gonorrhea
Dr. med. Fabian Sinowatz is a freelancer in the medical editorial team.
More about the experts All content is checked by medical journalists.Tripper (also called gonorrhea) is a sexually transmitted disease that is caused by an infection with bacteria (gonococci). An inflammation of the genital and urinary organs with purulent discharge from the urethra is typical for gonorrhea. But other parts of the body can also be affected by gonorrhea. Using condoms can drastically reduce the chances of contracting gonorrhea. Read everything you need to know about gonorrhea here.
ICD codes for this disease: ICD codes are internationally recognized codes for medical diagnoses. They can be found, for example, in doctor's letters or on certificates of incapacity for work. A54
Tripper: description
Tripper (gonorrhea) is a sexually transmitted disease (English: sexually transmitted disease, short: STD). Tripper is caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae (gonococci), which was discovered in 1879 by the dermatologist Albert Neisser.
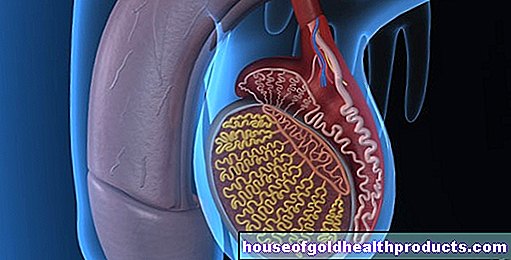
Tripper causes inflammation of the genital organs and the urinary tract. A purulent discharge from the urethra is typical of gonorrhea in men. In women, the symptoms are usually much weaker, so gonorrhea often goes undetected in women. If left untreated, the gonococci can also spread throughout the body. The gonococci are spread through unprotected sex with an infected person.
Infection of the child during birth by the mother is also possible. This form of gonorrhea used to be the most common cause of blindness in children in the western world ("neonatal blennorrhea"). To prevent this, a one percent silver nitrate solution was dripped into the eyes of the newborns (Credé prophylaxis). Today antibiotic eye drops or ointments can be used for this purpose.
Occurrence and frequency of gonorrhea
Tripper is common all over the world. Only people get this sexually transmitted disease (STD). According to estimates by the World Health Organization (WHO), gonorrhea is the third most common sexually transmitted disease (STD) with around 106 million new cases per year.
The number of gonorrhea has been falling for a number of years. Since the mid-1990s, an increase in the incidence of gonorrhea has also been observed in Germany. Young adults in particular are affected by gonorrhea, and men and women alike can become ill. The average age is around 30 years. Until 2000, gonorrhea was a reportable disease. However, most of the gonorrhea were not reported, so the reporting requirement in Germany has been withdrawn. For this reason, there is hardly any current, reliable data on the frequency of gonorrhea in Germany.
Some strains of gonococci are resistant to antibiotics
According to estimates by the World Health Organization (WHO), gonorrhea could pose great problems for mankind in the coming years. The reason for concern is the observation that some gonococcal strains have become resistant to the usual antibiotic therapy for gonorrhea. (Antibiotic resistance). Tripper (gonorrhea) is already treated with a combination of two antibiotics, as one preparation alone is no longer sufficient. More and more completely resistant gonococcal strains are found worldwide, especially in Asia.
Gonorrhea: symptoms
You can read everything you need to know about the typical signs of gonorrhea in the article gonorrhea symptoms.
Tripper: causes and risk factors
The cause of gonorrhea (gonorrhea) is an infection with the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae (gonococci). Tripper is primarily transmitted through unprotected sex with an infected person. Body fluids containing bacteria must come into direct contact with the mucous membrane (e.g. urethra, cervix, rectum, throat, conjunctiva). Outside the human body, gonococci perish very quickly, which is why transmission takes place almost exclusively through unprotected vaginal, oral and anal intercourse. The bacteria first multiply locally at the infection site and trigger inflammation there. This can spread further if left untreated.
Pregnant women who have gonorrhea can also infect their baby during birth. This can mainly cause a serious infection of the eyes ("neonatal blennorrhea"). Infection can be prevented by preventive (prophylactic) treatment with antibiotic eye drops or ointments.
Especially in women, the symptoms of gonorrhea (gonorrhea) are often very mild and difficult to recognize. This allows the disease to spread easily. People who offer or use sexual services, as well as people with frequently changing sexual partners, are particularly at risk from gonorrhea. The use of condoms can drastically reduce the likelihood of infection with gonorrhea.
Tripper: examinations and diagnosis
A specialist in skin and venereal diseases is the right person to contact if you suspect gonorrhea (gonorrhea). These doctors are also known as "venereologists". Venereology is the study of sexually transmitted diseases. Your family doctor or your gynecologist can also be your first point of contact if you suspect gonorrhea.
