Stuffy nose
Astrid Leitner studied veterinary medicine in Vienna. After ten years in veterinary practice and the birth of her daughter, she switched - more by chance - to medical journalism. It quickly became clear that her interest in medical topics and her love of writing were the perfect combination for her. Astrid Leitner lives with daughter, dog and cat in Vienna and Upper Austria.
More about the experts All content is checked by medical journalists.A stuffy nose is uncomfortable, but mostly harmless. The most common cause of the restricted nasal breathing is a viral infection (runny nose) or a crooked nasal septum, but other triggers are also possible. Find out here which medications, home remedies and alternative healing methods allow you to breathe more freely again!

Brief overview
- Treatment: nasal sprays or nasal drops, nasal aspirators, increase the humidity in the bedroom, elevate the upper body, surgery, home remedies, homeopathic remedies, acupressure, Schuessler salts
- Causes: Acute or chronic respiratory infections (runny nose), allergies, external influences such as dry air, hormones, crooked nasal septum
- Description: Impaired nasal breathing, those affected get little or no air through the nose
- When to see a doctor? Nose blocked for more than ten days, nasal congestion on one side, suspected foreign bodies in the nose, frequent nosebleeds, pain or swelling in the face, fever
- Diagnostics: Examination by the ENT doctor: nasoscopy, rhinomanometry, smell test, allergy test, if necessary ultrasound, computer tomography or magnetic resonance tomography
- Prevention: General hygiene measures to avoid infections, drink enough, increase the humidity in bedrooms, avoid known allergens, do not use decongestant nasal drops for more than ten days
What can you do about a stuffy nose?
A stuffy nose is usually harmless but uncomfortable. Therapy is only given if the symptoms are very pronounced. Which treatment the doctor chooses depends on the cause of the restricted nasal breathing.
Nasal spray or nasal drops
In the case of an acutely blocked nose (for example with infections or irritated mucous membranes), decongestant nasal sprays or nasal drops are suitable for treatment. They constrict the blood vessels and thus have a decongestant effect.
Decongestant nasal sprays and nasal drops should not be used for longer than seven days at a time, as they quickly become used to the habit: As soon as the decongestant effect wears off, the nasal mucous membranes are supplied with increased blood again, which again leads to a blocked nose.
If the nose is blocked by allergies, the doctor may prescribe a cortisone-containing nasal spray or nasal drops. Cortisone has anti-inflammatory and decongestant effects and quickly clears the nose again. Here, too, the treatment should only last as long as prescribed by the doctor.
So-called nasal patches are available to prevent snoring when the nose is blocked. They open the nose mechanically, thereby widening the nostrils.
Dry nasal mucous membranes (with subsequent nosebleeds) are best treated with a nasal ointment containing the active ingredient dexpanthenol.
Anyone who cannot breathe through their nose permanently (chronic nasal breathing obstruction) should take regular nasal showers with saline solution.
Treatment in infants and babies
Nasal aspirator: Soft mucus in babies' blocked noses can be removed from the pharmacy with a special nasal aspirator. Nasal aspirators for infants and toddlers are available in different designs. Ask your pharmacist how to use the respective teat correctly.
Nasal drops with table salt or sea salt: These drops do not contain any medicinal substances, but moisturize the nasal mucous membrane and make it easier to breathe through the nose.
Decongestant nasal drops: In persistent cases, the pediatrician will prescribe decongestant nasal drops.
Elevate the upper body: Place a towel under the baby's mattress so that the head is a little higher. This helps the mucus to flow out of the nose through the throat.
Humidity in the bedroom: Dry air allows the mucous membranes to dry out. Place a wet towel over the radiator to increase the humidity in the room. Alternatively, a humidifier is suitable. Also ventilate regularly!
surgery
Straightening the nasal septum
If you have a severe curvature of the nasal septum, surgery may be necessary. The aim of the treatment is to ensure that the same amount of air flows in continuously on both sides of the nose after the operation. Doctors refer to this form of treatment as "nasal septoplasty". It is usually carried out from the age of 18.
The result of the nasal septum surgery is not immediately recognizable - the nose is still clogged up to four weeks after the operation with swelling, mucus and crust formation. It takes up to three weeks for those affected to breathe freely again.
Reduction of the turbinate
If chronic enlargement of the turbinates cannot be treated with local therapy, an operation (conchotomy) is sometimes necessary. The surgeon surgically reduces the nasal concha.
Home remedies
Drink enough: Drink enough fluids throughout the day, preferably 1.5 to two liters of water or unsweetened tea. Fluid intake is important for the mucous membranes. If the mucous membranes are too dry, pathogens penetrate the body more easily.
