Excessive drinking: alcohol blocks wound healing
All content is checked by medical journalists.MunichDrunk people injure themselves easily: They stumble, cause traffic accidents or burn themselves. This is doubly fatal - because wounds heal worse than usual with them. Researchers at Loyola University in Chicago have discovered the reason for this: Excessive alcohol consumption apparently weakens critical immune defense mechanisms that are involved in wound healing. This can also be noticeable in the hospital after an operation.
Inhibited immune power
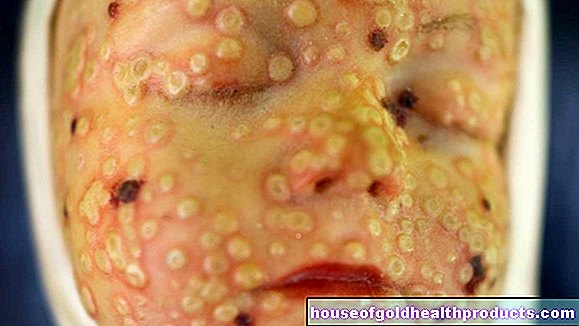
The researchers led by Katherine Radek were able to show for the first time that heavy alcohol consumption reduces the number of certain white blood cells - the so-called macrophages. The task of these phagocytes is to eliminate harmful bacteria and dead cell material from the body. If only a few of them are on site, wounds become infected more quickly, for example with the dreaded Stphylococcus aureus.
In experiments with mice, the researchers were able to show that excessive alcohol consumption blocks the production of a certain protein - MIP-1alpha. It usually signals the macrophages and attracts them to damaged areas of the body.
Advantage for bacteria
Another component of the immune system is hampered by excessive alcohol consumption: CRAMP is a small protein with an important function. It occurs in the outer layer of the skin, the epidermis. Its job is to kill bacteria there directly and to call up macrophages and other cells of the immune system to fight off infections.
Both effects of excessive alcohol consumption, which were discovered, lead to a delay in wound healing and an increased likelihood of infections under alcohol abuse. (cf)
Source: Brenda J. Curtis et al .: Episodic Binge Ethanol Exposure Impairs Murine Macrophage Infiltration and Delays Wound Closure by Promoting Defects in Early Innate Immune Responses; Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research. doi: 10.1111 / acer.12369
Tags: Diagnosis palliative medicine hospital