Levofloxacin
All content is checked by medical journalists.The active ingredient levofloxacin is one of the most important remedies for bacterial diseases such as pneumonia, cystitis and conjunctivitis. It is generally considered to be well tolerated, but in rare cases it can lead to gastrointestinal complaints and fungal infections. Patients under the age of 18, pregnant and breastfeeding women should not take drugs containing levofloxacin. Here you can read everything you need to know about levofloxacin.
This is how levofloxacin works
The human immune system protects the body from the implantation and spread of foreign invaders. As soon as a pathogen finds its way into the organism, the immune system reacts immediately and fights it with various mechanisms. As a rule, people do not even notice when the immune system is active, or only mild symptoms arise as a result of the disease.
Sometimes, however, the body's defenses do not immediately manage to fight the pathogen successfully. The symptoms then become more severe. If the body can no longer cope with the pathogens, drugs can support the defensive fight.
These drugs include the antibiotic levofloxacin. It intervenes in the genetic make-up (DNA synthesis) of the bacteria, which kills the germs. The immune system only has to take care of eliminating the bacteria and the symptoms of the disease improve very quickly.
Levofloxacin uptake, breakdown and excretion
After ingestion through the mouth, the active ingredient is almost completely absorbed from the intestine into the blood. After distribution in the body, levofloxacin is excreted largely unchanged via the kidneys.
When is levofloxacin used?
The areas of application (indications) for levofloxacin include:
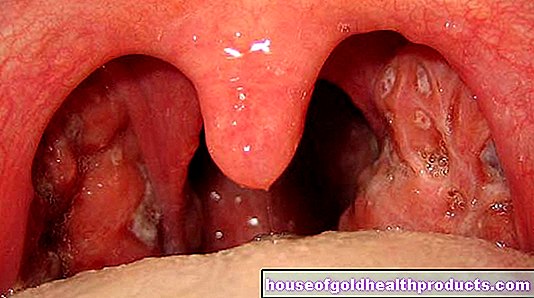
- lung infection
- complicated urinary tract infections (involving the renal pelvis)
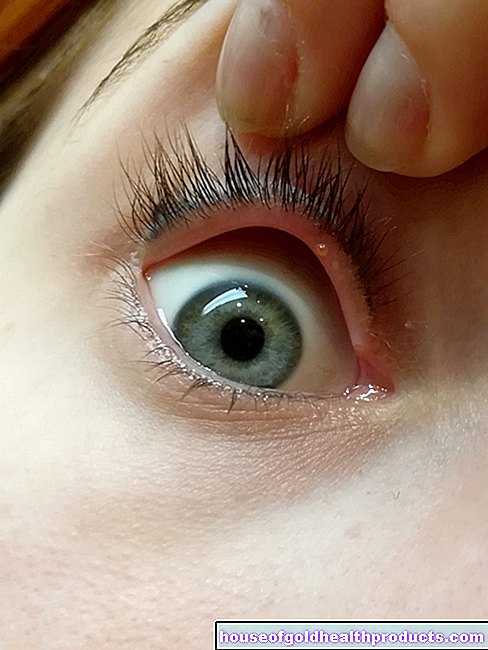
- Conjunctivitis caused by bacteria
This is how levofloxacin is used
The active ingredient levofloxacin is used in the form of tablets or eye drops, and in the case of very severe infections also by infusion (given directly into the blood).
When taken orally (in the form of tablets), the dosage is usually between 250 and 500 milligrams per day. The duration of treatment is between seven and 28 days, depending on the severity of the infection.
Levofloxacin eye drops are instilled into the affected eye four to eight times a day. Here, too, the duration of treatment depends on the severity of the disease.
The amount of active ingredient given directly into the bloodstream (infusion) is usually determined individually.
Patients with impaired renal function receive a reduced dose.
What are the side effects of levofloxacin?
Levofloxacin often causes side effects such as gastrointestinal complaints, i.e. in one to ten percent of those treated.
Occasionally (less than one percent of those treated), fungal infections, weight loss, drowsiness, depression and allergic reactions occur after taking levofloxacin.
Even less often, the intake of levofloxacin leads to changes in the blood count, muscle and joint problems and damage to the tendons (tendopathy).
Few cases are known in which levofloxacin has led to a certain cardiac arrhythmia (QT time prolongation).
If the active ingredient is used in the form of eye drops, usually only local side effects (such as allergic reactions or temporary impairment of vision) occur.
What should be considered when using levofloxacin?
Levofloxacin should only be given in combination with other agents that also affect the heart rhythm after a strict medical benefit-risk assessment. Such agents are, for example, various active substances against cardiac arrhythmias (antiarrhythmics) such as quinidine, procainamide, amiodarone and dronedarone.
Contraindications
Patients with convulsions (epilepsy) or cardiac arrhythmias (arrhythmias), pregnant women, breastfeeding women and children and adolescents under 18 years of age must not be treated with the active ingredient levofloxacin.
Interactions
Simultaneous use with iron supplements or heartburn remedies (with aluminum or magnesium salts) impairs the absorption and thus the effectiveness of the antibiotic.
The effects of the following substances are increased by taking levofloxacin at the same time:
- Warfarin and phenprocoumon (blood thinners)
Driving and using machines
An impairment of the ability to react can occur as a side effect. Therefore, patients should not actively drive or use heavy machinery while taking levofloxacin.
Age restrictions
Medicines containing levofloxacin should not be given to children and adolescents who are growing (younger than 18 years).
pregnancy and breast feeding period
The active ingredient can attack the cartilage tissue, especially when the body is growing. For this reason, the active ingredient should not be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Instead, better proven alternatives for treating bacterial diseases are available with penicillin, cephalosporins (such as cefalexin) and macrolides (e.g. erythromycin).
How to get levofloxacin medication
Medicines containing levofloxacin require a prescription and are therefore only available from a pharmacy with a prescription from a doctor.
How long has levofloxacin been known?
Levofloxacin is a relatively new active ingredient. It was developed from another drug for bacterial diseases by slightly changing its chemical structure. As a "fluoroquinolone" of the second generation, levofloxacin is better tolerated and with comparable effectiveness.
More interesting facts about levofloxacin
Medications containing levofloxacin increase the risk of getting sunburn. This is why the following applies particularly during the treatment: apply high levels of sun protection and avoid sunbathing!
Tags: skin care Baby Child palliative medicine





.jpg)