The sun is so healthy
Dr. Andrea Bannert has been with since 2013. The doctor of biology and medicine editor initially carried out research in microbiology and is the team's expert on the tiny things: bacteria, viruses, molecules and genes. She also works as a freelancer for Bayerischer Rundfunk and various science magazines and writes fantasy novels and children's stories.
More about the experts All content is checked by medical journalists.Unrestrained sunbathing is risky - it increases the risk of skin cancer. Nevertheless, humans are not shady plants: a lack of sunlight is harmful to body and soul.

Turn on the spring fever
Everyone knows one function of the sun: It lifts the mood. When the gray, dusky winter days are finally over and spring comes, most people feel fresh and full of energy.
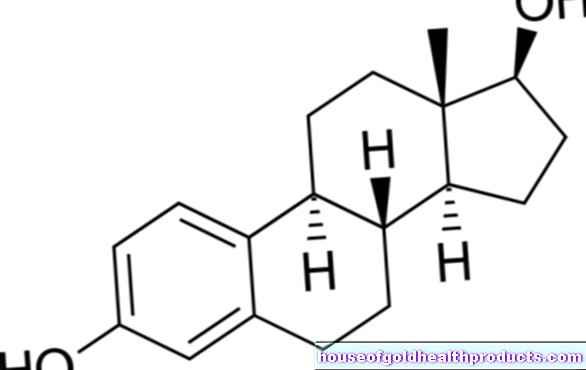
Washington University School of Medicine researchers conducted a 2006 study showing that there was a link between low mood and vitamin D deficiency. A winter vitamin D deficiency can even lead to seasonal depression. Vitamin D is also found in foods such as fish. The body covers almost 90 percent of its needs through its own production in the skin - using sunlight (UVB light). Incidentally, just 15 minutes of warm solar radiation on the face and arms are sufficient to enjoy the positive effects. In order for the body's cells to stimulate vitamin D production, you don't have to lie in the sun for hours.
The production of the "sleep hormone" melatonin, which is set in motion by a lack of light, also plays a role here. Against a gloomy mind, it helps to go out and stock up on light.
Diabetes caused by lack of sun
Various studies indicate that too little vitamin D promotes the development of diabetes mellitus. Researchers were able to show in Finnish children that taking vitamin D reduced the risk of type 1 diabetes by 80 percent.
Type 2 diabetes is also less common if you occasionally bathe in the sun. Researchers at the Public Health Institute in Helsinki, which is not exactly sun-drenched, examined 1,400 men and women over a period of 22 years. A particularly clear correlation was found among the participating men: Men with too little vitamin D in their blood were 72 percent more likely to develop type 2 diabetes.
The reason: In diabetes mellitus, either the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas are defective or there is insulin resistance, which means that the body's cells respond poorly to the hormone and can therefore hardly absorb sugar from the blood. Vitamin D counteracts both problems: On the one hand, it boosts insulin production in the beta cells. On the other hand, it has the effect that more docking sites for insulin are formed on fat and muscle tissue cells. This increases the sensitivity of the body's cells to the hormone - and the risk of diabetes decreases.
However, the scientists warn against swallowing vitamin D supplements lightly. An oversupply can have harmful consequences. So first talk to your doctor about whether it makes sense to take vitamin D for you and in what dosage.
The sun strengthens the bones
Calcium makes the bones strong. But it doesn't get into bone tissue easily. This requires a key and that is called vitamin D. Sunlight is also important for the strength of the skeleton and thus protects against osteoporosis. This is understood to mean a pathologically reduced bone mass.
In addition, a severe vitamin D deficiency can also lead to softening of the bones (osteomalacia). In childhood, this clinical picture is called rickets. It was especially widespread in the past - for example among children of poor people who grew up in dark alleys and were poorly nourished. External signs of rickets include a sagging chest and crooked legs.