Doctors are bound by confidentiality: So don't be afraid to see a doctor if you have symptoms that could be related to gonorrhea. If there is a purulent discharge from the urethra or vagina, an examination is always useful. All partners of infected people or people with unclear inflammatory abdominal complaints should also undergo gonorrhea control.It is also important for men under 40 with inflammation of the testicles or epididymis to get checked for gonococcal infection.
For the diagnosis of gonorrhea, the pathogens (gonococci) must be detected. The gonococci can be detected microscopically in a smear taken from the urethra, uterus, throat, anus or conjunctiva. In order to confirm the diagnosis of gonorrhea, cultural evidence must also be provided. This means that gonococci can multiply from a smear on a suitable nutrient medium and can then be reliably detected.
For effective gonorrhea therapy, different antibiotics are also tested for their effectiveness in the bacterial culture (antibiogram). This shows which antibiotics the gonococci are particularly sensitive to and which active ingredients are ineffective. In the past few years, bacteria that were resistant to the usual antibiotics could be detected again and again. (Antibiotic resistance). For gonorrhea infected people without symptoms (asymptomatic), test procedures based on a laboratory reproduction of the bacterial genome (PCR, polymerase chain reaction) are more accurate than the bacterial cultures. Even if there are no complaints, it is possible for other people to be infected.
Gonorrhea: treatment
Antibiotics are suitable for gonorrhea therapy. In the past, primarily penicillin was used to treat gonorrhea. Penicillin-resistant gonococcal strains from Asia and Africa have appeared more frequently in recent years. Therefore, other antibiotics (especially so-called cephalosporins and gyrase inhibitors) are now recommended for the treatment of gonorrhea. At least two different antibiotics are used in combination.
In most cases of gonorrhea, the gonococci die after a single dose of antibiotics and are then no longer detectable. Nevertheless, it is not advisable to discontinue gonorrhea therapy too early: This promotes the development of resistance - and resistant germs are difficult to treat.
All sexual partners of those infected with gonorrhea must also be examined and, if necessary, treated. This applies to sexual contacts within two weeks before the onset of symptoms. If a gonorrhea infection was discovered accidentally without symptoms, all sexual partners should undergo gonorrhea therapy within the last 90 days. Until the end of therapy, it is important for all those affected to refrain from unprotected sex.
Newborns with purulent conjunctivitis caused by gonorrhea are given a single dose of antibiotics in the muscle (intramuscular) or in the vein (intravenous). In addition, the eyes and conjunctiva should be rinsed regularly with saline solution.
Tripper: disease course and prognosis
The prognosis for gonorrhea (gonorrhea) is usually good: If gonorrhea is treated in good time, you do not have to expect any long-term consequences.
If gonorrhea is not treated, it can lead to serious long-term effects. Such long-term consequences of gonorrhea are chronic inflammation of the internal genital organs with persistent pain, sticking of the egg or spermatic ducts and thus infertility. Therapy is therefore very important.
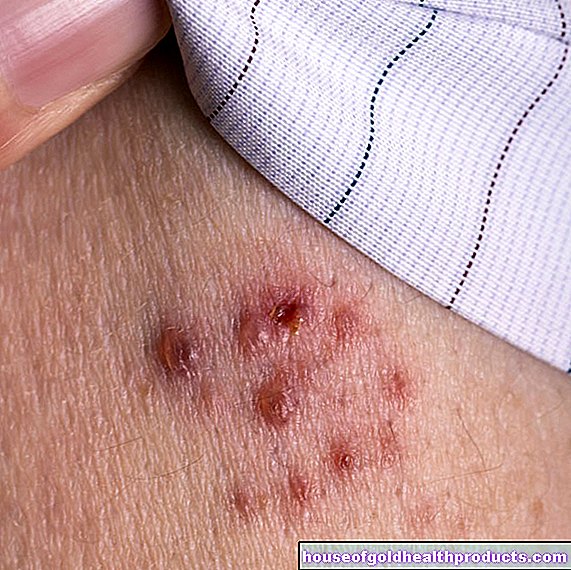
Without gonorrhea treatment, the gonorrhea pathogens can, in very rare cases, spread through the bloodstream throughout the body. Doctors speak of a disseminated gonococcal infection (DGI). The consequences are inflammation of the joints and tendons, characteristic skin rashes with red pustules or small hemorrhages (petechiae), fever and chills.
In severe cases, the disseminated gonococcal infection is followed by inflammation of the meninges (meningitis) and inflammation of the lining of the heart (endocarditis). Tripper (gonorrhea) can only be prevented through the consistent use of condoms.
Tags: medicinal herbal home remedies elderly care unfulfilled wish to have children