Do not drink alcohol if you have a stuffy nose! It expands the blood vessels and increases the swelling of the nasal mucous membranes!
Sea salt spray: Sea salt nasal sprays moisten and clean the mucous membrane, the nasal secretion becomes thinner. The cilia in the nose move better again and ward off dust and pathogens.
Elevated sleeping position: nasal congestion often worsens at night. Those affected sleep poorly, often wake up at night or wake up in the morning with a severely blocked nose. The reason for this is not the time of day, but lying down. In a horizontal position, the nasal secretion does not flow down the throat as well, but remains in the nose - it becomes blocked. Use an additional pillow so that the upper body is a little higher.
Steam inhalation: heat and water vapor loosen the mucus and clear the nose again.
- Fill a large bowl with hot water (caution, risk of scalding!)
- Now bend your head over the bowl and place a towel over your head to prevent the steam from escaping.
- Breathe in deeply through your nose, closing your eyes.
- If you want, you can add chamomile flowers, sage leaves or thyme to the hot water. Alternatively, essential oils with peppermint or camphor are suitable.
Essential oils are not suitable for infants and children as well as asthma patients. They may cause shortness of breath.
Nasal rinsing with salt water: salt water cleanses the nose and moisturizes the mucous membranes.
- Pour one liter of water at body temperature into a bowl.
- Dissolve nine grams of salt in it.
- Hold one nostril closed and draw in the liquid with the other nostril.
- Now open the previously closed nostril and let the salt water run off through the other.
- Repeat the process three times for each nostril.
- Special nasal showers (vessels with special nasal attachments) are available from pharmacies.
Spicy food: Those who like and tolerate spicy food will choose foods such as mustard, horseradish, onions, garlic or ginger. The essential oils, sulfur substances and mustard oils it contains help to clear the nose of mucus.
homeopathy
There are some homeopathic remedies for nasal congestion. If there are organic reasons for the restricted nasal breathing - such as a crooked nasal septum, abscesses or tumors in the nose - you should not use globules, but consult a doctor who will treat you according to conventional medicine.
If you want to use homeopathy for your stuffy nose, you can get the appropriate remedies in the pharmacy. Alternatively, you can visit a homeopath (e.g. a naturopath or a doctor who offers homeopathy). It determines which remedy is appropriate in your case.
Examples of homeopathic remedies used for nasal congestion:
- Arsenicum album
- Euphrasia
- Galphimia glauca
- Hepar sulfuris
- Potassium bichromicum
- Lycopodium
- Nux vomica
- Pulsatilla
- Sambucus nigra
- Silicea
The concept of homeopathy and its specific effectiveness are controversial in science and not clearly proven by studies.
Acupressure
Acupressure is part of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) and is closely related to acupuncture. Instead of using needles, pressure is applied to certain points (acupressure points) with the fingers. The aim is to activate the body's self-healing powers.
- Acupressure Point YinTang: Point where the eyebrows would meet just above the nose. Press the point for 20 seconds with your index and middle fingers, repeating 3 times a day.
- Di 20: dots right next to the crease between the nostrils and corners of the mouth. Press the points with your index fingers for 20 seconds, repeating 3 times a day.
Schuessler salts
If you want to alleviate the symptoms of a blocked nose with Schüßler salts, it is best to use Kalium chloratum (No. 4) and Calcium sulfuricum (No. 12).
The concept of Schüßler salts and their specific effectiveness are controversial in science and not clearly proven by studies.
Why does the nose keep getting blocked?
In most cases, a harmless runny nose is the cause of nasal congestion. In some cases, however, other causes are hidden behind obstructed nasal breathing.
Inflamed nasal mucous membrane
Acute inflammation of the nasal mucosa
If the nasal mucous membrane is inflamed, the cavernous bodies in the nasal mucous membrane are supplied with more blood and form more secretions. Affected people are not able to breathe through their nose, or only to a limited extent. Possible causes for this are:
Acute infections (mostly viral rhinitis, rhinitis simplex acuta): First, the mucous membrane forms liquid secretion that becomes increasingly slimy. If a bacterial infection (superinfection) occurs due to the damaged mucous membrane, the mucus becomes greenish. Other symptoms are fatigue, headache, and sometimes fever.
Allergies (hay fever, pet hair allergy, house dust mite allergy, mold): Typical symptoms are blocked nasal breathing, runny nose, increased phlegm formation, itching and sneezing attacks. In the case of allergies that occur all year round (animal hair, house dust, mold), the symptom of nasal congestion is in the foreground.
