Diphallia
Florian Tiefenböck studied human medicine at the LMU Munich. In March 2014, he joined as a student and has supported the editorial team with medical articles ever since. After receiving his medical license and practical work in internal medicine at the University Hospital Augsburg, he has been a permanent member of the team since December 2019 and, among other things, ensures the medical quality of the tools.
More posts by Florian Tiefenböck All content is checked by medical journalists.Doctors use diphalia to describe an extremely rare malformation of the penis, the double penis. The male member is either completely or partially doubled. There have only been about 100 cases of diphallia in the past. Therefore, researchers can only guess what causes the disease. The double penis is usually corrected surgically. Learn more about the diphallia here.
ICD codes for this disease: ICD codes are internationally recognized codes for medical diagnoses. They can be found, for example, in doctor's letters or on certificates of incapacity for work. Q55

Diphallia: description
Diphallia is a very rare, congenital penile malformation in which those affected have a double penis. The term comes from the Greek (di- = double, phallos = penis). Usually the male limb consists of three cavernous bodies. Two lie at the top and are called corpora cavernosa. Underneath is the corpus spongiosum, in the middle of which the urethra runs. The glans penis finally emerges from it.
Scientists believe that errors in the child's embryonic development cause diphallia. Therefore, the double penis is one of the so-called embryopathies. With diphallia, either the whole penis is doubled or only part of it (e.g. the glans). The division can either be a mirror image (symmetrical) or unequal (asymmetrical). The two penises can lie next to or on top of one another. In addition, both can differ significantly in shape and size. According to Schneider, the diphallia is divided into three groups:
- Diphallus glandularis = only the penis glans is double
- Diphallus bifidus = penis divided into two parts (cavernous body divided)
- complete diphallia / double penis = complete doubling of the male member
Based on this classification, a classification was introduced that is still valid today. The diphallia are split into two main groups, each of which is subdivided again.
|
Main group |
Subgroup |
Explanation |
|
true diphallia |
complete diphallia |
Sufferers have two penises with three cavernous bodies each |
|
partial diphallia |
One penis is correctly shaped, the other smaller or completely atrophied | |
|
Phallus bifidus |
complete phallus bifidus |
The shaft of the penis is divided up to its exit, but each limb has only one corpus cavernosum |
|
partial phallus bifidus
|
The split affects only part of the penis, for example the glans of the penis |
The diphallia occurs in around one in 5.5 million births, so it is very rare. It was first described in 1609 in Bologna, Italy. Since then, doctors have recorded about 100 cases of a double penis. Those affected often suffer from other malformations, for example from a double kidney or shrunken testicles. In addition to diphallia in men, comparable symptoms have also been described in women. The doubling here affects the clitoris. It is accompanied, for example, by doubled labia minora.
Diphallia: symptoms
The symptoms of diphallia differ from case to case. In most cases, at least one penis will function normally. The stunted penis of a partial diphallia, on the other hand, is of no use. In a true complete diphallia, both limbs may be aroused to the point of ejaculation. The same applies to a phallus bifidus. Therefore, in some cases of pure diphallia, it is more of a cosmetic than a functional problem. However, psychological problems often arise, especially with increasing age (feelings of inferiority, shame, self-doubt, etc.).
In addition, urination problems have often been observed with diphallia. Urine usually trickles out of the underdeveloped penis in an uncontrolled manner (incontinence). In addition, the urine stream sometimes seems weaker than usual. Furthermore, many of those affected are sterile (or fertile to a limited extent). In addition, the patients can suffer from other malformations (malformations) that have been observed together with a diphallus. Researchers have found that these malformations are far more common in a true diphallia than in a phallus bifidus. These include, for example:
- Defects in the rectum (anorectal malformations), e.g. B. connecting ducts between the intestine and bladder (fistulas) or a narrowing of the anus
- Incorrect position of the urethral orifice (hypo- / epispadia), excess urethra
- urinary bladder open to the outside (bladder exstrophy)
- Dislocating pubic bones
- Defects in the skeletal or heart muscles
- Spinal malformations, including spina bifida, where the spinal cord may be exposed
- Duplication of the large intestine, urinary bladder or kidneys, some of which are located elsewhere (e.g. in the pelvis)
- Shriveled testicles, incorrect testicles
Diphallia: causes and risk factors
The causes of diphallia have not been fully researched due to their rare occurrence. Researchers believe that errors in embryonic development lead to a double penis. The embryonic phase begins in the second and ends around the tenth week of pregnancy. During this time, the child's organs are formed. They arise from the three adjacent cotyledons: ento- and ectoderm with the mesoderm in between. At the ends, the ento lies directly on top of the ectoderm. The lower part is called the cloacal membrane. This is where the anus and the urinary and genital organs are formed later. Defects in these cell aggregations lay the foundation for a diphallia.
