Roundworms
Martina Feichter studied biology with an elective subject pharmacy in Innsbruck and also immersed herself in the world of medicinal plants. From there it was not far to other medical topics that still captivate her to this day. She trained as a journalist at the Axel Springer Academy in Hamburg and has been working for since 2007 - first as an editor and since 2012 as a freelance writer.
More about the experts All content is checked by medical journalists.
Nematodes or roundworms in humans are among the most common infectious agents worldwide. They include parasites such as roundworms, pinworms and whipworms. The infection usually occurs through the consumption of raw or insufficiently cooked food that is contaminated with the eggs or larvae of roundworms. Read more about the possible complaints caused by roundworms, drugs against the parasites and the chances of recovery from an infestation!

Roundworms: description
Roundworms (nematodes) are the parasites that most commonly affect humans. They are mainly found in tropical developing countries. However, some representatives also live in Europe - that is why one can contract such a worm disease in this country too.
What are nematodes
Nematodes are elongated, thread-like worms that can reach a length of a few millimeters to one meter - and thus look similar to threads of different lengths. They meander forward.
Adult roundworms mostly live in the human intestinal lumen, where they mate and lay eggs. The larvae that hatch from the eggs also remain in the intestines in some nematode species, while in others they migrate through the body.
The development cycle of the animals proceeds from the egg through several larval stages up to adult male and female worms. Well-known parasitic representatives of roundworms are roundworms, pinworms, whipworms, trichinella, hookworms and filariae.
Roundworms
Roundworm infection is the most common worm disease in humans. You can read about how an infestation with these roundworms can be noticed and treated in the article roundworms.
Pinworms
An infection with the pinwormOxyuris vermicularis (Enterobius vermicularis) is known as oxyuriasis (enterobiasis) and mainly affects children - including in Germany. You can read more about these roundworms in the article pinworms.
Whipworms
Whipworms belong to the species Trichuris trichiura. Tropical and subtropical areas are the main distribution area of these roundworms, which are about four centimeters long. Humans and animals (monkeys, pigs, etc.) are possible host organisms, but humans are the main hosts. Children in particular are infected with whipworms.
Trichinella
Different representatives of the genus Trichinella can lead to an infection (trichinellosis) in humans. The larvae of this type of roundworm that you get infected with are called trichinae.
Trichinella use mammals, birds and as hosts. In addition to the infestation of dogs, cats and horses, especially domestic pigs and wild pigs infected with roundworms, which can be infected by consumption, are of importance to humans.
Trichinellosis occurs worldwide, but has become rare in Germany due to the legally required meat inspection.
Hookworms
Hookworms that infest humans are Ancylostoma duodenale and Necator americanus. These blood-sucking roundworms, about one centimeter long, are widespread around the world, especially in warm regions with poor hygienic conditions. They owe their name to their hook-shaped curved front end.
Filaria
These tropical roundworms are transmitted by insects and cause different forms of filariasis depending on the species. You can find out more about this in the article Filariasis.
Roundworms: symptoms
Not every nematode infestation triggers complaints. This depends, among other things, on the number of parasites ingested. The type of symptoms depends on which roundworms are responsible for the infection and where the animals are in the human body.
Roundworm infestation: symptoms
The migration of roundworms through the human body can trigger a variety of complaints. If the animals stay in the intestines, it can cause stomach pain and nausea. Lung involvement, on the other hand, is more likely to trigger allergic reactions such as coughing and mild fever.
The roundworms rarely migrate into the bile ducts and obstruct the bile duct and pancreatic duct. Possible consequences include biliary blockage (cholestasis) and inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis). Other possible complications of infection with these roundworms include:
- Intestinal obstruction (ileus): Roundworms can form "balls" in the intestine
- Appendicitis
- cramps
- shock
Pinworm Infestation: Symptoms
An infection with these roundworms causes nocturnal itching of the anus (anus) because the females lay their eggs in this region. In addition, appendicitis can develop.
Whipworm Infestation: Symptoms
These roundworms partially penetrate the intestinal lining, which can lead to bleeding and anemia. If the worm infestation is very severe, possible symptoms are: abdominal pain, indigestion, inflammation of the colon (colitis) and diarrhea. In addition, the roundworms restrict the absorption of nutrients in the intestine, which in turn can trigger an undersupply and a slowdown in growth (in children).
