Erysipelas therapy
Fabian Dupont is a freelance writer in the medical department. The human medicine specialist is already doing scientific work in Belgium, Spain, Rwanda, the USA, Great Britain, South Africa, New Zealand and Switzerland, among others. The focus of his doctoral thesis was tropical neurology, but his special interest is international public health and the comprehensible communication of medical facts.
More about the experts All content is checked by medical journalists.Erysipelas therapy should always be started as soon as possible after the diagnosis by the attending physician. The drug of choice in erysipelas therapy is the consistent administration of an antibiotic. In some cases, the erysipelas go away on their own, but there are also serious complications such as blood poisoning, heart or kidney infections. You can find out more about erysipelas treatment here.
ICD codes for this disease: ICD codes are internationally recognized codes for medical diagnoses. They can be found, for example, in doctor's letters or on certificates of incapacity for work. A26A46

The standard in erysipelas therapy
Depending on the expert opinion, the erysipelas therapies differ slightly. However, some basic approaches have prevailed:
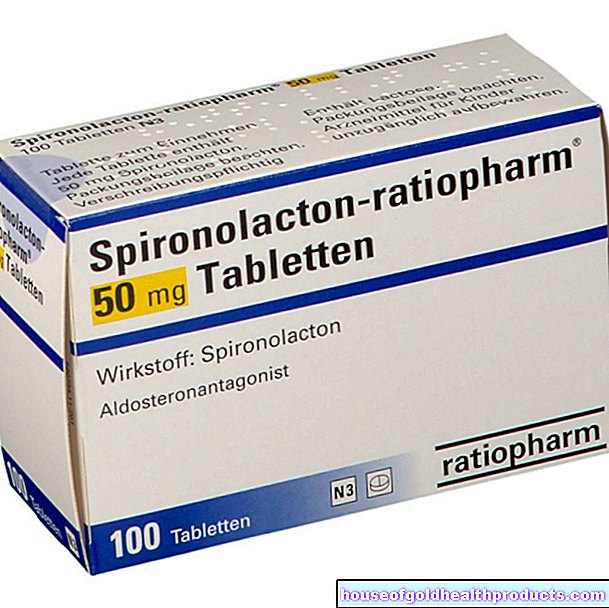
The standard erysipelas therapy consists of 10 to 14 days of antibiotics. Since erysipelas are usually caused by streptococci (group A, C, G), the antibiotic penicillin is particularly suitable for erysipelas therapy. Symptoms improve after just a few days. Some patients are allergic to penicillin, in which case other antibiotics such as erythromycin or clindamycin are used.
If the patient is feeling bad, the rose treatment is also started by infusion. As soon as improvement occurs, antibiotic therapy with tablets can be stopped and the patient can usually leave the hospital.
What also needs to be considered:
In addition to antibiotic therapy, erysipelas therapy consists of other measures that support the body in fighting the infection.
- Bed rest and elevation of the affected extremity: In this way, the lymphatic drainage is improved and the sore rose can swell faster.
- Pain is also treated with painkillers. Often these are drugs that counteract inflammation and swelling at the same time.
- Blood thinning (anticoagulation) can be important depending on the location and size of the erysipelas. The risk of a blood clot increases with prolonged immobilization and inflammatory reactions. For this reason, depending on the severity, a thrombosis injection is advisable.
- Compression therapy should be carried out as soon as the swelling of the rose has subsided somewhat. With the help of support stockings or a compression bandage, it is prevented that fluid is stored in the tissue again.
- Fighting the causes: During the examination of the erysipelas, particular attention must be paid to the entry point for the bacteria. If an injury is visible, the doctor should ensure that it heals quickly. In the case of a skin fungus or other skin disease, appropriate therapy can even prevent renewed erysipelas.
Alternative healing methods
Many people prefer homeopathic therapeutic approaches for a wound rose. However, erysipelas is a serious infectious disease that must be treated accordingly. Since life-threatening infections can occur, antibiotics should not be delayed unnecessarily. In addition, homeopathic ointments can help and support the healing process. However, the wound rose is not suitable for self-diagnosis or self-therapy. A visit to the doctor is essential, especially to prevent complications and to select an individually suitable erysipelas therapy.
Recurring sore roses (recurrences)
Some people often suffer from wound roses and therefore often have to be treated several times. New studies have shown that in such cases long-term antibiotics can reduce the recurrence rate (recurrence rate). There are various dosage forms for this special form of erysipelas therapy, either as a tablet or as an injection every few months. With these regular antibiotics, a bacterial infection can be combated at an early stage, before the infection occurs. In this way, people can also be treated who repeatedly develop rose golds.
Tags: stress parasites elderly care