Sun vitamin stops multiple sclerosis
AIn the area of the central nervous system, vitamin D can prevent aggressive immune cells from attacking the protective myelin layer of the nerve cells (neurons). This is the case, for example, with the autoimmune disease multiple sclerosis (MS). Researchers at the American John Hopkins University were able to show in mice that vitamin D prevents multiple sclerosis. This is consistent with the observation that fewer people develop MS in countries with a lot of sunlight.
The vitamin also has a positive effect on existing MS: It slows down the progression of the disease.
Radiant blood pressure reducer
More people die of heart attacks or strokes in winter than in summer. The reason for this could be the lack of sunlight in the dark half of the year. Because UV rays convert nitrite and nitrate in the skin to nitric oxide. This substance relaxes the arteries and thus lowers the pressure in the blood vessels. A small study by the University of Edinburgh with 24 test persons showed: If you lie on the sunbed for 20 minutes, your blood pressure lowers by an average of 2 mmHG (millimeters of mercury). How much sun would be necessary to lower blood pressure in the long term is still unclear.
Vitamin D against cancer
Those who have a lot of vitamin D in their blood are less likely to develop colon cancer. This was the result of a meta-study with 520,000 people. The test group with the highest vitamin level even had a 40 percent lower cancer risk than the participants with the lowest value.
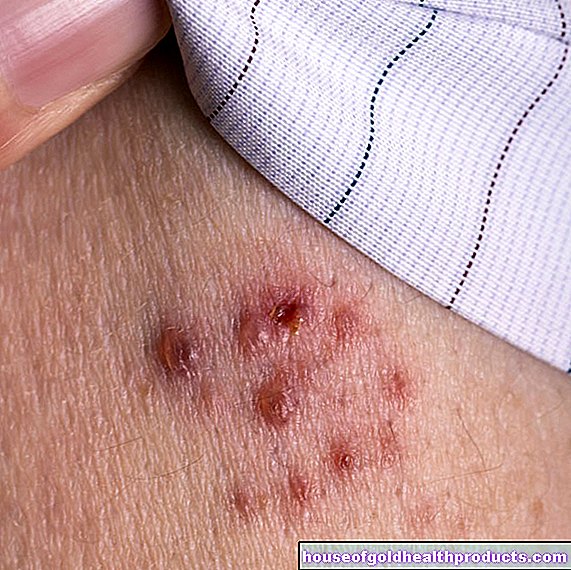
A high vitamin D level also helps people with skin cancer: The cancer is then usually more harmless and less often fatal.
Turbo for the immune system
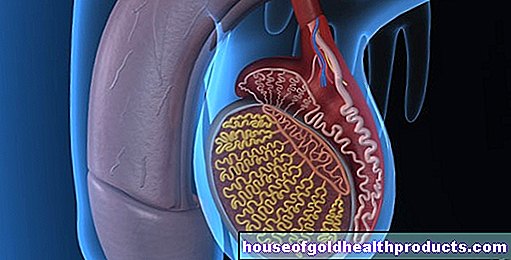
Vitamin D activates the immune system, more precisely the T cells. This is a special type of lymphocyte. When T cells discover an intruder in the body, they deploy a kind of antenna. It is equipped with a receptor that searches for vitamin D. Only when the sun vitamin is available do the T cells transform from harmless immune cells into active killer cells that eliminate bacteria or viruses, for example. If there is a lack of vitamin D, on the other hand, the cells remain inactive.
Skin cancer paradox
Even if it sounds strange: A little sun can even protect against skin cancer. This is what a team of researchers from Dresden and Ulm found out when they examined 500 skin cancer patients in comparison with a control group. Participants without skin cancer had been outdoors more often as children or adults than the cancer patients.
The scientists suspect that if the skin is not used to the sun too little, it loses its ability to build up natural sun protection. Because with sufficient exposure to the sun, in addition to the protective dark skin color, a fine thickening of the cornea, the so-called light callus, forms. But if you are seldom in the sun and then suddenly expose yourself to a high degree (e.g. when sunbathing extensively on Mediterranean beaches), you will quickly get sunburn. And that in turn increases the risk of skin cancer. The results of the study are by no means a license for careless use of the sun!
Tags: nourishment prevention pregnancy