Lyme disease therapy
and Martina Feichter, medical editor and biologistFabian Dupont is a freelance writer in the medical department. The human medicine specialist is already doing scientific work in Belgium, Spain, Rwanda, the USA, Great Britain, South Africa, New Zealand and Switzerland, among others. The focus of his doctoral thesis was tropical neurology, but his special interest is international public health and the comprehensible communication of medical facts.
More about the expertsMartina Feichter studied biology with an elective subject pharmacy in Innsbruck and also immersed herself in the world of medicinal plants. From there it was not far to other medical topics that still captivate her to this day. She trained as a journalist at the Axel Springer Academy in Hamburg and has been working for since 2007 - first as an editor and since 2012 as a freelance writer.
More about the experts All content is checked by medical journalists.
Borreliosis therapy includes the administration of antibiotics for several weeks. When selecting the active ingredients and the dosage, the doctor takes into account, among other things, the stage of the disease and the age of the patient. Read everything you need to know about Lyme disease treatment here!
ICD codes for this disease: ICD codes are internationally recognized codes for medical diagnoses. They can be found, for example, in doctor's letters or on certificates of incapacity for work. M01G01A68
Lyme disease therapy: the earlier, the better!
Borreliosis therapy consists of the administration of antibiotics. The following applies: the earlier treatment is initiated, the faster the Lyme disease symptoms regress. At the same time, the complication rate decreases with early and correct treatment. Lyme disease is a serious disease that, if left untreated, can cause complications and consequential damage.
