phosphate
and Eva Rudolf-Müller, doctorDr. med. Andrea Reiter is a freelance writer for the medical editorial team.
More about the expertsEva Rudolf-Müller is a freelance writer in the medical team. She studied human medicine and newspaper sciences and has repeatedly worked in both areas - as a doctor in the clinic, as a reviewer, and as a medical journalist for various specialist journals. She is currently working in online journalism, where a wide range of medicine is offered to everyone.
More about the experts All content is checked by medical journalists.Phosphate is mainly stored in the bones. However, it is also an integral part of the genetic material DNA and, in certain chemical compounds, an energy carrier and supplier. The phosphate concentration in the blood and in the bones is influenced by calcium, vitamin D and various hormones. Read here when and why the phosphate level in the blood is determined and what the measured values say.
What is phosphate
Phosphate is a salt of phosphoric acid. 85 percent of it occurs in the bones and teeth, 14 percent in the body cells and one percent in the space between the cells. Phosphate binds to calcium in the bones and is stored as calcium phosphate (calcium phosphate).
In addition, phosphate is an important supplier of energy: The cell plasma contains high-energy phosphate compounds (ATP) which, through a chemical reaction, provide the cells with energy for various metabolic processes. Phosphate is also part of DNA and acts as an acid buffer in blood and urine.
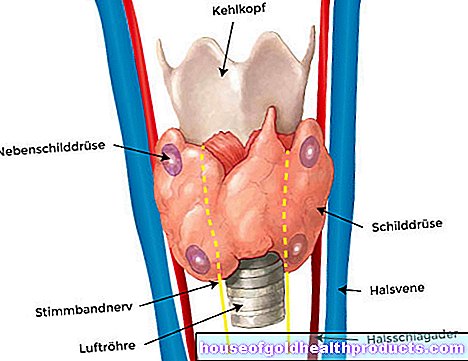
The so-called parathyroid hormone, which is produced in the parathyroid glands, promotes the excretion of phosphate through the kidneys. Growth hormones, thyroid hormones, insulin and cortisone reduce phosphate excretion.
The phosphate metabolism is closely linked to the calcium and vitamin D balance. If the blood contains a lot of phosphate, it is also low in calcium and vice versa.
Serious phosphate deficiency can lead to confusion, epileptic fits or even a coma. Breathing and swallowing are disturbed, bowel movements become sluggish, muscles and heart become weak. Since the element is increasingly released from the bones with a reduced concentration of phosphate in the blood, the bones become brittle in the long term and fractures can suddenly occur.
Too much phosphate in the blood is called hyperphosphatemia. Severe itching, calcification of the heart valves or gouty joint problems can occur.
When is the phosphate value determined?
The doctor determines a patient's phosphate level if he suspects a calcium metabolism disorder. The measurement is also indicated for kidney stones. In addition, the phosphate value is determined as part of control examinations in the case of chronic kidney failure, after thyroid surgery, in the case of severe digestive disorders and alcohol abuse.
The phosphate determination is carried out from the blood serum, from heparin plasma or from the urine collected over 24 hours (24-hour urine). The patient should be sober when taking the blood sample.
Phosphate - normal values
|
Standard value | ||
|
adult |
0.84 - 1.45 mmol / l | |
|
children |
Newborn |
1.6-3.1 mmol / l
|
|
up to the 12th month |
1.56 - 2.8 mmol / l | |
|
1 - 6 years |
1.3-2.0 mmol / l | |
|
7-13 years |
1.0 - 1.7 mmol / l | |
|
over 13 years |
0.8 - 1.5 mmol / l |
Conversion: mg / dl x 0.323 = mmol / l
The normal range of phosphate in the 24-hour urine collection is 16 to 58 mmol / 24 hours.
When is the phosphate level increased?
If there is too much inorganic phosphate in the blood, it is called hyperphosphatemia. The following diseases can be the cause:
- Kidney failure (renal failure)
- Acromegaly (hormonal disease with overproduction of growth hormone)
- Bone tumors and metastases (see tumor markers)
- Blood cell breakdown (release of phosphate from blood cells)
Even with a vitamin D overdose, the blood level of phosphate is increased.
When is the phosphate level lowered?
The phosphate levels in the blood are decreased in:
- Alcohol withdrawal in chronic alcoholism
- low levels of calcium in the blood
- Vitamin D deficiency
- Kidney failure (renal failure)
- artificial nutrition (occasionally)
Elevated phosphate levels in the urine can indicate an overactive parathyroid gland.
What to do if the phosphate levels change?
The phosphate value should always be determined together with the calcium value. If both values are changed, the doctor will also measure the concentration of the parathyroid hormone in the blood. Only then is it possible to make a statement about the reason for changed phosphate levels.
If you are deficient in phosphate, you should eat foods that are high in phosphate and vitamin D. These include, for example, milk and carbonated drinks. Conversely, in the case of hyperphosphatemia, the absorption of phosphate and vitamin D should be reduced. The regulation of the phosphate balance must always be carried out under medical supervision, because the concentration of phosphate can also have an influence on the heart function, among other things.
Tags: fitness Baby Child digital health












.jpg)