Guaifenesin
Benjamin Clanner-Engelshofen is a freelance writer in the medical department. He studied biochemistry and pharmacy in Munich and Cambridge / Boston (USA) and noticed early on that he particularly enjoyed the interface between medicine and science. That is why he went on to study human medicine.
More about the experts All content is checked by medical journalists.The active ingredient guaifenesin is an active ingredient for the treatment of productive coughs, i.e. coughs with mucus formation in the lower respiratory tract. It has both a liquefying and expectorant effect, which is why it should not be taken before going to bed. Here you can read everything you need to know about guaifenesin: use and effects, side effects and interactions.
This is how guaifenesin works
In the case of respiratory infections caused by viruses or bacteria, the body tries to remove the germs that have penetrated the airway through the increased production of secretions from the lungs. Small cilia on the surface of the lining of the lungs help the mucus to be removed from the lungs. Since the surface from the bronchi to the windpipe is greatly reduced, there, near the larynx, more mucus accumulates. He then triggers an urge to cough and is either coughed up or swallowed. In this way, the invading pathogens are also removed.
Often, however, the mucus is too thick to simply cough up. This can be especially the case with dry air and insufficient hydration. Then the secretion liquefier (secretolytic) guaifenesin can help: Experts assume that it stimulates the glands of the lungs to secrete more fluid through a kind of reflex reaction after irritation of the gastric mucosa. This liquefies the mucus and can be removed more easily.
Guaifenesin Protocol
The so-called "Guaifenesin Protocol" is an alternative medical treatment concept for the treatment of fibromyalgia with guaifenesin. Fibromyalgia (literally "fiber-muscle pain") is a serious and incurable disease that causes pain in the muscles, joints and back. Fatigue and weakness are other symptoms of fibromyalgia. Guaifenesin has been used in fibromyalgia as part of a proprietary treatment concept since the 1990s. So far, however, the efficacy has not been able to withstand tests in placebo-controlled clinical studies.
Uptake, degradation and excretion of guaifenesin
After ingestion, the secretion liquefier will probably already take effect in the stomach. In the intestine, the active ingredient is then absorbed into the blood and transported to the liver, where it is broken down. Most of the breakdown products are excreted with the kidneys.Just one hour after reaching the maximum blood level, the concentration of the active substance in the blood has fallen by half again.
When is guaifenesin used?
The expectorant guaifenesin is approved for:
- Treatment of increased mucus build-up in the bronchi
Treatment usually takes place over the duration of the infection.
There is no approval for use in fibromyalgia: Guaifenesin is not approved.
This is how guaifenesin is used
The active ingredient guaifenesin is mostly used as a syrup, juice or drinking solution. Typically, depending on the severity of the cough, 200 milligrams of guaifenesin are taken up to six times a day (about every four hours). The active ingredient should not be taken immediately before going to bed, as the liquefied mucus leads to increased coughing up, which can be uncomfortable in a lying position and disturb sleep.
The effect of the secretolytic is not diminished if more liquid is drunk.
What are the side effects of guaifenesin?
After taking the active ingredient, you may experience warmth, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, stomach intolerance, heartburn, pain, rash, itching and allergic reactions.
What should be considered when taking guaifenesin?
Simultaneous use of guaifenesin and sedative, sleep-inducing, and muscle-relaxing drugs (such as benzodiazepines) can increase their effects in unpredictable ways.
The combined intake with a cough suppressant or cough blocker (such as codeine, dihydrocodeine, pentoxyverine and dextromethorphan = DXM) can lead to an accumulation of secretions and is therefore not advisable. However, to ensure a restful sleep, you can take a cough suppressant at night and treat the cough with guaifenesin during the day.
The active ingredient guaifenesin should not be taken in severe muscle weakness (myasthenia gravis) or impaired kidney function without first consulting a doctor.
The cough remover guaifenesin must not be taken during pregnancy and breastfeeding, as a risk to the child cannot be safely ruled out.
Children over 14 years of age, adults and the elderly may be treated with guaifenesin.
How to get medication with guaifenesin
Preparations for cough treatment are available from pharmacies without a prescription. They are not approved for use in fibromyalgia.
Since when is guaifenesin known?
The active ingredient guaifenesin is a derivative of the natural substance guaiacol, a secondary plant substance from the guaiac trees that grow in tropical and subtropical America. The boiled wood of the tree was already used in the Mayan culture as a medicine to treat the venereal disease syphilis. The active ingredient guaifenesin was first approved as a medicinal product by the American health authority FDA in 1952.
Tags: medicinal herbal home remedies laboratory values skin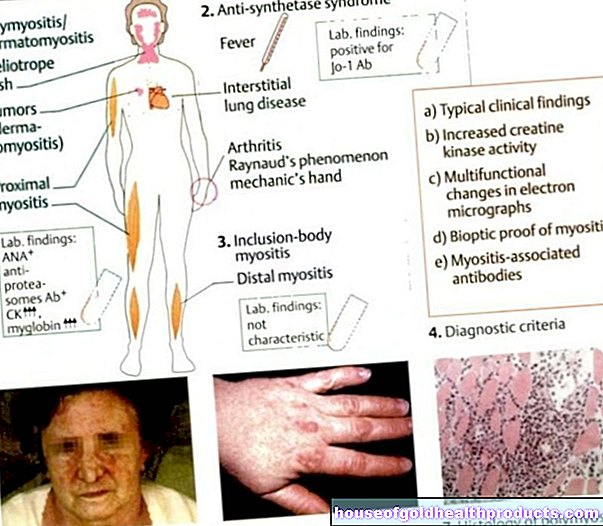




.jpg)