Which antibiotics the doctor prescribes for how long in individual cases depends, among other things, on the symptoms of Lyme disease (early or late manifestations), the age of the patient and a possible pregnancy or breastfeeding period.
Borreliosis treatment for early onset
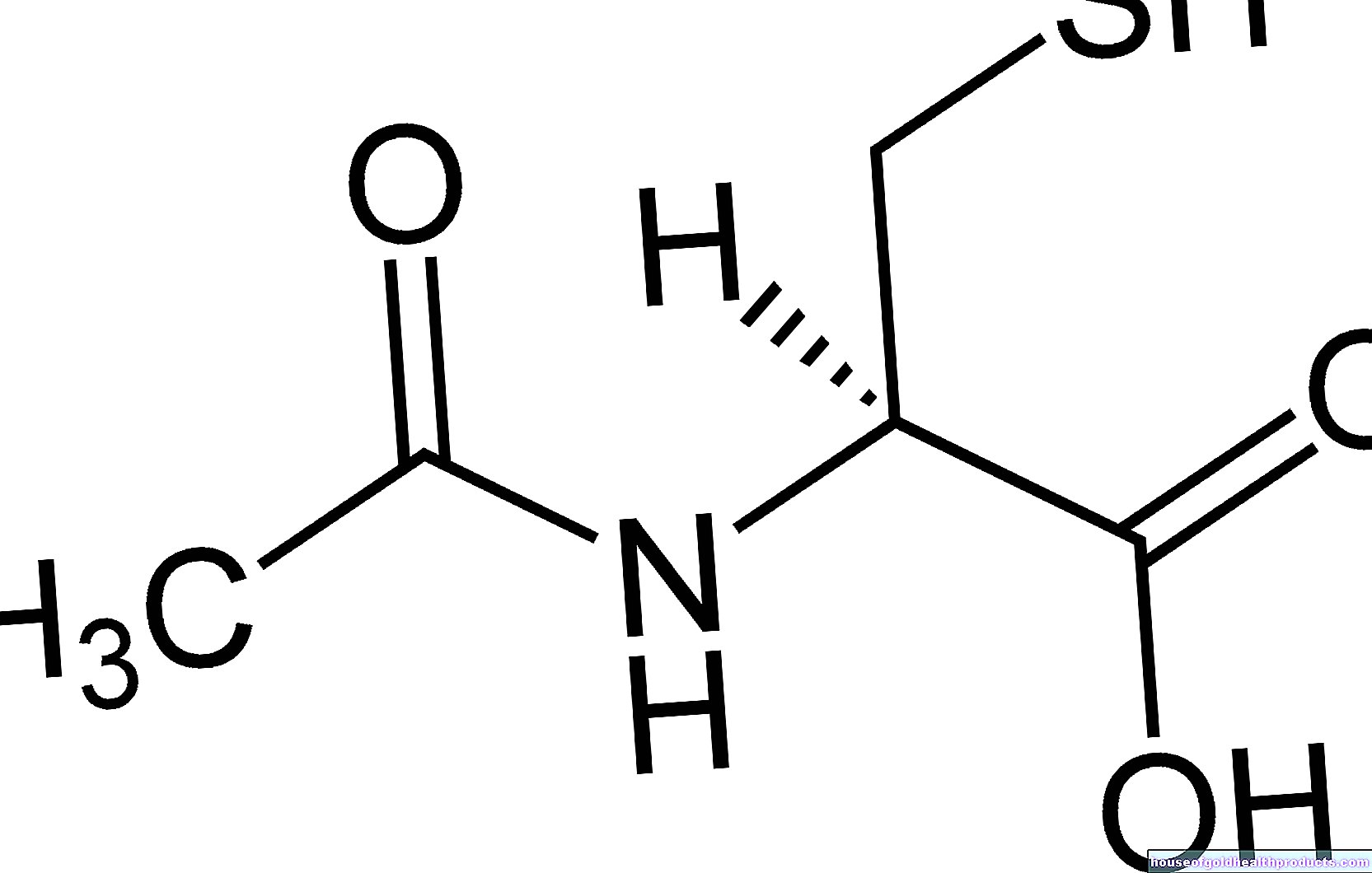
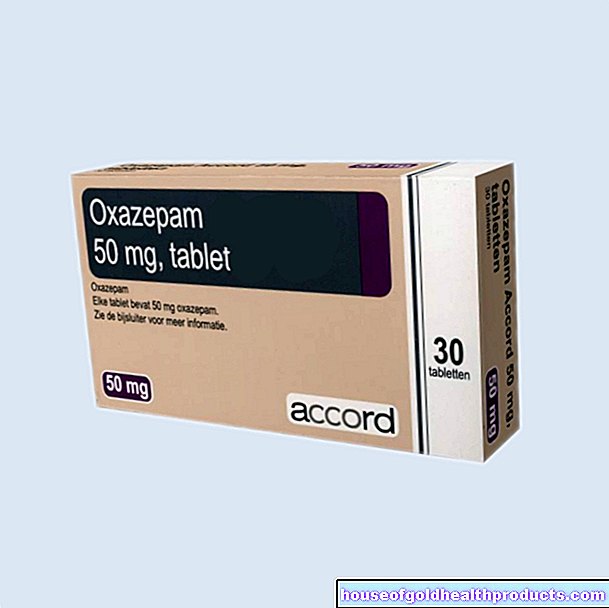
In the case of early manifestations such as the typical "wandering redness", doctors usually use doxycycline or amoxicillin for the treatment of Lyme disease. These antibiotics are taken in the form of tablets or juice (often several times) a day. The doctor usually prescribes the medication for 10 to 21 days (the exact duration of therapy depends on the duration and severity of the symptoms and the antibiotic).
Doxycycline is effective and usually well tolerated. However, pregnant women should not take this antibiotic. You will be given amoxicillin instead. Amoxicillin is also preferred to doxycycline for early Lyme disease treatment in nursing mothers.
Children from the age of 9 can be treated with doxycycline like adults. Younger children, on the other hand, are usually given amoxicillin (sometimes other antibiotics as well). The reason: Doxycycline can cause tooth discoloration and damage to tooth enamel, among other things. Therefore, it should only be given after the enamel has formed.
Possible alternatives to doxycycline and amoxicillin (for example in the case of allergies) are the antibiotics cefuroxime and azithromycin.
Treatment of early neuroborreliosis
For the treatment of early neuroborreliosis, doctors often prescribe the use of doxycycline for 14 days.
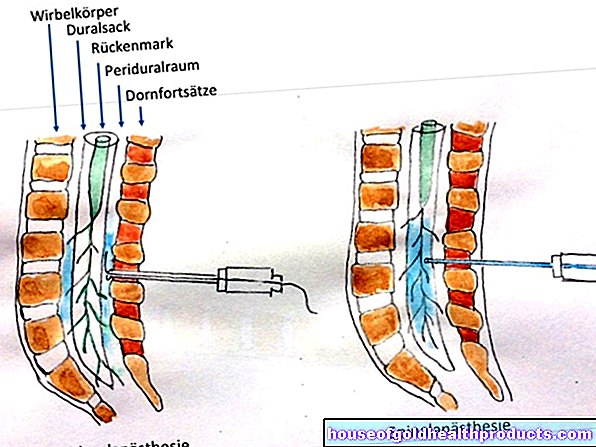
The antibiotics ceftriaxone, cefotaxime and penicillin G are available as alternatives. It is administered as an infusion directly into a vein (intravenous). This guarantees the highest possible level of active substances in the blood. As with doxycycline, the specialist societies recommend a therapy duration of 14 days.
