Cefpodoxime
Benjamin Clanner-Engelshofen is a freelance writer in the medical department. He studied biochemistry and pharmacy in Munich and Cambridge / Boston (USA) and noticed early on that he particularly enjoyed the interface between medicine and science. That is why he went on to study human medicine.
More about the experts All content is checked by medical journalists.The active ingredient cefpodoxime belongs to the class of cephalosporin antibiotics, so it works against bacterial infections. As a third generation cephalosporin, rs acts against a large number of bacteria and is more stable against bacterial degradation than older representatives of this class of active ingredients. Here you can read everything you need to know about cefpodoxime: mode of action, application as well as interactions and side effects.
This is how cefpodoxime works
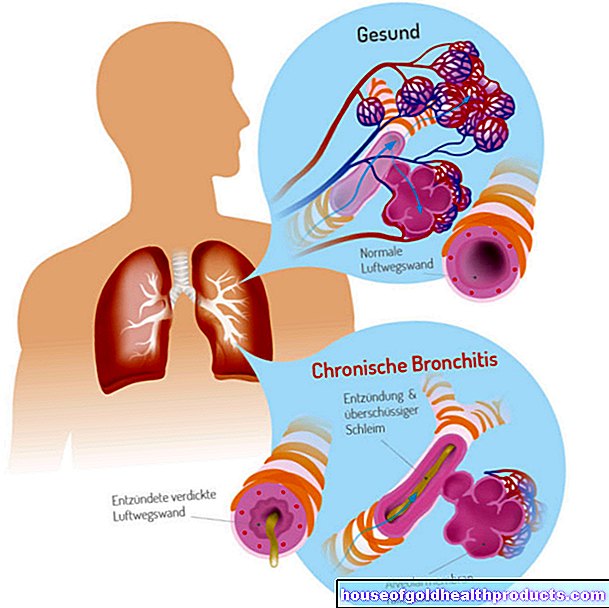
Cephalosporins such as cefpodoxime impair the structure of the bacterial cell wall. This solid shell enables bacteria to be resistant to sometimes very extreme environmental conditions. Many bacteria survive drought, high salt concentrations, high and low temperatures and other harsh environmental influences. With every cell division, which can sometimes take place every 20 minutes under optimal conditions, bacteria have to split up their cell wall, form anew and cross-link it again.
This last step - cross-linking - can be prevented by cefpodoxime in many bacteria. The germs are no longer adequately armed against harsh environmental conditions such as changes in the salt content or water content and die off. Cefpodoxime thus has a bactericidal effect - it causes bacteria to die. Other antibiotics only inhibit their reproduction, i.e. they have a bacteriostatic effect.
Uptake, degradation and excretion of cefpodoxime
The antibiotic is taken as cefpodoxime proxetil, a so-called “prodrug”, which is only converted into the active form cefpodoxime (in the intestinal mucosa) after it has been absorbed in the body. The advantage of the prodrug form is that it can be better absorbed into the blood through the intestines than the active ingredient. Effective blood levels are achieved two to three hours after ingestion. Most of the antibiotic is excreted unchanged via the kidneys with the urine. After about two and a half hours, the maximum blood level has halved again.
When is cefpodoxime used?
The antibiotic can be used against infections with pathogens sensitive to cefpodoxime. Examples are infections of the ear, nose and throat area, the respiratory tract, the urinary tract, the skin and soft tissues as well as sexually transmitted diseases (such as gonorrhea = "gonorrhea").
However, attention should be paid to the proper handling of the drug: Each antibiotic must be used exactly according to the doctor's instructions, especially with regard to dosage and duration of use.
This is how cefpodoxime is used
Depending on the location of the infection, 100 to 200 milligrams of cefpodoxime are taken with a sufficient amount of liquid twice a day with meals. The maximum daily dose of 400 milligrams should not be exceeded. The duration of therapy is usually set at five to ten days. An exception is uncomplicated gonorrhea, for which a single dose of 200 milligrams is sufficient. Even if the symptoms improve quickly due to the antibiotic, the therapy must be continued for the prescribed duration. Otherwise, some bacteria could survive and become resistant to the antibiotic.
Liquid cefpodoxime preparations are available for infants, children and patients with swallowing disorders.
What are the side effects of cefpodoxime?
During treatment with cefpodoxime, one to ten percent of patients develop side effects such as allergic reactions (rash, itching, redness) and gastrointestinal discomfort. The latter can manifest as nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, gas or diarrhea. They are caused by the fact that the antibiotic not only affects the disease-causing bacteria, but also the healthy intestinal bacteria.
Occasionally, cefpodoxime side effects such as headache, ringing in the ears, abnormal sensations, dizziness, anemia, increased liver enzyme values, malaise, fatigue and weakness are seen.
What should be considered when taking cefpodoxime?
The additional intake of gastric acid inhibitors can hinder the absorption of cefpodoxime. Examples are ranitidine, cimetidine and basic active ingredients such as calcium and magnesium carbonate, magaldrate, sucralfate and hydrotalcite. They should be taken two to three hours apart from cefpodoxime.
The antibiotic may affect the effectiveness of hormonal contraceptives (the pill). Additional non-hormonal contraceptive measures such as condoms should therefore be used for the rest of the cycle.
The antibiotic reaches the child through the placental barrier and also passes into breast milk. Therefore, the drug is not recommended during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Cefpodoxime can hinder the colonization of the intestines in the infant with beneficial bacteria, especially during breastfeeding, which can later have consequences for the immune system.
Infants, children, adolescents and patients with impaired renal function can be treated with cefpodoxime in a correspondingly reduced dose.
How to get medicines with cefpodoxime
Like other antibiotics, cefpodoxime is only available from pharmacies with a doctor's prescription. This is to ensure that the drug is used responsibly.
Since when is cefpodoxime known?
The first cephalosporin was discovered in a mold at the University of Cagliari in 1945. However, it had only a weak effect against bacteria. By changing its structure chemically, it was possible to develop new cephalosporins with a broader spectrum of activity and greater stability. Cefpodoxime was approved as the third generation cephalosporin in Europe in 1991. Since the patent protection has now expired, there are also generics with the active ingredient cefpodoxime.
Tags: drugs skin care news