From the fourth week onwards, embryonic connective tissue cells accumulate around the cloacal membrane. Genital bumps, folds and bulges develop. The penis (or the clitoris) usually grows from the genital hump. The genital folds later form the erectile tissue. And the testicles arise from the genital bulges. Again, mistakes can lead to diphallia. The cloaca, in turn, is divided into a so-called urogenital sinus and an anorectal canal by an ingrowing fiber plate (septum urorectale). This ultimately gives rise to further parts of the urinary and reproductive system as well as the rectum.
Risk factors alcohol, nicotine, drugs and some medications
These stages of development are particularly susceptible to harmful substances such as alcohol, nicotine, other drugs, and some medications. For example, they prevent the correct separation of the individual cell groups or damage the genetic material in the cells. With the neighboring position of the embryonic structures, scientists also try to explain why several malformations occur together in a diphallia.
A connection between the diphallia and genetic diseases in the family of the person concerned has been discussed, but has not yet been proven. In addition, the diphallus has not been inherited to this day.
Diphallia: diagnosis and examination
A diphallia is usually diagnosed immediately after birth. It is a so-called eye diagnosis, as you can see the double penis with the naked eye. Doctors may ask about medications or harmful substances that may have been taken during labor that may have caused the diphallia. There are also cases when patients did not see a doctor until they were adults. Here the doctor will ask the person concerned about possible problems with urination or sexual intercourse.
If a diphallia is diagnosed, the doctor searches the body for further malformations. He checks unnatural connecting passages with a probe and ultrasound. He can use the stethoscope to listen to possible heart defects. An ultrasound machine will also help in examining internal organs. For example, duplicate or misplaced kidneys can be detected in this way. Ultimately, ultrasound (sonography) also plays a decisive role when doctors plan the surgical procedure for diphallia. Because with its help, the individual erectile tissue of the double penis are also shown. In the case of larger malformations, the doctor will order a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan. Soft tissues in particular can be assessed well on the basis of the images generated.
Diphallia: treatment
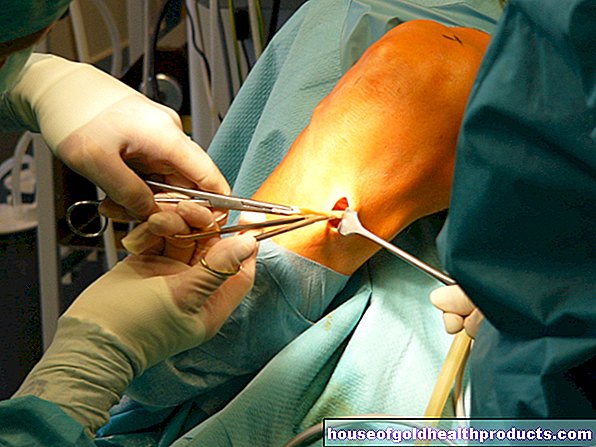
The diphallia or phallus bifidus are treated surgically. Other malformations are also usually corrected by surgeons. Attempts are always made to treat as many defects as possible at once and thus restore the natural normal state. After the procedure, the patient should be able to fully control urination, among other things. In addition, the surgeons are extremely careful with every operation so as not to damage any nerves. Maintaining an erection is also a main goal of the usually quite complex diphallia treatment.
Doctors proceed differently depending on the type of double penis. In the case of a phallus bifidus (divided erectile tissue), the surgeons try to bring the divided penis together. The urinary structures (especially the urethra) may have to be re-created. In the case of a true diphallia (two separate penises), the excess penis is separated off. The procedure for a complete phallus bifidus or a complete diphallia (split or doubling up to the pelvis) is usually a little more complicated. In these cases, the double penis is usually attached to the pubic bone, which makes the amputation more difficult (higher risk of complications).
In all cases, the wishes of the patient or his / her guardian (parents) are decisive for the choice of diphallia treatment. Although the operation is the only therapy for a double penis, not all malformations associated with it need to be treated. For example, a single kidney is sufficient to detoxify and drain the body sufficiently. Even minor heart defects are not operated on.
Diphallia: disease course and prognosis
The chances of illness with a diphallia are usually strongly related to the success of the operation. In addition to infertility that cannot be changed (e.g. due to shriveled testicles), the penis may no longer become stiff (erectile dysfunction). Treatment measures can also result in a shorter limb, scarring, and deformation of the penis. Usually those affected later suffer from severe psychological stress. Especially during puberty, an already emotionally difficult development phase, patients with diphallia are insecure and shy. Shame and feelings of inferiority dominate the emotional state. These sensations are particularly pronounced if the double penis has not been treated.
Prevent diphallia
At the moment the following recommendations can be made: Do not take any harmful substances, especially during pregnancy! Refrain from alcohol, cigarettes and other drugs! If you are on medication and plan to become pregnant, always consult a doctor beforehand about possible side effects. He can adjust and change the medication accordingly. And get your child treated as early as possible! In this way you can spare him the later psychological burden of a diphallia!
Tags: alcohol hair drugs