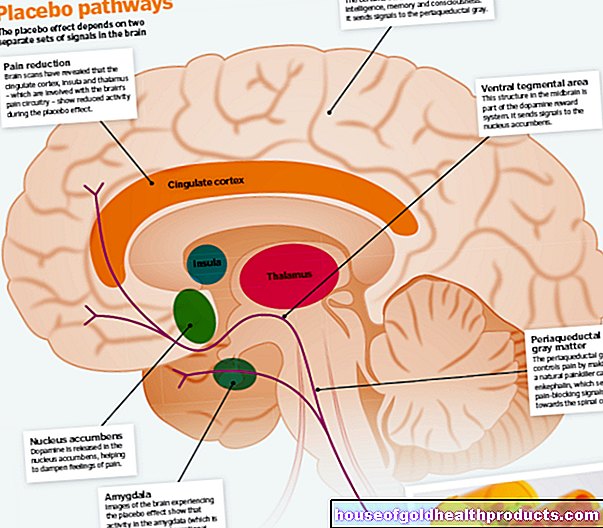
Colposcopy
Valeria Dahm is a freelance writer in the medical department. She studied medicine at the Technical University of Munich. It is particularly important to her to give the curious reader an insight into the exciting subject area of medicine and at the same time to maintain the content.
More about the experts All content is checked by medical journalists.With colposcopy, the vagina and the cervix (cervix uteri) are examined with the help of a special microscope, the colposcope. The colposcopy is carried out as part of the gynecological check-up and is primarily used for the early diagnosis of cervical cancer and its preliminary stages. Read all there is to know about colposcopy, how it is performed, and what the risks are.
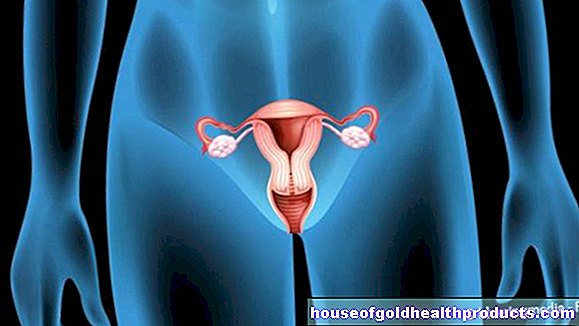
What is a colposcopy?
Colposcopy is a pelvic examination. The doctor looks at the vagina and cervix with the colposcope like a magnifying glass. Due to the six to 40 times magnification, changes can be seen under lighting that are difficult to assess with the naked eye. If the doctor dabs the cervix with special solutions, he can draw conclusions about cancer or precancerous stages by staining certain cells. Colposcopy is an important tool in the early detection of cervical cancer.
When do you do a colposcopy?
Colposcopy is performed as part of the gynecological check-up and is also used to diagnose diseases or abnormalities in the cervix and vagina:
- Suspected cancer
- Suspected precancerous lesions
- suspicious cytological smears, e.g. PAP smears
- Cancer follow-up
- proven infections
- Changes in the cervix
- Bleeding of no known origin
- persistent discharge from the vagina
- Inflammation
If tumors are suspected, a tissue sample can be taken during a colposcopy as part of a biopsy.
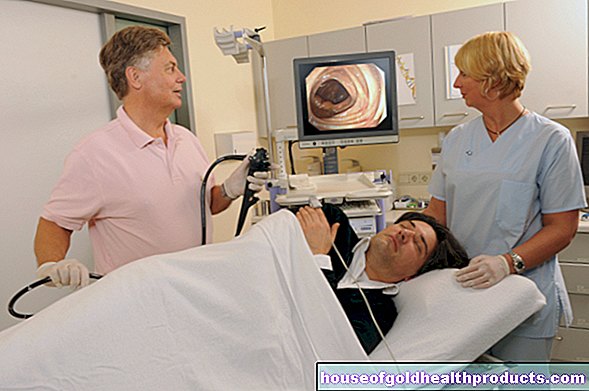
What do you do with a colposcopy?
Colposcopy is an outpatient procedure and the patient can go home after the examination. One day before the colposcopy, tampons and sexual intercourse should be avoided, and the examination date should not coincide with the menstrual period.
The doctor first takes the anamnesis and asks about the symptoms. For the colposcopy, the patient sits in a gynecological chair. First the doctor expands the vagina with an examination instrument, positions the colposcope in front of it - it is not inserted - and focuses it. When inspecting the mucous membrane of the cervix, the doctor pays special attention to surface irregularities and anomalies of the vessels.
During colonoscopy, injuries or changes can be made visible with the help of special solutions.
Acetic acid sample
The doctor dabs the mucous membrane with a three to five percent acetic acid solution, which can cause a slight burning sensation. Healthy tissue does not change, while changed cells turn whitish. This finding is also called "white vinegar". If white areas are visible even before the acetic acid is applied, it is called leukoplakia. This can also indicate cancer cells.
Schiller’s iodine sample
Then an iodine solution is dabbed on for the extended colposcopy. Healthy mucous membrane turns brown, so it is iodine-positive. Altered mucous membrane does not or only slightly discolored.
Finally, the vagina and external genitalia are examined. If there are any abnormalities, the doctor takes a tissue sample with small forceps for a tissue examination in a laboratory. Since the uterus is almost insensitive to pain, it is usually removed without anesthesia.
What are the risks of a colposcopy?
Colposcopy is a safe and uncomplicated examination. The acetic acid may cause a slight stinging sensation. In rare cases, the removal of the tissue sample may cause bleeding. Infections are very rare. If you suffer from iodine intolerance or an overactive thyroid, you must inform your doctor of this before the colposcopy. Colposcopy does not pose a risk to the child during pregnancy.
What do I have to consider after a colposcopy?
After the colposcopy, there may be light bleeding or brownish discharge. But this is completely normal. For the first few days after the colposcopy, you should avoid full baths, swimming, tampons and sexual intercourse. If you experience sudden pain or abnormally heavy bleeding, please contact your doctor immediately.
Tags: medicinal herbal home remedies prevention desire to have children






.jpg)


-der-giraffentrick.jpg)