
The effects of cigarette smoke on humans are complex. “Among other things, smoking affects the brain,” explains Bogdan Petre from Northwestern University in Chicago. He and his colleagues discovered that the smoke specifically strengthens the sensation of pain in the thinking organ in the case of back problems and also makes it less resilient to pain.
Mapping the brain
Their study was based on 160 patients who suffered from severe back pain for the first time. They underwent a brain scan using MRI at five different times within a year. Their general health status was also recorded, including whether they smoked. The subjects also filled out scales in which they stated how intense their back pain was. The comparison groups served were 35 perfectly healthy individuals and 32 people who had been suffering from chronic back pain for five years.
More often chronic in smokers
After one year, it was found that back pain in smokers was three times more likely to be chronic than in non-smokers.
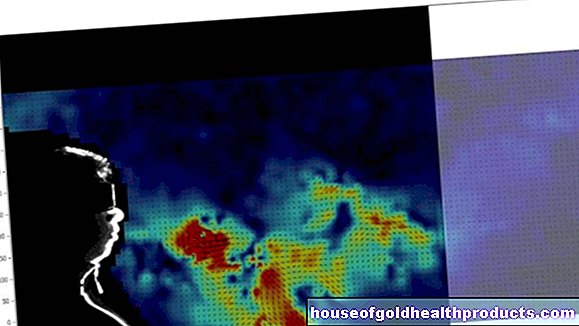
The researchers paid special attention to the images of the brains for their evaluation. There they focused on two areas that are related, among other things, to the development of addictive behavior. These two regions “speak” to each other. The more they interact, the more susceptible a person is to chronic pain.
"The connection was particularly strong and active in the brains of smokers," said Petre. This could explain why they develop chronic pain particularly often.
Quitting smoking as a therapy option
Meditation or anti-inflammatory drugs did help patients cope better with their pain. However, these therapy options did not change the intensive communication between the two brain regions.
On the other hand, only one thing helped: to give up the unhealthy lifestyle. "We saw a dramatic decrease in activity when people stopped smoking". After the stop, the pain sensitivity decreased significantly within a short time.
For the treatment of chronic back pain, help should also be given in future to stop smoking, the scientists demand. This could be an effective strategy for healing and also preventing back pain. (lh)
Source: Petre B. et al. , Smoking increases risk of pain chronification through shared corticostriatal circuitry. Hum. Brain Mapp. doi: 10.1002 / hbm.22656
Tags: pregnancy birth menopause therapies