Trichinae infestation: symptoms
Experts estimate that symptoms do not appear until 100 to 300 Trichinella are consumed. The stage that the parasites are currently going through is also decisive for the symptoms. The type of trichinella and the strength of the human immune system also play a role and influence the severity of the disease.
A few days after infection, diarrhea and abdominal pain are possible if the intestinal trichinae is more severe. The patients get a high fever (around 40 degrees Celsius), chills, pronounced muscle pain and swelling (edema) around the eyes.
Other possible symptoms are rash, bleeding under the nails, conjunctivitis, headache, insomnia, swallowing disorders, dry cough, punctiform bleeding from the skin and mucous membranes (petechiae) as well as painful movement disorders of the eye muscles and even chronic rheumatic complaints.
Some people affected by these roundworms develop dangerous and sometimes even life-threatening complications. This includes:
- Inflammation of the heart muscle (myocarditis), irregular heartbeat
- Inflammation of the brain (encephalitis)
- lung infection
- "Blood poisoning" (sepsis)
- Circulatory failure
- Underactive adrenal glands (adrenal insufficiency)
- psychotic states
- Coma and seizures
Hookworm Infestation: Symptoms
Itching and reddening of the skin develop where the larvae of these roundworms have invaded the skin. The larvae migrate to the lungs via the blood or lymphatic system, where they cause shortness of breath, coughing and pneumonia, for example.
The larvae enter the larynx by coughing up and are swallowed. In the small intestine, the parasites develop into sexually mature nematodes that can survive here for years. They cause symptoms such as upper abdominal pain, bloating, flatulence, constipation or diarrhea.
Serious infection with these blood-sucking nematodes can lead to life-threatening iron deficiency anemia (anemia due to iron deficiency) and hypoproteinemia (protein deficiency in the blood). In children, this greatly delays growth and development.
Filarial infestation: symptoms
Which symptoms these roundworms trigger depends on the type of parasite and the disease it causes (such as loa-loa filariasis, onchocerciasis, etc.). Possible are, for example, swelling and inflammation of the lymph vessels and nodes, attacks of fever, massive swelling of the legs, genitals or other parts of the body (elephantiasis), itching, skin lumps or eye disorders.
Roundworms: causes and risk factors
Roundworms find their way into the human body in different ways:
Food contaminated with roundworm eggs
Roundworms often get into the human organism through food that has been contaminated with the eggs of the parasites. Trichinella can be infected by eating raw or undercooked meat (especially pork) - these roundworms like to infect domestic pigs.
Salad and raw vegetables can also become sources of infection if they come into contact with contaminated faeces (for example from manure from faeces) - sick people and animals excrete the eggs of roundworms with their stool.
Contaminated items
Pinworms are also infected in other ways:
The females living in the human intestinal lumen lay their eggs at the anus. This itches and causes patients to scratch themselves there. This is how the eggs of the pinworms get on the fingers and under the nails. In the case of poor hygiene, they can be transferred not only to food but also to objects (such as doorknobs) and from there they can be ingested by other people.
Other ways of infection
For some types of roundworms, other ways of infection can also be considered: They can penetrate the human body in larval form through the skin (like hookworms), ingested by fleas living in water, or transmitted by insects (like filariae).
Roundworms: examinations and diagnosis
Anyone who discovers worms or worm parts in the stool and / or has been suffering from unspecific abdominal pain for a long time should see a family doctor or pediatrician. The same applies if a previously unknown anus itch occurs repeatedly. Roundworms could be the cause of such complaints. In order to clarify this, the doctor will first have the patient's complaints described in detail and ask questions such as:
- When does the anus itch occur?
- Have you been traveling recently?
- Has anyone in your community recently suffered from a worm infestation?
Stool sample shows nematode infestation
In order to detect roundworms such as roundworms, pinworms, whipworms or hookworms, a stool sample from the patient is examined for eggs and larvae of the parasites. If the infestation is severe, living worms can sometimes be seen in the faeces with the naked eye.
Lung X-ray for roundworms
When the larvae of roundworms are currently wandering through the lungs, this can sometimes be recognized by cloud-like "shadows" (light spots) on an X-ray of the chest.
