Propranolol
All content is checked by medical journalists.The active ingredient propranolol is a so-called beta blocker and has a positive effect on the heart. It can lower blood pressure and normalize the heart rhythm. Propranolol is therefore primarily suitable for the treatment of high blood pressure and various heart diseases. Here you can read everything you need to know about the use, effects and side effects of propranolol.
This is how propranolol works
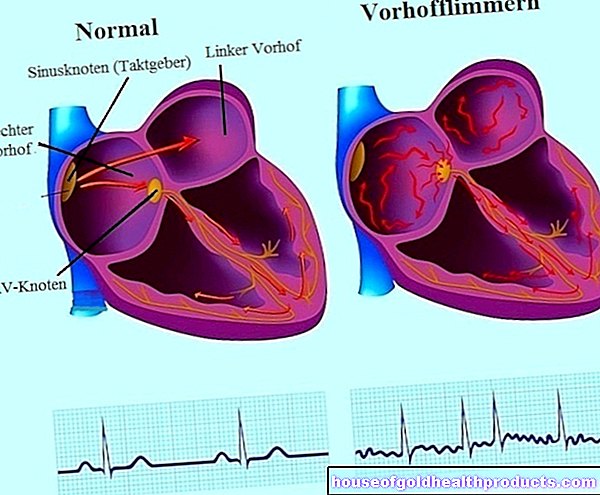
Propranolol belongs to the drug class of beta-receptor blockers (beta blockers). This means that it attacks the autonomic (autonomic) nervous system, which controls blood pressure and the work of the heart, among other things. In both cases, regulation takes place via certain neurotransmitters, above all via adrenaline. The hormone is produced in the adrenal medulla, can bind to certain docking points (beta receptors) on the heart and thus give the signal for an acceleration of the heartbeat. In addition, adrenaline can widen the bronchi and stimulate and increase the metabolism (glycogen and fat breakdown).
Propranolol competes with adrenaline for the beta receptors in the heart and ultimately displaces the messenger substance. As a result, adrenaline can no longer develop its heartbeat-increasing effect - with the result that the heartbeat slows down and blood pressure drops. Another important effect is that the heart's consumption of oxygen is reduced.
Propranolol uptake and breakdown
Propranolol is taken as a tablet and enters the blood through the intestinal wall. The active ingredient is broken down in the liver, the breakdown products are mainly eliminated via the kidneys. Just four to five hours after ingestion, half of the original amount of active ingredient has been removed from the body.
When is propranolol used?
The beta blocker propranolol is an important drug in cardiovascular diseases. Areas of application in detail are:
- attack-like chest pain (angina pectoris)
- Prevention of a new heart attack (re-infarction prophylaxis)
- Non-organic (functional) cardiovascular complaints such as accelerated heartbeat and increased blood pressure (hyperkinetic heart syndrome)
Propranolol is also used for migraine prophylaxis and as an accompanying therapy for an overactive thyroid gland (hyperthyroidism). The active ingredient can also suppress excessive tremors for unknown causes and provide relief from simple anxiety states (such as stress anxiety or fear of an exam).
This is how propranolol is used
Propranolol is usually administered through the digestive tract, such as in tablet form. How often and in what dosage the active ingredient must be taken is determined individually by the doctor.
In some cases, the beta blocker is given intravenously, that is, injected directly into a vein.
What are the side effects of propranolol?
Some propranolol side effects are caused by the effects on other receptors in the autonomic nervous system. This often leads to dizziness, headaches, sweating, sleep disorders, numbness and coldness in the limbs and gastrointestinal complaints. A drop in heart rate is also possible.
An existing heart muscle weakness (heart failure) or existing asthma can worsen further. The same applies to peripheral circulatory disorders.
What should be considered when taking propranolol?
Propranolol should not be used in the following cases:
- low blood pressure (hypotension)
- Heart failure associated with water retention in the tissue and shortness of breath (acutely decompensated heart failure)
- shock
Some drugs can negatively affect the effects of propranolol on the heart and circulation and must therefore not be taken at the same time. This includes:
- so-called calcium antagonists of the verapamil or diltiazem type)
- Cardiac glycosides (used to treat heart failure and irregular heartbeat)
- Anesthetics (narcotics)
- Phenothiazines (used for example against psychosis)
If there is severe kidney or liver weakness (insufficiency), the propranolol dosage must be adjusted.
The beta blocker can be used during pregnancy if necessary. Monitoring of the unborn or newborn may subsequently be necessary.
Propranolol can also be used while breastfeeding.
How to get drugs with propranolol
Drugs containing propranolol require a prescription. So they are only available with a prescription.
Since when has propranolol been known?
Propranolol was the first representative of the beta blocker group of active ingredients. It was developed in the 1960s by the later Nobel Prize winner James Whyte Black and came on the market in 1964.
Tags: nourishment laboratory values Diseases