External influences (dry heating air, air-conditioned rooms, dust, cigarette smoke)
Chronic inflammation of the nasal mucosa
As a result of chronic inflammation of the nasal mucosa, the turbinates enlarge. Doctors speak of "turbinate hyperplasia". It leads to constant (longer than three months) obstruction of nasal breathing and has the following possible causes:
- Excessive use of decongestant nasal sprays or nasal drops (rhinitis medicamentosa)
- Side effects of certain medications (antihypertensive drugs such as ACE inhibitors or estrogen-based contraceptives such as the "pill")
- Hormonal: During pregnancy, the levels of estrogen and progesterone rise. The hormonal change causes, among other things, the nasal mucous membrane to be supplied with more blood and swell. However, if there are no other signs of pregnancy, a blocked nose alone does not indicate pregnancy.
- Nasal polyps
- Chronic sinusitis, sore throat, laryngitis
"Vasomotor" runny nose
Cold, alcohol, hot drinks and psychological stress can cause a runny or blocked nose. The reasons for this are largely unknown. Often there are also complaints such as a reduced sense of smell and headaches.
Crooked nasal septum
The nasal septum (nasal septum) divides the nose into a right and a left nasal cavity. It usually runs roughly down the middle of the nose. If it is crooked, a nasal cavity is severely narrowed, which in turn severely impairs nasal breathing. Doctors refer to this curvature as "nasal septal deviation". In most cases it is congenital, rarely it develops later in life due to a broken nasal bone or tumors of the nose.
Other causes
- Injuries to the nasal septum
- Abscesses of the nasal septum
- Choanal polyp (a special form of nasal polyps that almost only occur in children and adolescents; one-sided nasal breathing is typical)
- Tumors of the nasal cavities or sinuses
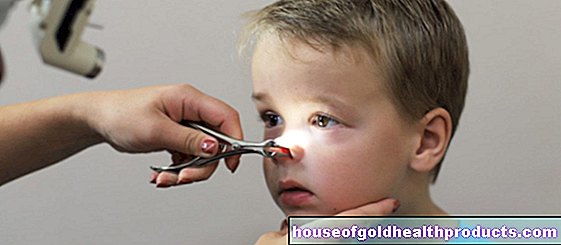
- Foreign bodies in the nose (typical signs are mouth breathing, nasal language, nosebleeds, increased secretion, ear pain, poor hearing, discharge on one side)
- Dry nasal mucous membrane with crust formation (can result from constant inhalation of dry and dusty air, cigarette smoke or sniffing cocaine)
Nasal congestion in infants
Babies breathe exclusively through their nose in the first few months of life. In addition, the nasal passages are still very narrow by nature. Any irritation of the nasal mucous membrane (such as an infection) therefore makes nasal breathing difficult.
If the nasal mucosa is swollen, the infants continue to try to breathe through the nose because they are not yet able to breathe through the mouth. A typical sign is a ragged breathing. In addition, affected newborns and babies often have great difficulty drinking, sleep poorly and often wake up at night.
description
Normally, except when speaking, you breathe through your nose. When the air gets into the nose, it is first heated, moistened and cleaned. This process protects the organism from germs, dust and air that is too cold. If the nose is blocked, those affected get less air and subconsciously breathe through the mouth. This may lead to further health problems in the long term.
A stuffy nose is uncomfortable, but usually harmless. The most common rhinitis virus leads to acutely impaired nasal breathing. The lining of the nose swells and forms a clear or purulent secretion that clogs the nasal cavities. If the nose is chronically blocked, there may be a crooked nasal septum behind it, which makes it difficult to breathe through the nose. Chronic inflammation of the nasopharynx sometimes leads to the turbinates enlarging and the affected person getting less air through the nose.
Those who breathe through their mouth for a long time run the risk of unpleasant consequences. These include:
- Dry mouth
- Bad breath
- Sore throat
- cough
- Sinus infection
- Sore throat
- Laryngitis
- bronchitis
- Tubular catarrh: inflammation and occlusion of the Eustachian tube (connection between the pharynx and the ear)
- Olfactory disorders
- Hearing impairment
- snoring
- Nosebleeds
- headache
What are the turbinates?