Adhesive tape method for pinworms
If pinworms are suspected, the adhesive tape method is often used for clarification: A piece of transparent adhesive tape is stuck to the skin of the anal region, then peeled off and examined under the microscope to see whether worm eggs can be seen. For a reliable diagnosis, it is best to prepare such a preparation on three consecutive days, because these roundworms do not lay eggs every day.
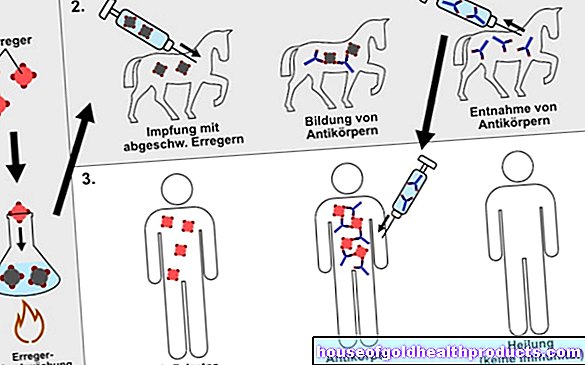
Antibody test and muscle biopsy in trichinellosis
An infection with roundworms that cause trichinellosis is diagnosed primarily by the detection of specific antibodies in the blood. The examination is usually possible at an early stage. Sometimes the antibodies can only be detected in the 3rd or 4th week of the disease.
Sometimes a sample of muscle tissue (from the biceps, pectoral, or deltoid muscles) is taken and examined for the parasites in trichinella. This is because the larvae of these roundworms migrate into the skeletal muscles (especially into muscles with good blood circulation), where they destroy muscle fibers.
Laboratory values
With a roundworm infection (or other parasitic infection) the number of certain immune cells in the blood (eosinophils) is increased. The increase in this subset of white blood cells is known as eosinophilia.
Other blood changes often occur, such as an increase in creatine kinase in trichinellosis. In the case of this roundworm infection, a urine sample is also examined for changes, for example increased excretion of protein (proteinuria) as a result of kidney involvement.
Roundworms: treatment
The doctor prescribes special anti-helmintics for roundworms. They contain different active ingredients. For example, pyrantel can paralyze the roundworms, whereupon they are excreted in the stool. Other drugs such as mebendazole, however, kill the parasites, whereupon they are also excreted in the feces. In the event of a pinworm infection, close relatives should also be treated to be on the safe side.
When used for a short period of time, wormer products are usually well tolerated. The longer they are taken, the more likely it is to experience side effects such as abdominal pain, nausea and diarrhea.
In addition to the anti-helmintics, the patients may also be given other medication. In the case of trichinella, for example, it may be necessary to administer antipyretic agents (antipyretics), pain relievers (analgesics) and anti-inflammatory corticosteroids.
In the case of a roundworm infection, careful hygiene must also be observed, for example frequent hand washing. In the case of pinworms, further measures are recommended, such as wearing tight underpants (to prevent scratching at night), shortening the fingernails, as well as boiling underclothes and bedclothes, towels, washcloths, etc. This is to prevent the spread of the roundworms.
Roundworms: disease course and prognosis
A roundworm infestation has a good prognosis: The infection can generally be treated with medication without any problems.
Preventing roundworms
In order to avoid infection with roundworms or other parasitic worms, one should pay attention to hygiene and wash one's hands frequently - especially before eating, after using the toilet, after contact with pets and gardening. Children should be admonished not to scratch their buttocks (nematodes of the Oxyuris type = pinworms!).
Pinworms in particular can be transmitted by pets such as dogs and cats, so have them regularly dewormed by the vet.
Carefully clean plant-based foods before consuming them, especially if they are consumed raw (salad, vegetables, fruit). Meat should always be heated well (from 70 degrees Celsius, about trichinae die). Freezing (at minus 25 degrees Celsius) also kills the Trichinella larvae.
When traveling (especially in regions with poor hygienic conditions), the following advice applies when eating: “Cook it, peel it or forget it!”. Especially in tropical areas you should avoid walking barefoot and other direct skin contact with the ground.
With these tips you can often prevent roundworms from entering the body!
Tags: toadstool poison plants prevention Baby Child