Epidural anesthesia
All content is checked by medical journalists.The epidural anesthesia (PDA or epidural anesthesia) is a procedure for numbing the spinal cord nerves. Since the spinal cord transmits the nerve signals from the trunk and extremities to the brain, epidural anesthesia can be used to numb various areas of the body over a large area. The patient no longer feels any pain there, but remains awake. Read all about the procedure, when it is done, and the risks involved.

What is a PDA?
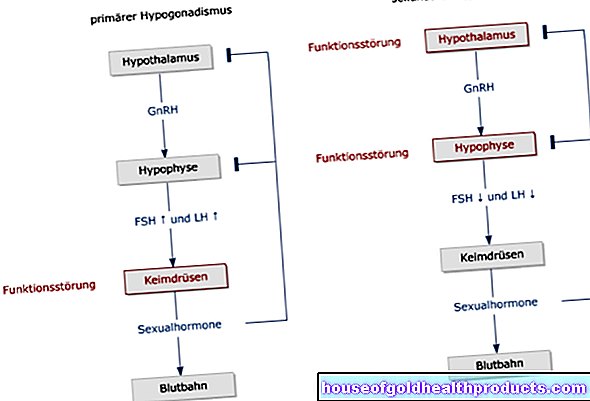
In epidural anesthesia, the signal transmission of the spinal cord nerves is interrupted by injecting a drug. The spinal cord runs along the spine in the vertebral canal and transmits nerve signals between the brain and the body. With a PDA, sensitive nerve signals no longer reach the brain due to pain, temperature or pressure. Movement impulses from the brain to the muscles are also interrupted.
The level at which the spinal cord nerves are blocked is essential for the effectiveness of epidural anesthesia. Because the PDA only affects the areas of the body below. Depending on the location of the epidural anesthesia, either only the legs or the pelvis, abdomen and even the chest are anesthetized.
When do you use epidural anesthesia?
In many operations, epidural anesthesia is a gentle alternative to general anesthesia. They can be used to numb large areas of the body without the patient losing consciousness. It is also used for long-term relief of acute and chronic pain. The procedure also enables childbirth with little pain, which is why many women want a PDA injection for delivery.
Further information: PDA birth
An epidural is often used during childbirth to relieve pain in labor. You can read more about this in the article PDA at birth.
What do you do with epidural anesthesia?
To numb the spinal cord nerves as part of an epidural anesthesia, the doctor sticks a special needle into the disinfected skin above the spine and pushes it between two vertebral bodies. It penetrates various ligaments in the spine until it reaches the so-called epidural space. This area surrounds the so-called spinal cord membranes.
The doctor then pushes a small plastic tube (catheter) into the epidural space via the guide needle and uses it to inject the medication. So they are administered close to the spinal cord and not directly into the spinal cord.
While the needle is withdrawn, the tube remains in the epidural space. This enables the doctor to be able to give the medication for a longer period of time. With the help of syringe pumps, which the patient can control himself if necessary, pain can also be adequately treated after an operation. The application of a PDA is rarely painful, as the doctor first anesthetizes the area of the puncture locally. However, the procedure is still described by many as uncomfortable.
What are the risks of epidural anesthesia?
The epidural anesthesia is a routine procedure in many clinics and is considered a safe anesthetic procedure. Nevertheless, a PDA carries risks, including allergic reactions to the drugs used, the spread of blood clots in the area of the puncture site and infections that can lead to an accumulation of pus or meningitis. The doctor rarely injures the spinal cord during epidural anesthesia. In the worst case, this, like the formation of bruises, would lead to permanent damage with symptoms of partial or complete paraplegia.
Other PDA side effects include temporary urinary retention that needs to be treated with a urinary catheter or a sudden drop in blood pressure. Headaches after PDA installation are mostly caused by accidentally piercing the skin of the spinal cord. Usually these can be treated well with pain relievers.
Accidental injection of the painkillers used into a vein is feared. If the active ingredients are distributed throughout the body via the bloodstream, seizures and severe cardiac arrhythmias can occur.
What do I have to consider after epidural anesthesia?
You are not allowed to drive a car for 24 hours after an epidural anesthesia has been applied. In consultation with your doctor, you will also have to lie quietly in bed for some time. Physical rest lowers the risk of side effects such as nausea, vomiting or shortness of breath, as well as chest, head or back pain. After PDA installation, you should immediately report the occurrence of such symptoms to the nursing staff or the doctor who performed the epidural anesthesia.
Tags: foot care toadstool poison plants alternative medicine
.jpg)