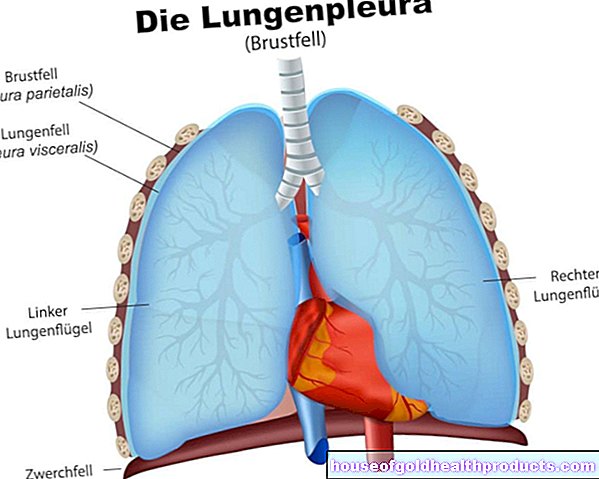
The nostrils form the entrance to the two nasal cavities. There are three turbinates in each nasal cavity. They protrude from the side into the nasal cavity and consist of thin plates of bone that are covered with mucous membrane. Between the mucous membrane and the bones there are densely branched, finest blood vessels (cavernous bodies). If these are supplied with more blood, they swell and enlarge.
The function of the turbinates is to warm and humidify the air. Small hairs (cilia) free the inhaled air from dirt particles and germs.
Nasal cycle
The nasal mucosa is subject to a natural cycle: the nasal mucous membranes of both nasal cavities swell alternately at irregular intervals (one to seven hours) without external stimulus. Doctors suspect that the reciprocal swelling serves to regenerate the nasal mucosa.
In the puffy state, the nose “works” - it warms, filters and cleans the inhaled air. The other, swollen side regenerates. Usually people are unaware of the mutual function. With a cold, on the other hand, the phenomenon becomes clear: If the nasal mucous membrane is already swollen, sometimes one nostril feels more clogged, then the other.
When to the doctor
A stuffy nose is usually harmless and rarely a reason to see a doctor. But see a doctor if the symptoms last longer than ten days, only one nostril is blocked (without a runny nose or cold) or a strange smell comes out of the nose. The same applies if there is pain or swelling in the face or if there is a fever.
What does the doctor?
The first point of contact for a blocked nose is an ear, nose and throat specialist (ENT doctor).
anamnese
In the initial consultation, the doctor asks about the medical history and current complaints in order to get an initial overview of the situation. For example, the doctor asks the following questions:
- How long have you had a stuffy nose?
- Are both nostrils affected or just one nostril affected?
- Do you have other cold symptoms such as runny nose or fever?
- Do you have frequent nosebleeds?
- Does the nose congestion in certain situations (outdoors, after animal contact, at night)?
- Are you pregnant? Are you taking contraceptives that contain estrogen, such as the pill?
- Do you have facial / nose pain?
- Do you hear and smell normally?
- Have you already treated your nasal congestion yourself? If so, with what?
- In the case of children: Have you seen whether the child has stuck a foreign object up their nose?
ENT examination
With the help of a nasoscopy (rhinoscopy) it is possible for the doctor to examine the inside of the nose, the paranasal sinuses and the nasopharynx for changes. This is a special endoscope that the doctor inserts through the nose or mouth. At the front end of the endoscope there is a light source and a small camera that transmits the image to a monitor.
The doctor pays particular attention to the following changes:
- Is the nasal septum deformed?
- Are the turbinates enlarged?
- Are the nasal passages or sinuses narrowed by pus or polyps?
- What does the nasal mucosa look like? Does it produce clear or purulent mucus?
Rhinomanometry
Rhinomanometry is an examination that can be used to measure nasal patency or air resistance when breathing through the nose. The doctor measures the air flow on both sides of the nose, i.e. whether and to what extent the nose is open. The examination is carried out with a special breathing mask, takes only a short time and is painless.
Smell test
The test (olfactometry) is used to objectively assess the olfactory ability. For this, the doctor offers the patient various standardized smells (such as vanilla). The patient then selects the right substance (smell) from four different answers.
Imaging procedures
Doctors use imaging techniques such as ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) to detect structural changes in the nose or paranasal sinuses (such as a crooked nasal septum, polyps or tumors).
Allergy test: Prick and RAST
If an allergic cause for the blocked nose is suspected, the doctor will perform various allergy tests. These include the prick test and the RAST test.
Prevent
It is not always possible to prevent a blocked nose. These tips will help reduce the risk:
- Regular ventilation increases the humidity in the room.
- Drink enough throughout the day, preferably 1.5 to two liters of water or unsweetened tea
- If the heating air is dry: hang up wet towels or use a humidifier
- Prevent respiratory infections, wash your hands regularly with soap
- In the case of allergies: Avoid the trigger of the allergy (pollen, animal hair, house dust mites), treat complaints
- Do not use decongestant nasal sprays or nasal drops for more than ten days!