Lyme disease treatment for late onset
Late manifestations of Lyme disease usually affect the joints (Lyme arthritis). Borreliosis treatment usually consists of taking doxycycline or - if doxycycline is not allowed to be given (e.g. for pregnant women or children under eight years of age) - taking amoxicillin for 30 days.
The same applies to Lyme disease treatment for chronic skin inflammation (acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans): If the nervous system is not involved, the doctor will prescribe doxycycline or amoxicillin for 30 days.
If neurological symptoms accompany the chronic skin inflammation, patients usually receive infusions with penicillin G, ceftriaxone or cefotaxime. The duration of this intravenous Lyme disease therapy is 14 to 21 days, i.e. two to three weeks.
Treatment of late neuroborreliosis
Even without simultaneous skin inflammation, doctors treat late neurological manifestations of borreliosis (late neuroborreliosis) either with doxycycline tablets or infusions with penicillin G, ceftriaxone or cefotaxime. The application is also carried out here for 14 to 21 days.
Extend or repeat antibiotic therapy?
Some Lyme disease activists (including individual doctors) recommend using antibiotics for longer than the guidelines recommended on the basis of various studies in the event of (persistent) Lyme disease symptoms (such as chronic skin inflammation or neuroborreliosis). Some neuroborreliosis patients take antibiotics for months or even years.
Such long-term treatment with antibiotics for Lyme disease can have serious side effects. In addition, there is no evidence that it is more effective than the recommended antibiotic therapy for two weeks (early neuroborreliosis) or two to three weeks (late neuroborreliosis).
If Lyme disease symptoms persist in the skin area and doctors detect Borrelia there, they will prescribe antibiotics again.
If, on the other hand, symptoms such as numbness or paralysis still persist in neuroborreliosis six months after the recommended antibiotic treatment, doctors repeat the antibiotic Lyme disease therapy - provided that a new examination of the nerve fluid (liquor) still shows an increased number white blood cells are detected.
The medical societies do not recommend months of antibiotic therapy, multiple repetitions or combinations of several active ingredients!
Further measures of Lyme disease therapy
The antibiotic borreliosis treatment for chronic joint inflammation (Lyme arthritis) can be supplemented by doctors with painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs if necessary. So-called NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) such as diclofenac or ibuprofen are used.
If necessary, the doctor can also prescribe pain relievers for neuroborreliosis. In addition, depending on the type and severity of the neurological symptoms, further therapeutic measures can be useful. These include, for example, physiotherapy, physical therapy, occupational therapy, logotherapy and psychosocial measures.
Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction
Before antibiotic therapy, doctors explain what is known as the Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction or similar side effects. This reaction rarely occurs when treating a disseminated Lyme disease infection. Shortly (usually a few hours) after the start of the Lyme disease therapy, many bacterial toxins (endotoxins) are released because the pathogens disintegrate.
Those affected suffer from a strong feeling of illness with fever, headache and muscle pain, racing heart and nausea. Typical rashes can also increase again. This condition usually disappears after a few hours. As a support, doctors often prescribe NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as diclofenac or ibuprofen), and occasionally cortisone.
It is usually not necessary to stop taking the antibiotic!
Homeopathy in Lyme Disease Therapy
Some people also rely on homeopathic treatment to relieve the symptoms of Lyme disease. Homeopathy is not suitable as an alternative to antibiotic therapy for Lyme disease, but can only be used as a supplement.
The concept of homeopathy and its specific effectiveness have not yet been scientifically proven.
Keyword: Lyme disease vaccination
The best protection against Lyme disease would certainly be a vaccination. However, there are, among other things, several sub-forms of the pathogen. This makes vaccine development difficult. It has therefore not yet been possible in Europe to develop a safe and effective vaccination against Lyme disease, although research is still being conducted into it.
In the USA, however, there was already a vaccine against Lyme disease. For commercial reasons, however, the manufacturer withdrew the product from the market after a few years.
As long as there is no effective vaccination against Lyme disease available, in addition to protective measures (e.g. long clothing, professional tick removal), Lyme disease therapy remains the most effective measure against Lyme disease and its sometimes serious long-term consequences.
Tags: interview alternative medicine toadstool poison plants